Atomic Mass Units
advertisement

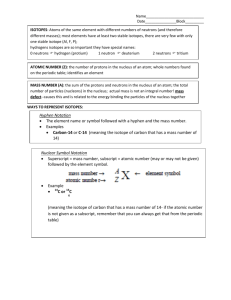
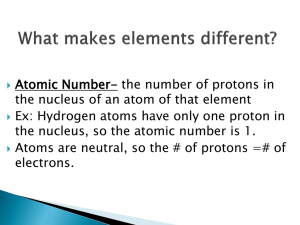
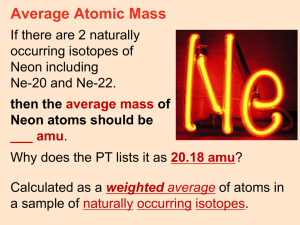
By convention there is color, By convention sweetness, By convention bitterness, But in reality there are atoms and space. -Democritus (c. 400 BCE) AT O M ATOM NUCLEUS NUCLEUS ELECT RONS ELECTRONS PROT ONS PROTONS NEUT RONS NEUTRONS P O S IT IV E POSITIVE N E U T R AL NEUTRAL C H AR G E CHARGE C H AR G E CHARGE Mass Number N E G AT IV E CHARGE C H AR G E NEGATIVE Atomic Number equals the # of... Scale of the atom atomic mass unit (amu) = the mass of one proton 1.66 -27 10 g Sum of the protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom Always a whole number # of neutrons = mass # - atomic # The number of protons within the nucleus Atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons Isotope symbol: Mass # Atomic# 6 C “Carbon-12” How to calculate the average atomic mass of an element: List all isotopes, mass numbers, and percent relative abundance of an element Multiply the mass number of each isotope by its relative abundance Add all the products together = atomic mass An example: Chlorine-35 (35Cl) has 17 protons and 18 neutrons and has a relative abundance of 75.8% Chlorine-37 (37Cl) has 17 protons and 20 neutrons and appears 24.2% of the time. Multiply the mass number of each isotope by its relative abundance (Chlorine-35) 35 amu × 0.758 = 26.53 amu (Chlorine-37) 37 amu × 0.242 = 8.95 amu Add all the products together = atomic mass 26.53 amu + 8.95 amu = 35.48 amu