4Wastewater Treatment8
advertisement

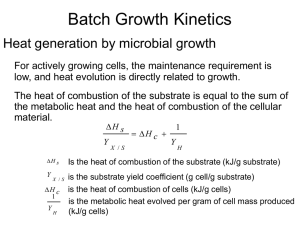
IV. Wastewater Treatment Technologies Topic IV. 8. Biological Processes of Wastewater Treatment: Fazes, Kinetics - Monod’s Equations Basic Fazes of Biological Processes General mechanism of substances micro-biological transfer: Extracellular substrate degradation by external enzymes Substrate particles attachment at the cells walls Substrate diffusion into the cells through the cells membranes Cell metabolism (biochemical transformations) Metabolism products diffusion out of the cells 1 Basic Fazes of Biological Processes General mechanism of substances micro-biological transfer: Substrate necessary composition BOD20 : N : P 100: 5 : 1 Processes of substrate dissimilation (breathing) C x H y Oz N ( x 0,25y 0,33z 0,75)O2 enzymes xCO2 (0,5 y 1,5) H 2 O NH 3 Energy Processes of substrate assimilation (cell growth) C x H y Oz N NH 3 O2 enzymes C5 H 7 NO2 H 2 O CO2 Energy Processes of the cells substances dissimilation (endogenous respiration) C5 H 7 NO2 5O2 enzymes NH 3 O2 enzymes HNO2 5CO2 NH 3 2H 2 O Energy ; O2 enzymes HNO3 2 Basic Fazes of Biological Processes Biological Processes Kinetics Biomass Growth Kinetics 1 - lag-faze; 2 - exponential growth faze; 3 - steady-state faze; 4 - endogenous respiration faze 3 Biological Processes Kinetics Equations of Monod Rate of biomass growth S m. Ks S dX / dt X k d X X - biomass concentration, g/m3 - coefficient of specific biomass growth rate, d-1 kd - coefficient of endogenous respiration, d-1 m - maximal value of the coefficient , d-1 S - substrate concentration, g/m3 Ks - half-saturation constant, g/m3 Rate of substrate utilisation dS / dt X / Y m Y . S. X Ks S Y - biomass yeld coefficient, gX/gS 4 Biological Processes Kinetics Transformations of Monod’s Equations Substrate utilisation specific rate - U 1 dS . U , gS/gX.d X dt Y Biomass age - x X x dX / dt ,d Biomass growth rate 1 / x Y .U k d , d-1 5 Biological Processes Kinetics Kinetic Parameters Use in the Practice In the bioreactors design 1 dS . U X dt S t S0 0 dS U . X dt S0 S t X .U t - necessary design hydraulic retention time to achieve S 6 Biological Processes Kinetics Kinetic Parameters Use in the Practice In the real process regulation S0 S S0 - necessary degree of purification in respect to S S0 - substrate concentration at the influent S - substrate concentration at the effluent U Y m .S Y .(K s S ) Then S and U 1 1 ( kd ) Y x U .K s K s (1 / x k d ) K s Y .S , or x m U .Y Y ( m 1 / x k d ) Y .S.( m k d ) K s .k d Therefore, the necessary effluent concentration S can be maintenance by maintenance of the relevant values of U and x. The value of the 7 later can be achieved by the excess biomass regulation.