Bonding and Electronegativity
advertisement

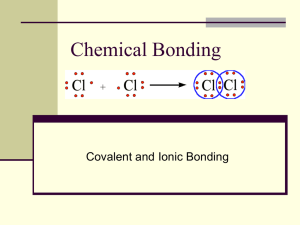
Homonuclear & Heteronuclear bonds Ethane (C2H6) Homonuclear bonds Hydrazine (N2H4) Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) Hetronuclear bonds Polar bonds IONIC COMPOUNDS Salt crystals are repeating patterns of positive+ cations and negative- anions held together by electrostatic attraction. COVALENT COMPOUNDS Biological molecules are covalently bound Most consist of the non-metals Carbon, Oxygen, Hydrogen, and Nitrogen. SO….. Ionic and covalent bonds are very different, but how do we predict if a bond will be ionic or covalent? The ELECTRONEGATIVITY of an element electronegativity helps us understand the difference between ionic and covalent bonding • Electronegativity is the measure of the ability of an atom in a bond to attract electrons. • With only a few exceptions, electronegativity values increase as you move from left to right in any period of the periodic table. • Within any group, electronegativity values decrease as you go down the group. That means that the most electronegative elements are in the upper-right corner of the table. Every element has an electronegativity value Francium has the lowest electronegativity 0.7 Fluorine has the highest 4.0 Elements with a HIGH electronegativity have a STRONG pull on electrons. Elements with a LOW electronegativity have a WEAK pull on electrons. When two atoms bond their DIFFERENCE in difference electronegativity determines thein bond type. electronegativity A large difference in electronegativity means one atom will win the “tug of war” and take the electrons completely. This is an ionic bond. When the electronegativity of two bonding atoms is very similar, neither atom wins the “tug of war” and the electrons are shared equally. This produces a covalent bond In a true covalent bond electrons are shared equally IONIC COVALENT Transfer electrons Share electrons Between an atom of high electronegativity and an atom of low electronegativity NaCl Between two atoms of equal or very close electronegativities N2 If the electronegativity difference between two bonded atoms is very high the bond is ionic. If the electronegativity difference is very low the bond is covalent. What if the difference in electronegativity between the two bonded atoms is in-between? A POLAR COVALENT BOND occurs when two atoms share electrons unequally. The atom with a high electronegativity value holds the bonding electrons more often, but it doesn’t remove the electrons completely. Are the bonds polar covalent, non-polar covalent, or ionic? 1) H-C 2) K-Cl 5) C-N 3) O-F 6) S-O 4) Cl-Cl 7) B-S A polar bond has a partial positive charge (+) and a partial negative charge (-) The N-H bond is polar, with N being the most electronegative. + + + The N-H bond is polar, with N being the most electronegative. Bond polarity and 3D shape determine if a molecule is polar Bond polarity --- When a bond has a partial negative charge on one atom and a partial positive charge on the other atom. Molecule shape--- the arrangement of atoms in three dimensions (3-D) A polar molecule has polar bonds and asymmetry Polar bonds Non-polar molecule Polar bonds Polar molecule δPositive side δ+ δ- δ- δSymmetry- all sides are the same δδ+ negative side Asymmetry- has different sides If the electrons are not distributed equally, the molecule is said to be polar. The molecule has a negative end and a positive end. Polar molecules are affected by electric fields It has two poles and is polar; it has a measurable dipole moment. POLAR MOLECULES INTERACT!! A partial positive charge (+) is attracted to negative ions and negative partial charges (-) of other polar bonds. POLAR MOLECULES INTERACT!! A partial negative charge (-) is attracted to positive ions and partial positive charges (+) of other polar bonds. + Water is a molecule that consists of two polar covalent O-H bonds. The electrons are not distributed evenly so the water molecule is polar. The negative end of the molecule is the oxygen end. O is more electronegative than H and pulls the negative electrons toward itself. Also, there are two lone pairs around oxygen. negative end positive end Na+(aq) A dissolved sodium ion Practice- Draw the 3D structures for these molecules and label the bond polarity and the molecule polarity. 1. H2O 7. CO2 2. CH4 8. CH2CH2 3. CH3F 9. HCN 4. CH3CH3 10. 5. CH3CH2OH 11. 6. NH3