tuberkulin skin testing

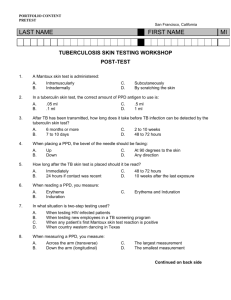
TUBERKULIN SKIN TESTING
(MANTOUX TEST) OR PROTEIN
PURIFIED DERIVATIVES
SKILLS LAB
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
DEFINITION
Tuberculin skin test
- Used to determine whether a person has tuberculosis (TB) infection. It is not a vaccine
- Tuberculin testing is useful for : a. Examining a person who isn’t sick but may have TB infection b. Screening groups of people at risk of TB disease once infected c. Examining a person who has symptoms of TB disease
Mantoux Test/PPD Test
- The both terms are used interchangeably
- Intradermal injection of Purified Protein Derivative
(PPD)
- PPD
highly purified protein fraction
culture filtrates of human type strains of M. Tuberculosis
- Standar dose
2 tuberculin units ( 2 TU )
Types of Skin tests a. Mantoux skin test (purified protein derivative or PPD)
1. Only standarized method available for identifying persons infected with M. tuberculosis
2. Administration
- 0,1 ml of PPD tuberculin containing two tuberculin units injected intradermally on the volar surface of the forearm
- gloves are not necessary for proper intradermal injections.
However, individual institution or agency policies may vary
3. Reading
- patient’s arm is inspected 48 to 72 hours after tuberculin is injected
- the reaction is the area of induration, or swelling, around the injection site. Erythema or redness should be ignored when assessing induration
* diameter of the indurated area is measured across the forearm and recorded in millimeters
* erythema, or redness, is not measured . The presence of erythema does not indicate that a person has TB infection
- a clearly positive reaction may read up to one week (day 7) after testing
B. Multiple –puncture test
1. Easy to give and convenient, but not as accurate as
Mantoux skin test
Amount of tuberculin entering the skin cannot be measured
2. Positive reactions to multiple-puncture tests should be confirmed with a Mantoux skin test
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION
Mantoux
• PPD solution plastic walls of syringes
• Injection intradermally flexor surface forearm
• The site cleansed with alcohol dried with cotton ball
• Inject 0,1 ml PPD solution ½ inch 26-or 27gauge needle
• If placed correctly
6-10 mm wheal formed
• Avoid injecting subcutaneously no local reaction develop
Positioning The Needle
•Stretch skin taut between your thumb and index finger
•Face the bevel of the needle upward and hold the needle
& syringe almost parallel to the skin
Insert properly
Insert the needle just beneath the skin surface.
When placed properly, the needle is under the epidermis. A 6-10 mm wheal should appear
Penyuntikan yang benar
Wheal 6-10 mm
The Needle is Too Deep (incorrect)
•Needle placed too deeply under epidermis
shallow, diffuse bulge instead of a tense white wheal
difficult to measure
Penyuntikan terlalu dalam
The Needle is Too Shallow (incorrect)
The bevel will barely penetrate the epidermis
Tuberculin → leaking from the injection
→ repeat the test in other arm
Penyuntikan terlalu ke permukaan
Method for Reading
-Read the site of the TST in good light with the forearm supported o a firm surface
-Look for the presence or absence of induration (swelling)
- Using a ballpoint pen, draw a line from the outer edge of the arm inward toward the induration, and stop when the pen comes against the border of the induration. Repeat the process on the other side ( Ballpoint-pen Sokal Method).
- Using a flexible millimeter (mm) ruler , measure across the induration between the two lines.
- Other method is palpation method
MANTOUX RESULTS
A. Readings : TB skin test are measured 48-72 hours after injection
1. A reaction usually consist of both induration and erythema. Measure only the induration.
2. Find → margin of induration
3. Diameter of induration → measured transversely
4. Using a millimeter ruler
B. Recording Results
•
All measurements in mm of induration
•
No induration 0 mm
C. Interpretation of Results
1. Positive Reactions a.
5 mm b.
10 mm
2. Negative Reactions
Any mm reaction < cut-points
3. False Negative and Positive Reactions
D. Counseling Inmates
Explain the significance of the (+) or (-) reactions
3. Contraindications
• Those already diagnosed with culture (+) active TB
• Those with a documented previous
(+) skin test a mm result