6D PowerPoint
advertisement

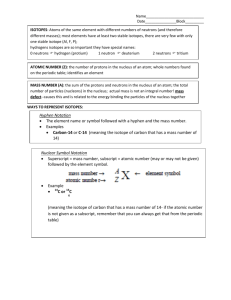
Average Atomic Mass Chemistry 6(D) Average Atomic Mass Lesson Objective • Calculate average atomic mass of an element using isotopic composition Contents of the Nucleus • Nucleus – center of the atom, where protons and neutrons are found – Neutron ( n 0 ) – neutrally charged subatomic particle • Mass of approximately 1 amu – Proton ( p + ) – positively charged subatomic particle • Mass of approximately 1 amu • Atomic number – number of protons of an element – Number of protons determines the identity of an element – Number of neutrons can vary without changing the element Isotopes • Isotopes – atoms of the same element that contain different numbers of neutrons Ex) What is the mass number of the isotope of carbon that has 6 neutrons? – Neutrons have mass • Different isotopes of an element have different masses – Isotopes are distinguished using mass numbers Mass number = n 0 + p+ Mass number = 6 n0 + 6 p+ = 12 Carbon-12 Isotopic Notation Isotopic notation Ex) How many neutrons does 17 O contain? 8 Mass Number n0 = 17 − 8 p+ = 9 n0 Atomic Number Element Symbol Isotopic Composition • Isotopic composition represents the relative amounts of each isotope of an element Average Atomic Mass Ex) Use the data table to find the average atomic mass of silver 1. 2. 3. Change the percent abundance to decimal form Multiply the mass of each isotope by its percent abundance in decimal form Add the values found in Step 2 together Isotope Percent Abundance Atomic Mass (amu) Silver-107 51.839% 106.91 Silver-109 48.161% 108.90 51.839 % = 51.839 = 0.51839 100 48.161 % = 48.161 = 0.48161 100 Silver-107 = 106.91 amu × 0.51839 = 55.421 amu Silver-109 = 108.90 amu × 0.48161 = 52.447 amu 52.421 amu + 55.447 amu = 107.87 amu Average Atomic Mass Lesson Objective • Calculate average atomic mass of an element using isotopic composition