Chemistry
advertisement

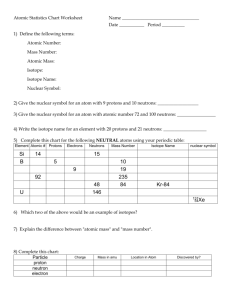
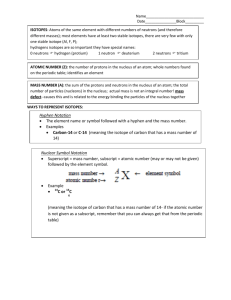
Chemistry Section _____ Name: ISOTOPE WS KEY _____________________________ Date: ________________________ Define the following terms. 1. atomic number (Z): The number of protons in the nucleus. __________________________________________________________________________ 2. mass number: The number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus. __________________________________________________________________________ 3. isotope: Atoms of the same element (same number of protons) having differing numbers of neutrons. 4. nuclide: Atoms of a given element which have the same number of neutrons. __________________________________________________________________________ Answer the following questions. 5. What is the result if the atomic number of a nuclide is subtracted from the mass number of that nuclide? The number of neutrons. Look at Table 4.3 on the top of page 114. Write the symbol for each of the following: 6. proton p or p+ 7. neutron n or n0 8. electron e– In the third paragraph of page 117, find the name of the method used to describe an isotope when written as copper-63: 9. isotope notation (or hyphen notation) Write the nuclear symbol method for showing copper-63 that shows the chemical symbol, mass number, and atomic number as shown in figure 4-16 at the top of page 117. 10. Cu The superscript in the symbol 14 6 C represents the 11. mass number while the subscript in the symbol 14 6 C represents the 12. atomic number Because the atomic number for any given element is always the same, the atomic number is often not written for a specific nuclide of that element. The atomic number can be found on any Periodic Table (like the one on page 9 of your reference tables). In other words, 12 6 C is often written simply as 12 C For each of the following nuclides, find the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons you would expect to find in a neutral atom. The first one has been done for you. 1H p+ = 1 n0 = 0 e– = 1 2H p+ = 1 n0 = 0 e– = 1 3H p+ = 1 n0 = 0 e– = 1 3He p+ = 1 n0 = 0 e– = 1 9B p+ = 5 n0 = 4 e– = 5 10B p+ = 5 n0 = 5 e– = 5 14C p+ = 6 n0 = 8 e– = 6 14N p+ = 7 n0 = 7 e– = 7 40K p+ = 19 n0 = 21 e– = 19 48Ca p+ = 20 n0 = 28 e– = 20 13. How many protons, neutrons and electrons are in an atom of chlorine-37? p+ = 17, n0 = 20, e– = 17 14. Write the nuclear symbol for an atom of boron-11. Last printed 10/15/2014 6:30:00 AM 15. Write the hyphen notation for the neutral atom of an element that contains 8 electrons and 10 neutrons. oxygen-10 16. The atomic mass unit, amu, is based on which nuclide? carbon-12 Copper is element number 29. Find the averaged atomic mass of copper on the Periodic Table on page 9 of your reference tables then write that mass in the space below. 17. 63.546 u If atomic mass is based on 12 6 C having a mass of exactly 12 amu, you may be wondering why there are decimals in the averaged masses of the elements. That is because the masses shown on your tables are the weighted average of all the naturally occurring isotopes. Here is an example of how to calculate these averages for the two naturally occurring isotopes of copper. 63 Cu has a mass of 62.929 599 amu and occurs 69.17% of the time 65 Cu has a mass of 64.927 793 amu with a natural abundance of 30.83%. First, convert the percentages to their decimal equivalents: 69.17% = 0.6917 and 30.83% = 0.3083. Now calculate the weighted averages of each nuclide and sum them together. + 63 Cu : 0.6917 x 62.929 599 amu 65 Cu : 0.3083 x 64.927 793 amu Cu = 63.55 amu Now it’s your turn. Begin the practice problems 18 – 24 from page 121 in your book. Answers to these questions are in the Teacher’s Edition of the text. Last printed 10/15/2014 6:30:00 AM