Atomic Mass
advertisement

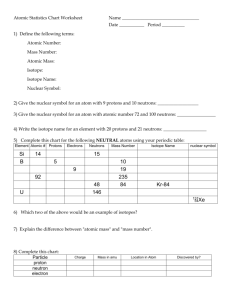
Modern View of Atomic Structure Protons Positively charged subatomic particles Located in the nucleus of an atom Make up most of the atom’s mass Pos. charge of proton = Neg charge of electron (e-) 1 proton has as much mass as around 1840 e-‘s Periodic table is arranged in increasing number of protons Neutrons Neutral subatomic particle Located in the nucleus of the atom DOES contribute to the mass of the atom Most common type of hydrogen (called protium) contains NO neutrons. However, deuterium (heavy hydrogen) does contain 1 proton and 1 neutron in the nucleus. Electrons Negatively charged subatomic particle Located in the space outside of the nucleus Mass of the electron is negligible Subatomic Particles Summary Subatomic Mass in grams Particle Electron (e-) 9.11 x 10-28 g Proton (p, +) 1.67 x 10-24g Neutron (n,o) 1.67 x 10-24 g Mass in amu 0.000549 amu 1.0073 amu 1.0087 amu Distinguishing between Atoms Atomic Number Is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom of an element Used to identify an element ALWAYS a whole number Mass Number Most of the atom’s mass is concentrated in the nucleus (protons and neutrons) Mass Number = # of protons + # of neutrons Electron mass is so small that it is NOT included in the mass # Number of neutrons = Mass # - Atomic # Isotopes All atoms of the same element have the same # of protons but may have DIFFERENT number of neutrons Isotope atoms of the same element with different # of neutrons Often identify an element by mass number Example: carbon-12, carbon-14 Atomic Mass Atomic masses shown on the PT (periodic table) represent a weighted average based on the relative abundance of each isotope of a particular atom. Atomic mass unit (amu) is a unit of mass equal to 1/12th the mass of a carbon-12 atom. amu’s are used instead of grams because the masses of subatomic particles are small More useful to compare the relative masses of atoms using a reference isotope as a standard Carbon-12 was chosen as the reference isotope. Average Atomic Mass The atomic mass on the periodic table is an average of all the isotopes of that particular element. Every element (except the synthetic ones) has one or more isotopes Σ (mass of isotope X relative abundance) Practice: 1. Neon has two isotopes: Ne-20 (having a mass of 20 u) and Ne-22 (having a mass of 22 u). Given the following abundances of these isotopes in nature, what is the average atomic mass of neon? Mass number Abundance Ne-20 90% Ne-22 10% 2. What is the average atomic mass of hafnium given the following abundance information on its isotopes? Mass number Abundance Hf-176 5% Hf-177 19 % Hf-178 27 % Hf-179 14% Hf-180 35% 3. Calculate the atomic mass of potassium if the abundance atomic masses of the isotopes making up its naturally occurring samples are as given below. Isotope Relative abundance Atomic Mass potassium-39 93.12 % 38.964 amu potassium-41 6.88 % 40.962 amu