Chapter 08
McGraw-Hill/Irwin
Valuing Stocks
Copyright © 2012 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
1
Copyright © 2012 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved
Common Stock
• Represents ownership in corporation
• Value of common stock based on
– Company’s profitability and growth potential
– Current market interest rates
– Overall stock market conditions
8-2
Stock Markets
• Provide liquidity through stock exchanges
• Provide means for buyers and sellers to transact
8-3
Stock Markets
•
•
•
•
•
New York Stock Exchange (NYSE)
American Stock Exchange (AMEX)
NASDAQ
FTSE
Nikkei
8-4
Stock Markets
• Stock market indexes
– Dow Jones Industrial Average tracks 30 large
industry-leading stocks
– Standard & Poor’s 500 tracks largest 500 U.S.
firms
– NASDAQ Composite Index primarily tracks
technology firms
8-5
Stock Markets
• Trading Stocks
– Quoted bid is highest price at which market
makers will buy
– Quoted ask is lowest price at which market
makers will sell
8-6
Stock Markets
• Trading Stocks
– Market order is filled at current ask price
– Limit order only executed if ask price is below
price target
8-7
Basic Stock Valuation
• Present value calculations used
• Unlike present value for bonds, stock cash flows
are unknown
– Dividends
– Future selling price
8-8
Basic Stock Valuation
• Find present value of future dividends and future
selling price
• One-year-holding-period timeline example
8-9
Basic Stock Valuation
• Today’s value = present value of next year’s
dividend and price
8-10
Basic Stock Valuation
• Two-year-holding-period timeline example
8-11
Basic Stock Valuation
• For a holding period of n years, the value of a
stock is measured by the present value of
dividends over n years plus the sale price
8-12
Dividend Discount Model
• Stock’s value is the present value of an infinite
stream of dividends and no future final sales
price
8-13
Constant Growth Model
• Assumes growth rate smaller than discount rate
• Next year’s dividend ÷ (Discount rate – Growth rate)
8-14
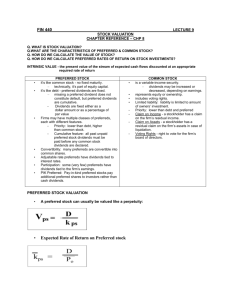
Preferred Stock
• Has priority over common stock in bankruptcy
• Pays a constant dividend
• Valued using constant-growth model
8-15
Expected Return
• Investors demand higher returns from higherrisk investments
• Dividend yield and expected stock price
appreciation comprise Expected Return
8-16
Variable Growth-Rate Valuation
• Combines present-value cash flow with
constant-growth-rate model
8-17
Two-Stage Growth Valuation
• Variable-growth-rate stock
• Stock value = Present value of each dividend
during first growth stage + Present value of second
growth stage
8-18