pH and buffers
advertisement

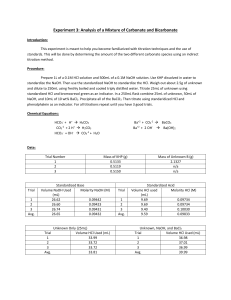
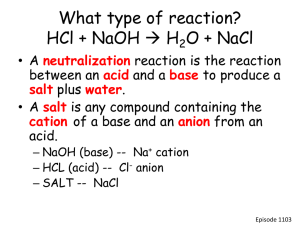
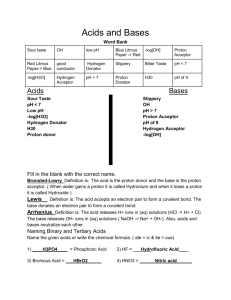
Acids and bases, pH and buffers Dr. Mamoun Ahram Lecture 2 ACIDS AND BASES Acids versus bases • Acid: a substance that produces H+ when dissolved in water (e.g., HCl, H2SO4) • Base: a substance that produces OH- when dissolved in water (NaOH, KOH) • What about ammonia (NH3)? Brønsted-Lowry acids and bases • The Brønsted-Lowry acid: any substance able to give a hydrogen ion (H+-a proton) to another molecule – Monoprotic acid: HCl, HNO3, CH3COOH – Diprotic acid: H2SO4 – Triprotic acid: H3PO3 • Brønsted-Lowry base: any substance that accepts a proton (H+) from an acid – NaOH, NH3, KOH Acid-base reactions • A proton is transferred from one substance (acid) to another molecule Ammonia (NH3) + acid (HA) ammonium ion (NH4+) + A- – – – – Ammonia is base HA is acid Ammonium ion (NH4+) is conjuagte acid A- is conjugate base Water: acid or base? • Both • Products: hydronium ion (H3O+) and hydroxide Amphoteric substances • Example: water NH3 (g) + H2O(l) ↔ NH4+(aq) + OH–(aq) HCl(g) + H2O(l) → H3O+(aq) + Cl-(aq) Acid-base reactions Acid + base salt + H2O • Exceptions: • Carbonic acid (H2CO3)-Bicarbobate ion (HCO3-) • Ammonia (NH3)- Acid/base strength Rule • The stronger the acid, the weaker the conjugate base HCl(aq) NaOH(aq) →H → Na + + Cl (aq) (aq) + (aq) + OH-(aq) HC2H3O2 (aq) ↔ H+(aq) + C2H3O2-(aq) NH3 (aq) + H2O(l) ↔ NH4+(aq) + OH-(aq) Equilibrium constant HA <--> H+ + A- Ka: >1 vs. <1 Expression • Molarity (M) • Normality (N) • Equivalence (N) Molarity of solutions moles = grams / MW M = moles / volume (L) grams = M x vol (L) x MW Exercise • How many grams do you need to make 5M NaCl solution in 100 ml (MW 58.4)? grams = 58.4 x 5 moles x 0.1 liter = 29.29 g Normal solutions N= n x M (where n is an integer) • n =the number of donated H+ Remember! The normality of a solution is NEVER less than the molarity Equivalents • The amount of molar mass (g) of hydrogen ions that an acid will donate – or a base will accept • 1M HCl = 1M [H+] = 1 equivalent • 1M H2SO4 = 2M [H+] = 2 equivalents Exercise • What is the normality of H2SO3 solution made by dissolving 6.5 g into 200 mL? (MW = 98)? Example • One equivalent of Na+ = 23.1 g • One equivalent of Cl- - 35.5 g • One equivalent of Mg+2 = (24.3)/2 = 12.15 g • Howework: Calculate milligrams of Ca+2 in blood if total concentration of Ca+2 is 5 mEq/L. Titration • The concentration of acids and bases can be determined by titration Excercise • A 25 ml solution of 0.5 M NaOH is titrated until neutralized into a 50 ml sample of HCl. What was the concentration of the HCl? • Step 1 - Determine [OH-] • Step 2 - Determine the number of moles of OH• Step 3 - Determine the number of moles of H+ • Step 4 - Determine concentration of HCl A 25 ml solution of 0.5 M NaOH is titrated until neutralized into a 50 ml sample of HCl • Moles of base = Molarity x Volume • Moles base = moles of acid • Molarity of acid= moles/volume Another method MacidVacid = MbaseVbase Note • What if one mole of acid produces two moles of H+ MacidVacid = 2MbaseVbase Homework • If 19.1 mL of 0.118 M HCl is required to neutralize 25.00 mL of a sodium hydroxide solution, what is the molarity of the sodium hydroxide? • If 12.0 mL of 1.34 M NaOH is required to neutralize 25.00 mL of a sulfuric acid, H2SO4, solution, what is the molarity of the sulfuric acid? Equivalence point Ionization of water H3O+ = H+ Equilibrium constant Keq = 1.8 x 10-16 M Kw • Kw is called the ion product for water PH What is pH? Acid dissociation constant • • • • Strong acid Strong bases Weak acid Weak bases pKa What is pKa? HENDERSON-HASSELBALCH EQUATION The equation pKa is the pH where 50% of acid is dissociated into conjugate base BUFFERS Maintenance of equilibrium What is buffer? Titration Midpoint Buffering capacity Conjugate bases Acid CH3COOH H3PO4 H2PO4- (or NaH2PO4) H2CO3 Conjugate base CH3COONa (NaCH3COO) NaH2PO4 Na2HPO4 NaHCO3 How do we choose a buffer? Problems and solutions • A solution of 0.1 M acetic acid and 0.2 M acetate ion. The pKa of acetic acid is 4.8. Hence, the pH of the solution is given by • Similarly, the pKa of an acid can be calculated Exercise • What is the pH of a buffer containing 0.1M HF and 0.1M NaF? (Ka = 3.5 x 10-4) Homework • What is the pH of a solution containing 0.1M HF and 0.1M NaF, when 0.02M NaOH is added to the solution? At the end point of the buffering capacity of a buffer, it is the moles of H+ and OH- that are equal Exercise • What is the concentration of 5 ml of acetic acid knowing that 44.5 ml of 0.1 N of NaOH are needed to reach the end of the titration of acetic acid? Also, calculate the normality of acetic acid. Polyprotic weak acids • Example: Hence Excercise • What is the pH of a lactate buffer that contain 75% lactic acid and 25% lactate? (pKa = 3.86) • What is the pKa of a dihydrogen phosphae buffer when pH of 7.2 is obtained when 100 ml of 0.1 M NaH2PO3 is mixed with 100 ml of 0.1 M Na2HPO3? Buffers in human body • Carbonic acid-bicarbonate system (blood) • Dihydrogen phosphate-monohydrogen phosphate system (intracellular) • Proteins Blood buffering Blood (instantaneously) CO2 + H20 H2CO3 Lungs (within minutes) H+ + HCO3Excretion via kidneys (hours to days) Roles of lungs and kidneys • Maintaining blood is balanced by the kidneys and the lungs • Kidneys control blood HCO3 concentration ([HCO3]) • Lungs control the blood CO2 concentration (PCO2) Calculations… Acidosis and alkalosis • Can be either metabolic or respiratory • Acidosis: – Metabolic: production of ketone bodies (starvation) – Respiratory: pulmonary (asthma; emphysema) • Alkalosis: – Metabolic: administration of salts or acids – Respiratory: hyperventilation (anxiety) Acid-Base Imbalances • pH< 7.35 acidosis • pH > 7.45 alkalosis 62 Respiratory Acidosis H+ + HCO3- H2CO3 CO2 + H O 2 Respiratory Alkalosis H+ + HCO3- H2CO3 CO2 + H2O Metabolic Acidosis + H + HCO - H CO 3 2 3 CO2 + H2O Metabolic Alkalosis H+ + HCO3- H2CO3 CO2 + H2O



![pH = - log [H + ]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/005622524_1-002df1ea50d2a849b15deb604928664e-300x300.png)