Pediatric Ventilation Survival Powerpoint
advertisement

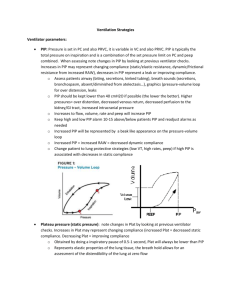
Pediatric Ventilation First few minute survival guide Scenario Emergency Department is flooded with people who have flu like symptoms. 14 people in two days have been intubated in the ED who had presented with the flu like symptoms ICU is full to capacity. (20 admissions in 2 days). It is suspected that many of these people are infected with H1N1 influenza There are two sick calls for staff this shift that we can not seem to replace You have just been informed that all elective surgery has been cancelled until further notice Scenario At 1300 hrs a toddler is carried in to the UH Emergency Room by her mother. The child is about 2 years old and weighs about 35 lb or 16 kg. The child is unresponsive and has decreased muscle tone. Scenario The vital signs are; RR ~60/min HR 170/min BP 110/70 Temp 38.1 SpO2 71% Child has +++ use of accessory muscles ++ in-drawing and tracheal tug Unresponsive Skin mottled What needs to be done? O2/IV/monitor Where do you find the paed nonrebreather mask? a) b) c) d) Neo box Back of Tower in the rescs room Arrest cart We don’t have any, you need to bag Actions The RTs place the child on 100 % via paeds non-rebreather mask found in the arrest cart The RNs immediately gain IV access and utilize the Brozelow tape to determine weight estimate and medication and fluid administration doses. The Emerg consultant wants to intubate. He is calculating the doses for sedation. Actions a) b) c) d) Patient is being bagged by the RT. Chest is not moving well, but it is noticed that the blow off valve for the bag is continually popping off. You next actions should be; Panic - run around in circles Check to make sure head position and bag valve mask technique is appropriate Call for a STAT CXR Insert a nasal airway Position and technique look good a) b) c) d) Chest still not moving well with the pop off valve blowing off. What now? Call a lawyer Disable pop off valve Get a larger bag Nothing - You will have to live with it Things are not going well a) b) c) d) The pop off valve is bypassed and the chest begins to move well, but SpO2 remains ~84% What should we do? Confirm patient is receiving 100% oxygen and move to intubate ASAP Scoop and run kiddie to Children’s Hospital Pray - Not much more can be done None of the above Equipment Prep You look to the Broselow tape to find what size ETT and blade to use. The tape recommends a 5.0 uncuffed ETT, but you think you should use a cuffed tube. Why? a) b) c) d) It is likely the child will require high pressures with ventilation and will therefore need a cuff to ventilate effectively Child may vomit since they were not NPO prior to coming in. If the tube size comes with a cuff that is what should be inserted Always put in a uncuffed tube on a child under 8 Intubating a child The RRT at UH can intubate a child if; a) b) c) d) They are >8 years old Any age, since this is an emergency Any age if the RT has met and maintained the training requirements Any age but only with a physician's order Intubating a child The patient is tubed easily by the ER consultant. ETT is taped, (what level) a) b) c) d) but SPO2 remains 88%. Next actions; Confirm placement with absence of sounds over the epigastrum,CO2 Detector and bilateral chest expansion Suction patient to confirm ETT is patent, and rule our mucus plug. Assess for bilateral breath sounds and chest expansion to rule out pneuomothorax All of the above Let’s Ship The ED & RT are working at capacity Paed/Neo Transport team is called to come to transport patient to VH Children’s Hospital. They can not respond to assist for another 6 hours (as they are on another run) Call to Children’s Hospital reveals they are not prepared to take the patient as PCCU is at capacity and they are currently arranging to alternative space to place that patient. They will need 3 - 4 hours What now? a) b) c) d) We are stuck with this very sick toddler for at least a few hours. – We need to ventilate this child. What vent do you choose? LTV 1000 ADU Vision PB 840 PB 840 Ok for use down to 25 mL Adult Circuit is good from 10 kg and greater Paed circuit is needed for a smaller child (<10 kg or ~ 1year old or less) Use _______ (circuits in the ED and RT Dept) Initial Parameters a) What to set them up on? A/C 30/min Vt 100mL, PEEP 3 cmH2O, FiO2 1.0 b) A/C 25/min, Press Control 15 (distending of 10 cmH2O) aim for VT of 5-8 mL/kg, PEEP 5, FiO2 1.0 c) Pressure Support 15cmH2O, aim for VT of 58 mL/kg, PEEP 5 cmH2O, FiO2 1.0 d) A/C 25/min, Press Control 15 (distending of 10 cmH2O) aim for VT of 5-8 mL/kg, PEEP 5, FiO2 0.4 (concern about rentenopathy) Paediatric Ventilation - Initial Parameters Use PB 840 with adult circuit (>1 year old or 10 kg) FiO2 1.0 PEEP 5 cmH2O Pressure control 10 cmH2O (above PEEP) Target Vt 5-8 mL/Kg Rate 25/min Ti 0.6 seconds for a 1 year old and gradually increase until reaching typical adult I times at about 13-14 years of age Consult with RTs in PCCU (15565) Initial Parameters Pressure Control of 10 cmH2O is likely not enough. Look for adequate chest expansion and exhaled Vt of ~5-8 mL/kg If baby wakes up, they could possibly breathe faster than the vent could respond. There maybe no choice but to sedate or paralyze. H1N1 infection apparently requires lots of sedation. Watch BP. It may drop due to; Increased intrathoracic pressure Sedation decrease work of Breathing Initial Parameters Consult with RTs in PCCU PEEP strategy is very similar to what we use in adults, but the levels may be a little lower due to; More compliant thorax Thinner and more friable Consult with RTs in PCCU (15565) Spontaneous breathing modes Careful with keeping the child on straight PSV for extended periods (during the acute phase) Response time for the vent may be too slow with the very rapid RR of the child. If the child is asynchronous with the vent, consider sedation or paralysis. Care for the ventilated child What needs to be done next? a) b) c) d) I/O line, fluid bolus Gases and CXR OG tube placement All of the above Maintenance Abgs (heal prick for babies, Cap gases (ear) for toddlers) CXR- Make sure head is neutral with the CXR is taken. If the head is flexed the tube will be further out. If the head is extended the ETT may be deeper. The younger the child the more pronounced the effect Infant Ventilation - Initial parameters Use _______with an infant circuit (<1 year or 10 kg) FiO2 1.0 PEEP 5 cmH2O Pressure control 10 cmH2O (above PEEP) Target Vt 5-8 mL/Kg Rate 30-35/min (more if very low pH pre ETT) – max rate ~50-55/min Ti 0.35 seconds for a 1 year old and lower Consult with RTs in PCCU (15565)