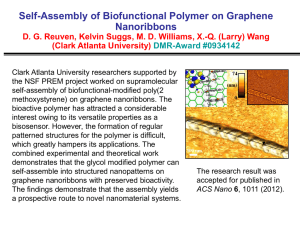
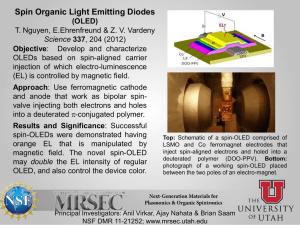
Polymer Synthesis CHEM 421
advertisement

Polycarbonates: Interfacial Polymerizations Polymer Synthesis CHEM 421 • Commercially Important Brunelle, D. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1990, pg. 2399. Brunelle, D., Macromolecules, 1991, pg. 3035. Step Growth Polymerization of Poly(bisphenol A carbonate) n HO OH Polycarbonate Oligomers 181-300 oC + + LiOH O O C O n OH (2n-1) Polycarbonate Oligomers O O C O O O C O OH m O O C O HO OH m O O C O O O C O m Polymer Synthesis CHEM 421 Traditional Routes Interfacial Route Polymer Synthesis CHEM 421 Advantages •High Molecular Weight •Excellent Optical Clarity O- O Phase + Transfer + H2O Catalyst and color Disadvantages •Phosgene based O CH2Cl2 + Cl C •Uses H2O and CH2Cl2 Cl O ( O C O )n Melt Condensation HO OH Advantages •Solvent Free •Potentially Phosgene Free + Disadvantages O O C O •Colored Product •Intermediate Molecular Weight CO2 & Polymer Processing Polymer Synthesis CHEM 421 Swelling and Plasticization of a Polymer Melt Impact: Lower T processing Melt Phase Condensation Polymerization Polymer Synthesis CHEM 421 • Viscosity () increases with conversion • High hinders mixing and removal of condensate, causing slower reaction rates • Addition of supercritical CO2 as a plasticizing agent decreases , increasing mobility • Supercritical CO2 extracts reaction byproducts, shifts equilibrium, increases DP CO2 + byproduct outlet CO2 inlet Swollen polymer melt Swelling Measurements 0 psi 2000 psi 3000 psi Polymer Synthesis CHEM 421 4000 psi 5000 psi • In a closed system, the polymer swelling correlates to CO2 mass uptake by the polymer • Swelling measurements allow for the determination of the diffusion coefficient of CO2 in the polymer Polymer Synthesis CHEM 421 P o l y c a r b o n a t e ( M = 5 , 0 0 0 g / m o l ) E x p o s e d n 0 t o S u p e r c r i t i c a l C O a t 2 3 5 C 2 t-V 0)/V 0]x10% 6 0 5 0 4 0 3 0 PercntSweling[(V 2 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 3 0 0 0 P r e s s u r e ( p s i ) 4 0 0 0 5 0 0 0 Solvent-Induced (CO2) Crystallization of Polycarbonate Polymer Synthesis CHEM 421 Polycarbonate Pellets Crystallized with Supercritical CO2 Amorphous Polycarbonate Pellets Solid State Polymerization Polymer Synthesis CHEM 421 Synthesize amorphous prepolymer Crystallize the prepolymer with supercritical CO2 to eliminate the need for organic solvents Heat the semicrystalline prepolymer between Tg and Tm Flow sweep fluid past the surface of the polymer particle to remove condensation byproduct Investigate the use of supercritical CO2 as a sweep fluid Amorphous region Crystalline region Solid State Polymerization: SolventPolymer Synthesis CHEM 421 Induced Crystallization Solvent induced crystallization presents a unique opportunity to study solid state polymerization PET PC -Thermally crystallizes crystallize -Fixed level of crystallinity -Uniform crystallinity -Does not readily thermally -Can control crystallinity -Can control morphology Solvent front Mw(g/mol) Mw versus Time as a Function of Temperature: SSP of Polycarbonate Beads (3.6 mm) with N2 as the Sweep Fluid Polymer Synthesis CHEM 421 Variable Temperature Profile: Hours 0-2: 180 °C Hours 4-6: 230 °C Hours 2-4: 205 °C Hours 6-12: 240 °C 2 5 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 0 V a r i a b l e T e m p e r a t u r e , I n i t i a l l y 5 , 0 0 0 g / m o l 1 5 0 0 0 V a r i a b l e T e m p e r a t u r e : I n i t i a l l y 2 , 5 0 0 g / m o l 1 8 0 C 1 0 0 0 0 1 6 0 C 5 0 0 0 0 0 2 4 6 8 1 0 1 2 T i m e ( H o u r s ) Macromolecules, 1999, 32, 3167. N2 flow rate 2 mL/min Role of Phenol Diffusion Polymer Synthesis CHEM 421 Phenol must diffuse from the particle to increase polymer molecular weight. core intermediate shell Segment Radius Core = 0.0 to 0.4 mm Inter = 0.4 to 1.4 mm Shell = 1.4 to 1.8 mm The sample was separated into three regions for analysis... -molecular weight -percent crystallinity -melting point (Tm) What is the role of…. -phenol diffusivity -tortuosity -end group mobility MW as a Function of Diameter? Polymer Synthesis CHEM 421 M v e r s u s T i m e a s a F u n c t i o n o f R a d i a l P o s i t i o n w [Condensate] 2 0 0 0 0 1 8 0 0 0 S H E L L 1 —— Xn2 1 6 0 0 0 1 4 0 0 0 Mw(g/mol) 1 2 0 0 0 I N T E R 1 0 0 0 0 8 0 0 0 C O R E 6 0 0 0 4 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 0 0 2 4 6 8 1 0 1 2 T i m e ( H o u r s ) C O R E 0 . 0 t o 0 . 4 m m I N T E R 0 . 4 t o 1 . 4 m m S H E L L 1 . 4 t o 1 . 8 m m T = 1 8 0 C 1 T = 2 0 5 C 2 T = 2 3 0 C 3 T = 2 4 0 C 4 Macromolecules, 2000, 33, 40. PC Beads=3.6 mm N2 Flow=2 mL/min Mw versus Time for the SSP of PC Powder (20 um) Using N2 as the Sweep Fluid Polymer Synthesis CHEM 421 40000 Variable Temperature M olecular W eight (M w ) 35000 30000 o T = 1 8 0 C f o r 2 h o u r s 1 o 25000 T = 2 0 5 C f o r 2 h o u r s 2 o T = 2 3 0 C f o r 2 h o u r s 3 20000 o T = 2 4 0 C f o r 1 8 h o u r s 4 15000 10000 180 ºC 5000 0 5 10 15 20 Time (hours) N2 flow rate 2 mL/min PDI versus Time for the SSP of PC Beads (d =3.6 mm) and PC powder (20 um) at a variable temperature program Polymer Synthesis CHEM 421 Polydispersity Index (M w /M n) 2.6 PDI of Bead 2.4 o T = 1 8 0 C f o r 2 h o u r s 1 2.2 o T = 2 0 5 C f o r 2 h o u r s 2 o T = 2 3 0 C f o r 2 h o u r s 3 o T = 2 4 0 C f o r 1 8 h o u r s 4 2.0 1.8 PDI of Powder 0 5 10 15 20 25 Time (hours) Significant molecular weight distribution broadening observed in larger polymer particles. Copolymers in Step Growth Polymerizations Polymer Synthesis CHEM 421