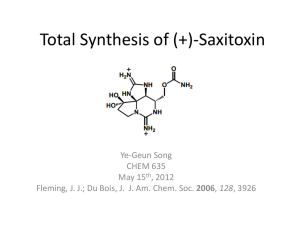
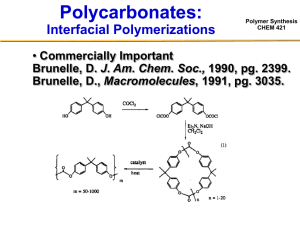
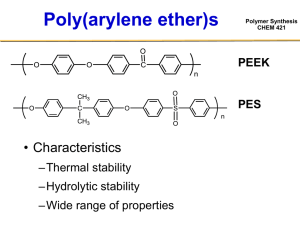
Polymer Synthesis CHEM 421
advertisement

Polymer Synthesis CHEM 421 • Odian Book 2-6, 2-14 a-e MW3.4 MW1.0 Critical MW for entanglements Molecular Weight “X” = tensile strength density Tg etc Viscosity Property “X” Viscosity and Molecular Weight Polymer Synthesis CHEM 421 How to control MW in Step Growth Polymerizations? • Conversion Xn = 1 p = 0.990, DP = 100 p = 0.995, DP = 200 Xn (1 – p) • Stoichiometry Polymer Synthesis CHEM 421 p Controlling MW in Step Growth Polymerizations • Recall Xn = Polymer Synthesis CHEM 421 1 (1 – p) • And that the value of Xn at any given time equals: Xn = [M]0 [M] • We can define a stoichiometric imbalance ratio (r ≤1.0) r = NA° NB° Controlling MW in Step Growth Polymerizations Polymer Synthesis CHEM 421 • Total # of monomers present at the start is: NA° + NB° = 2 –And we know that: r = NA° NB° = NB° NA° r • Substitute: = NA° + NA° / r 2 = NA° ( 1 +1/ r) 2 Controlling MW in Step Growth Polymerizations Polymer Synthesis CHEM 421 • Since A and B groups react in a 1:1 proportion, the fraction of B groups that have reacted when the extent of reaction has reached ‘p’ is: = p NA° – since: r = NA° NA° = r NB° NB° – Substitute: = p r NB° Controlling MW in Step Growth Polymerizations Polymer Synthesis CHEM 421 • The total # of chains at any given time equals what? The sum of unreacted A and B groups. And since each polymer molecule has two chain ends, the total number of chains is [ NA° (1 – p) + NB° (1 – rp) ] 2 • Recall Xn = [M]0 [M] = [NA0 (1 + 1/r) ] / r [ NA° (1 – p) + NB° (1 – rp) ] – Substitute: 2 DP = 1+r 1 + r - 2rp How to control MW in Step Growth Polymerizations? • As p goes to 1.0 DP = 1+r 1- r Polymer Synthesis CHEM 421 End Groups? Polymer Synthesis CHEM 421 PES 50% 25% 25% Controlled MW Poly(ether sulfone) Polymer Synthesis CHEM 421 Slight excess Controlled MW and controlled end groups Bismaleimides (BMIs) Excess diamine Polymer Synthesis CHEM 421 dianhydride polyamic acid Δ cyclodehydration Controlled MW Poly(ether sulfone): Polymer Synthesis CHEM 421 “Non-functional” End groups How to control MW in Step Growth Polymerizations? Polymer Synthesis CHEM 421 • Stoichiometric Imbalance (r) r’ = NA° NB° + 2NB’° Where NB’° = number of mono-functional B groups when A-A and B-B monomers are used, with a small addition of R-B • Degree of Polymerization at p = 1.0 is DP = 1 + r’ 1 - r’ Thermosets Polymer Synthesis CHEM 421 Xn • Xn → ∞ – Gel point » Beginning of network formation • Need to know…ahead of time! p Stages of Thermosetting Reactions Polymer Synthesis CHEM 421 1. Soluble • Branched system • Soluble, processible 2. “Gel Point” • Onset of network structure • Xn → ∞ • We need to know when this happens… • pcrit = ? 3. Network Densification • 5% soluble fraction not uncommon for “fully cured” system % Sol Fraction p Predicting the Gel Point • Recall # functional groups reacted p = # functional groups initially p = Polymer Synthesis CHEM 421 2 (No - N) No favg where N0 and N are the number of monomer molecules initially and at conversion p • Knowing that DP = N0 2 p = favg N • By definition @ gel point DP → ∞ • As favg↑ ; pcrit↓ pcrit = 2 favg - 2 DP favg Gelation vs Vitrification Polymer Synthesis CHEM 421 • Gelation – Characteristic of thermosets – Significant for processing » At or beyond the gel point, system is no longer processable • Vitrification – Distinct from gelation – Transformation from a viscous liquid to a glass – Onset of vitrification shifts rate of reaction from chemical control to diffusion controlled Gelation vs Vitrification Tg Molecular Weight Polymer Synthesis CHEM 421