M 1

• Odian Book
Chapter 6-2
Polymer Synthesis
CHEM 421
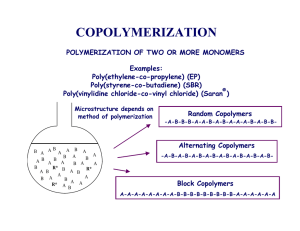
Copolymers
Polymer Synthesis
CHEM 421
• Copolymers involve the use of two or more monomers
• Copolymers allow us to tailor product properties
– Tg
– Tm
• Commercially important (chain growth) examples include:
– Styrenics
» Styrene/acrylonitrile (SAN): increased impact resistance and solvent resistance; 10-40% AN, Samsonite luggage
» Styrene/butadiene (SBR): 25% styrene/75% butadiene
» Largest volume synthetic rubber (tires)
» HIPS: High Impact PS (PBD-g-PS)
» Styrene Maleic Anhydride (SMA)
Copolymers
Polymer Synthesis
CHEM 421
• Commercially important copolymers (Cont’d)
–Vinyl chloride
» Rigid PVC: ca. 5% vinyl acetate, lowers Tg small amount allow to be processed a lower temperatures avoiding degradation
» Flexible: 20-40% vinyl acetate (tubing, sheets (e.g. shower curtains, etc.)
» Packaging: Saran Wrap® (90% vinylidene chloride)
Copolymers
• Commercially important copolymers (Cont’d)
– Ethylene (> 10 billion lbs/yr)
» LDPE (homopolymer!)
» High pressure free radical
» 30-40% x-tallinity
» HDPE (homopolymer!)
» Ziegler-Natta
» 75% x-tallinity
» Linear Low Density Polyethylene
» Linear copolymer with 1-5 mol% α-olefins
» EVA: Ethylene vinyl acetate: 2-40% vinyl acetate
» Packaging, molding
» EPR: Ethylene-propylene rubber (plus cure site monomer)
» Ethylene/acrylic acid: (1-10 mol% AA); ionomer
» Surlyn®
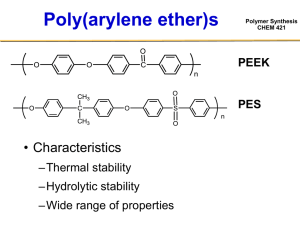
Polymer Synthesis
CHEM 421
Copolymers
Polymer Synthesis
CHEM 421
• Commercially important copolymers (Cont’d)
–Fluoropolymers
» PTFE: T m
= 335 °C, T g
= -70 °C
» PVDF: T m
= 180 °C
» FEP: T m
= 250 - 280 °C, T g
= 70 - 120 °C
» ETFE: T m
= 225 °C, T g
= 145 °C
» PFA: T m
= 300 °C
» Teflon AF:
» Nafion:
Copolymerization Kinetics
Polymer Synthesis
CHEM 421
Homo-propagation
Cross-propagation
Terminal Model
Copolymerization Kinetics
Polymer Synthesis
CHEM 421
Penultimate Model
Copolymerization Kinetics
Polymer Synthesis
CHEM 421
Terminal Model
Homo-propagation
Cross-propagation
Cross-propagation
Homo-propagation
Copolymerization Kinetics
Polymer Synthesis
CHEM 421
R p11
= k
11
[M
1
•] [M
1
]
R p12
= k
12
[M
1
•] [M
2
]
R p21
= k
21
[M
2
•] [M
1
]
R p22
= k
22
[M
2
•] [M
2
]
Terminal Model
Copolymerization Kinetics
Polymer Synthesis
CHEM 421
The rate of disappearance of M
1 and M
2 can be expressed as: d [M
1
]
——— = k
11 dt
[M
1
•] [M
1
] + k
21
[M
2
•] [M
1
] d [M
2
]
——— = k dt
12
[M
1
•] [M
2
] + k
22
[M
2
•] [M
2
]
Copolymerization Kinetics
The ratio of the two rates is then: d [M
1
] k
11
[M
1
•] [M
1
] + k [M
2
•] [M
1
] d [M
2
] k
12
[M
1
•] [M
2
] + k
22
[M
2
•] [M
2
]
Polymer Synthesis
CHEM 421
Simplify: d [M d [M
1
2
] [M
[M
1
2
] k
] k
11
12
[M
[M
1
1
•] + k
•] + k
21
22
[M
[M
2
2
•]
——— = ——— ——————————
] •]
Copolymerization Kinetics
Polymer Synthesis
CHEM 421
Assume the Steady State Approximation:
The concentrations of M
1
• and M
2
• are constant
Therefore:
The rate of addition of M
1
The rate of addition of M
2
• to M
2
• to M
1 will equal k
12
[M
1
•] [M
2
] = k
21
[M
2
•] [M
1
]
Define: r
1
= k
——— k
12 r
2
= k
——— k
21
Copolymerization Kinetics
Copolymer Composition Equation:
Polymer Synthesis
CHEM 421 d [M d [M
1
2
] [M
[M
1
2
] r
1
] [M
[M
1
1
] + [M
] + r
2
[M
2
2
]
——— = ——— ———————
] ]
Molar ratio of the monomers in the copolymer
Copolymerization Kinetics
Copolymer Composition Equation: f
1
= 1 – f
2
= —————
[M
1
[M
1
]
] + [M
2
]
Polymer Synthesis
CHEM 421
F
1
= 1 – F
2 d[M
= ——————— d[M
1
1
]
] + d [M
2
]
F
1
= r
1 f 2 +
—————————— r
1 f
1
2 + 2 f
1 f
2 f f
+
2 r
2 f
2
2
Copolymerization Examples
Polymer Synthesis
CHEM 421
• r
1
= r
2
= 1.0
–Monomers exhibit no preference for homo-propagation vs cross-propagation
–Truly random copolymer results
1.0
0.8
–F
1
= f
1
–Ethylene / vinyl acetate
F
1
0.6
0.4
0.2
0.0
A
0.0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0
f
1
Copolymerization Examples
Polymer Synthesis
CHEM 421
• r
1
• r
1
= r
2
= 1.0
= r
2
= 0.0
– Monomers exhibit tendency to cross-propagate
1.0
– Alternating copolymer results
0.8
0.6
– F
1
= 0.5
– Styrene / maleic anhydride
F
1
0.4
0.2
B
– TFE / ethylene
– 1-Butene / sulfur dioxide
0.0
A
0.0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0
f
1
Copolymerization Examples
Polymer Synthesis
CHEM 421
•
• r
1 r
1
= r
2
= r
2
= 1.0
= 0.0
• r
1 and r
2 between 0 and 1.0
1.0
– Common
– Cross-over point
» Azeotropic polymerization
F
1
0.8
0.6
0.4
C
B
0.2
0.0
A
0.0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0
f
1
Copolymerization Examples
Polymer Synthesis
CHEM 421
•
• r
1 r
1
= r
2
= r
2
= 1.0
= 0.0
• r
1 and r
2 between 0 and 1.0
1.0
• r
1
>> 1.0 and r
2
<< 1.0
– Significant drift in feed ratio
F
1
0.8
0.6
0.4
C
D
B
0.2
0.0
A
0.0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0
f
1