Equity Valuation
advertisement
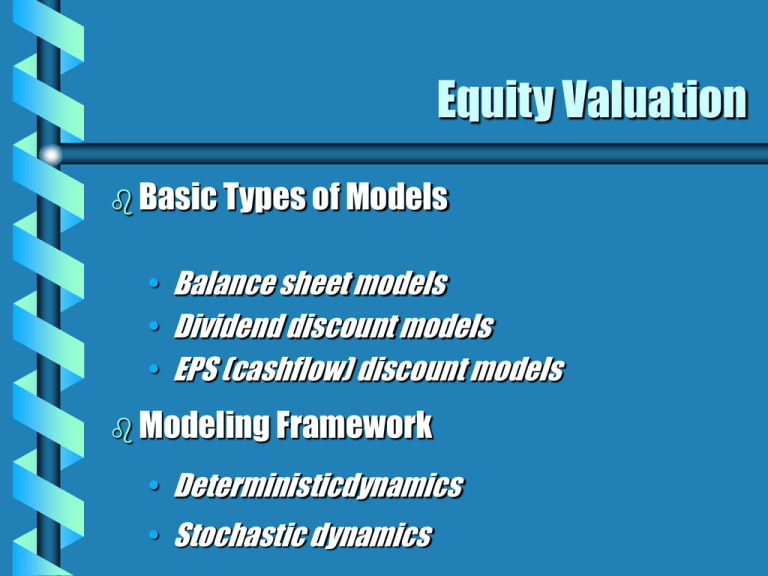
Equity Valuation Basic Types of Models • Balance sheet models • Dividend discount models • EPS (cashflow) discount models Modeling Framework • Deterministicdynamics • Stochastic dynamics Fair Value vs Market Price Fair Value • Self assigned Value • Variety of models are used for estimation Market Price • Consensus value assessment by all market participants Trading Signal • FV > MP: • FV < MP: • FV = MP: Buy Sell or Short Sell Hold or Fairly Priced Dividend Discount Models Dt Vo t t 1 (1 k ) V0 = Value of Stock Dt = Dividend k = required return No Growth Model D Vo k Where the stock has earnings and dividends that are expected to remain constant foreever. Example: Preferred Stock No Growth Model: Example D Vo k E1 = D1 = $5.00 k = .15 Then, V0 = $5.00 / .15 = $33.33 Constant Growth Model Do (1 g ) Vo kg g = constant perpetual growth rate Constant Growth Model: Example Do (1 g ) Vo kg E1 = $5.00 b = 40% (1-b) = 60% k = 15% D1 = $3.00 g = 8% (b: EPS retention ratio) V0 = 3.00 / (.15 - .08) = $42.86 Estimating Dividend Growth Rates g ROE b g = growth rate in dividends ROE = Return on Equity for the firm b = EPS retention rate (1- dividend payout ratio) Partitioning Value: Growth and No Growth Components E1 Vo PVGO k Do (1 g ) E1 PVGO (k g) k PVGO = Present Value of Growth Opportunities E1 = Earnings Per Share for period 1 Partitioning Value: Example ROE = 20% b = 40% E1 = $5.00 D1 = $3.00 g = .20 x .40 = .08 or 8% k = 15% Partitioning Value: Example 3 Vo $42.86 (.15.08) 5 NGVo $33.33 .15 PVGO $42.86 $33.33 $9.52 • Vo = value with growth • NGVo = no growth component value • PVGO = Present Value of Growth Opportunities Multi-Period Dividend-Discount Model P D D D ... V (1 k ) (1 k ) (1 k ) 1 0 N 2 1 2 PN = expected sales price of stock at time N N = number of years the stock is to be held N N Practical Difficulties with DDM Some firms do not pay dividends Can you forecast future dividends? Can you predict the terminal liquidation value Pn ? What about the discount rate k? (perhaps, the CAPM? The APT?) Multi-Period Earnings-Discount Model (1 b) E N P N (1 b) E1 (1 b) E 2 ... V0 (1 k )1 (1 k ) 2 (1 k ) N PN = expected sales price of stock at time N N = number of years the stock is to be held Practical Concerns with EDM EPS forecasts are available from I/B/E/S, First Call, Zacks, …. Dividend payout ratio (1-b) can be estimated, either based on cash dividend or dividendin-kind But, what about Pn and k? P/E Ratios P0 d E k g d: dividend payout ratio k: cost-of-capital (or, risk-adjusted discount rate) g: EPS growth rate P/E Example k = 12.5% Thus, g = 9% d = 40% P/E = (1 - .60) / (.125 - .09) = 11.4 If E = $2.73, we have P = 11.4 X 2.73 =$31.14 Problems with P/E Ratios What is E? • E = trailing 12-month EPS? • E = 12-month-forward EPS? What is g? • g = average historical EPS growth? • g = expected next-yr EPS growth? • g = long-run EPS growth?