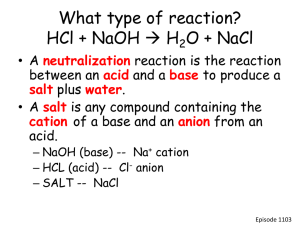
neutralized - Red Hook Central School District
advertisement

Strong acids All (100%) of the H ionize to H+ HCL, H2SO4, HNO3 are all strong acids Strong Bases All (100%) of the OH ionize to (OH)- NaOH and KOH are strong bases WEAK acids and bases Not all the hydrogen ions or hydroxide ions come off (ionize) in solution Carbonic acid and Phosphoric acids are weak Acid Base Reactions Acids + Metals In lab we did an experiment with Zinc and acid: Zn(s) + HCl (aq) H2(g) + ZnCl2 (aq) Is this equation balanced? Balance it! What type of reaction is it? If we used copper instead of zinc, what would happen? (hint: look at Table J) Neutralization Reactions Neutralization Reactions Acid + Base water + a salt This is true for any acid and base Because water (pH = 7= neutral) is produced, the acid and the base are neutralized Write Neutralization Reactions for… Nitric acid + potassium hydroxide Sulfuric acid + calcium hydroxide Magnesium hydroxide and hydrochloric acid Titration Equation Remember: Molarity (M) = Moles/Liter So…. moles = molarity x Liters Titration Equation In a neutralization reaction…… the number of moles of acid must be equal to the number of moles of base (or the end result will not be neutral! ) Titration Equation Therefore, in a neutralization reaction…. Moles of Acid = Moles of Base or Moles (A) = Moles (B) Titration Equation Since we know that Moles = molarity x Liter, We can substitute in for Moles Moles of Acid = Moles of Base Molarity(of acid) x liters(of acid) = Molarity(of base) x Liters (of base) Titration Equation We simplify this equation: (see Table T) Ma x Va = Mb x Vb Where Ma = molarity of acid Va = volume of acid (in liters) Mb = molarity of base Vb = volume of base (in liters) Ma x Va = Mb x Vb What is the concentration of HCl if 50 ml of a 0.25M KOH are needed to neutralize 20 ml of HCL solution? Ma = ? Va = 20 ml Mb = .25M Vb = 50 ml Ma x .02L = .25M x .05L Ma x Va = Mb x Vb What is the concentration of HCl if 50 ml of a 0.25M KOH are needed to neutralize 20 ml of HCL solution? Ma x .02L = .25M x .05L Ma = .25M x .05L .02L Ma = .625M Titration is used to very accurately measure the volumes of acids and bases during a neutralization reaction Phenolphthalein indicator is clear in acids, pink in bases Neutralization is reached when the clear solution turns a pale pink If solution turns a dark pink, too much base has been added and the solution is now basic, not neutral pH pH • pH =7 • pH 0-6 Acidic • pH 8-14 Basic Neutral (pure water) Indicators: Table M • Change colors in the presence of acids or bases • Phenolphthalein = clear in acids, pink in bases • Litmus = red acid Blue Base