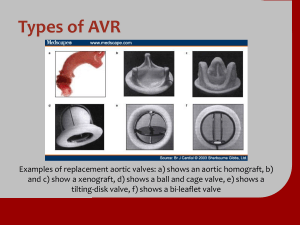
Lessons from TAVR Randomized
Trials and Registries
E Murat Tuzcu, MD
Professor of Medicine
Cleveland Clinic
Financial disclosures: None
PARTNER Executive Committee member
Edwards Transcatheter Valve Evolution
Untreated
Equine
Tissue
Andersen
Pig implant, May ’89
Untreated
Equine Tissue
Cribier-Edwards™
FIM, April 2002
Treated
Bovine Tissue
Edwards SAPIEN™
August, 2007
TFX Treated
Bovine /CC
Sapien XT™
January, 2010
CoreValve Revalving
Generation 1
Generation 2
Generation 3
25 Fr
21 Fr
18 Fr
2004-2005
Surgical Fem-Fem
CP By-Pass
2005-2006 (June)
CP By-Pass + TandemHeart
Percutaneous Support
Dec 2006
No Support
No Anesthesia
Transfemoral TAVI
30-day Mortality
Study (%)
n
Age
ES/STS
Mortality (%)
REVIVE/REVIVALa
161
83.7
34.3/13.1
11.2
VANCOUVERb
114
83.9
30.3/-
7.9
PARTNER EUc
59
82.3
25.7/11.3
8.1
SOURCEd
463
81.7
25.7/-
6.3
CANADIANe
345
81
-/9.8
10.4
FRENCH Regf
95
83.2
25.6/15.4
8.4
UK Regg
172
83
20
8.9
a. Kodali et al TCT 2008
b. Webb TCT 2008
c. Schachinger et al Euro PCR 2009
d. Thomas et al Euro PCR 2009
e. Rodes-Cabau et al. JACC 2010;55:In Press
f. Eltchaninoff H. AHA 2009
g. LudmanEuroPCR 2010
Transfemoral TAVI
One Year Survival
1.0
0.8
0.6
0.4
REVIVAL
VANCOUVER
SOURCE
CANADIAN
UK Registry
0.2
0.0
0
2
4
75.8%
73.8%
81.1%
75.0%
79.5%
6
Month
8
10
12
PARTNER Study Design
Symptomatic Severe Aortic Stenosis
ASSESSMENT: High-Risk AVR Candidate
3,105 Total Patients Screened
Total = 1,057 patients
N = 699
High Risk
Inoperable
2 Parallel Trials:
Individually Powered
N = 358
ASSESSMENT:
Transfemoral
Access
Yes
No
1:1 Randomization
N = 179
TF TAVR
Not In Study
N = 179
VS
Standard
Therapy
Primary Endpoint: All-Cause Mortality
Over Length of Trial (Superiority)
Co-Primary Endpoint: Composite of All-Cause Mortality
and Repeat Hospitalization (Superiority)
All Cause Mortality
100
Standard Rx
TAVI
All-cause mortality (%)
80
60
∆ at 1 yr = 20.0%
NNT = 5.0 pts
50.7%
40
30.7%
20
HR [95% CI] =
0.54 [0.38, 0.78]
P (log rank) < 0.0001
0
0
6
12
18
24
Months
Numbers at Risk
TAVI
Standard Rx
179
179
138
121
122
83
67
41
26
12
NYHA Class Over Time
All patients
P < 0.0001
P < 0.0001
P < 0.0001
Percent
P = 0.68
TAVI Standard Rx
Baseline
I
TAVI Standard Rx
TAVI Standard Rx
30 Day
II
6 Month
III
IV
TAVI
Standard Rx
1 Year
Dead
Treatment
Visit
Aortic Valve Mean Gradient (Core Lab)
(mmHg)
*
*
*
*
Douglas et al ACC 2011
Clinical Outcomes at 30 Days and 1 Year
per cent
Major Vascular
Complications
P<0.0001
TAVI (n=179)
P<0.0001
Standard Rx (n=179)
Major Stroke
P = 0.06
P = 0.18
Published Cost Effectiveness Estimates
Dollars per Life Year or QALY ($thousands)
$300
$250
$200
$150
$100
$50
$0
aspirin MI rosuvastatin
prevention high-CRP
ICD prim
prev
CRT-D v.
medical Rx
dabigatran
AF
PARTNER
Cohort B
AF ablation
vs. AAD
dialysis
PCI stable
CAD
LVAD
destination
Rx
Clinical Implications
• Balloon-expandable TAVI should be the new standard
of care for patients with aortic stenosis who are not
suitable candidates for surgery!
PARTNER Study Design
Symptomatic Severe Aortic Stenosis
ASSESSMENT: High-Risk AVR Candidate
3,105 Total Patients Screened
Total = 1,057 patients
N = 699
High Risk
Inoperable
2 Parallel Trials:
Individually Powered
ASSESSMENT:
Yes
Transfemoral
Access
Transfemoral (TF)
1:1 Randomization
N = 244
TF TAVR
VS
ASSESSMENT:
No
Transfemoral
Access
Transapical (TA)
1:1 Randomization
N = 248
N = 104
AVR
TA TAVR
N = 358
Yes
1:1 Randomization
N = 103
N = 179
AVR
TF TAVR
VS
Primary Endpoint: All-Cause Mortality at 1 yr
(Non-inferiority)
No
Not In Study
N = 179
VS
Standard
Therapy
Primary Endpoint: All-Cause Mortality
Over Length of Trial (Superiority)
Co-Primary Endpoint: Composite of All-Cause Mortality
and Repeat Hospitalization (Superiority)
Patient Characteristics (1)
Characteristic
Age (yr)
Male sex - %
STS Score
Logistic EuroSCORE
NYHA
II - %
TAVR (N = 348)
AVR (N = 351)
p-value
83.6 ± 6.8
84.5 ± 6.4
0.07
57.8
56.7
0.82
11.8 ± 3.3
11.7 ± 3.5
0.61
29.3 ± 16.5
29.2 ± 15.6
0.93
0.79
5.7
6.0
94.3
94.0
CAD - %
74.9
76.9
0.59
Previous MI - %
26.8
30.0
0.40
Prior CV Intervention - %
72.1
71.6
0.93
Prior CABG - %
42.6
44.2
0.70
Prior PCI - %
34.0
32.5
0.68
Prior BAV - %
13.4
10.2
0.24
29.3
27.4
0.60
III or IV - %
Cerebrovascular disease - %
Patient Characteristics (2)
Characteristic
TAVR (N = 348)
AVR (N = 351)
p-value
Peripheral vascular disease - %
43.0
41.6
0.76
COPD
Any
43.4
43.0
0.94
Oxygen dependent
9.2
7.1
0.34
Creatinine> 2mg/dL - %
11.1
7.0
0.06
Atrial fibrillation - %
40.8
42.7
0.75
Permanent pacemaker - %
20.0
21.9
0.58
Pulmonary hypertension - %
42.4
36.4
0.15
Frailty - %
15.6
17.6
0.58
Porcelain aorta - %
0.6
1.1
0.69
Chest wall radiation - %
0.9
0.9
1.00
Liver disease - %
2.0
2.6
0.80
Primary Endpoint:
All-Cause Mortality at 1 Year
0.5
HR [95% CI] =
0.93 [0.71, 1.22]
P (log rank) = 0.62
TAVR
AVR
0.4
26.8
0.3
0.2
24.2
0.1
0
0
6
No. at Risk
12
18
24
Months
TAVR
348
298
260
147
67
AVR
351
252
236
139
65
Clinical Outcomes at 30 Days and 1 Year
All Patients (N=699)
30 Days
Outcome
TAVR
(N = 348)
1 Year
AVR
TAVR
p-value
(N = 351)
(N = 348)
AVR
p-value
(N = 351)
Vascular complications
All – no. (%)
59 (17.0)
13 (3.8)
<0.01
62 (18.0)
16 (4.8)
<0.01
Major – no. (%)
38 (11.0)
11 (3.2)
<0.01
39 (11.3)
12 (3.5)
<0.01
Major bleeding – no. (%)
32 (9.3)
67 (19.5)
<0.01
49 (14.7)
85 (25.7)
<0.01
Endocarditis – no. (%)
0 (0.0)
1 (0.3)
0.32
2 (0.6)
3 (1.0)
0.63
New AF – no. (%)
30 (8.6)
56 (16.0)
< 0.01
42 (12.1)
60 (17.1)
0.07
New PM – no. (%)
13 (3.8)
12 (3.6)
0.89
19 (5.7)
16 (5.0)
0.68
Neurological Events at 30 Days and 1 Year
All Patients (N=699)
30 Days
Outcome
TAVR
(N = 348)
1 Year
AVR
p-value TAVR
(N = 351)
(N = 348)
AVR
p-value
(N = 351)
All Stroke or TIA – no. (%)
19 (5.5)
8 (2.4)
0.04
27 (8.3)
13 (4.3)
0.04
TIA – no. (%)
3 (0.9)
1 (0.3)
0.33
7 (2.3)
4 (1.5)
0.47
All Stroke – no. (%)
16 (4.6)
8 (2.4)
0.12
20 (6.0)
10 (3.2)
0.08
Major Stroke – no. (%)
13 (3.8)
7 (2.1)
0.20
17 (5.1)
8 (2.4)
0.07
Minor Stroke – no. (%)
3 (0.9)
1 (0.3)
0.34
3 (0.9)
2 (0.7)
0.84
Death/maj stroke – no. (%)
24 (6.9)
28 (8.2)
0.52
92 (26.5)
93 (28.0)
0.68
The Modified Rankin Scale
Minor
0 - No symptoms.
1 - No significant disability. Able to carry out all usual activities, despite
some symptoms.
Major
2 - Slight disability. Able to look after own affairs without assistance,
but unable to carry out all previous activities.
3 - Moderate disability. Requires some help, but able to walk
unassisted.
4 - Moderately severe disability. Unable to attend to own bodily needs
without assistance, and unable to walk unassisted.
5 - Severe disability. Requires constant nursing care and attention,
bedridden, incontinent.
6 - Dead.
Mortality and Major Stroke at 30 Days
All-Cause Mortality at 30 Days
All Patients
TF Patients
TA Patients
no. of patients ( %)
no. of patients ( %)
no. of patients ( %)
TAVR
AVR
p-value
TAVR
AVR
p-value
TAVR
AVR
p-value
ITT
12 (3.4)
22 (6.5)
0.07
8 (3.3)
15 (6.2)
0.13
4 (3.8)
7 (7.0)
0.32
AT
18 (5.2)
25 (8.0)
0.15
9 (3.7)
18 (8.2)
0.046
9 (8.7)
7 (7.6)
0.79
Major Stroke at 30 Days
All Patients
TF Patients
TA Patients
no. of patients ( %)
no. of patients ( %)
no. of patients ( %)
TAVR
AVR
p-value
TAVR
AVR
p-value
TAVR
AVR
p-value
ITT
13 (3.8)
7 (2.1)
0.20
7 (2.9)
4 (1.7)
0.37
6 (5.8)
3 (3.2)
0.37
AT
13 (3.8)
7 (2.3)
0.25
6(2.5)
3 (1.4)
0.37
7 (7.0)
4 (4.4)
0.45
Mortality and Major Stroke at 1 year
All-Cause Mortality at 1 Year
All Patients
TF Patients
TA Patients
no. of patients ( %)
no. of patients ( %)
no. of patients ( %)
TAVR
AVR
p-value
TAVR
AVR
p-value
TAVR
AVR
p-value
ITT 84 (24.2) 89 (26.8)
0.44
54 (22.2) 62 (26.4)
0.29
30 (29.0) 27 (27.9)
0.85
AT 81 (23.7) 78 (25.2)
0.64
51 (21.3) 55 (25.2)
0.33
30 (29.1) 23 (25.3)
0.55
Major Stroke at 1 Year
All Patients
TF Patients
TA Patients
no. of patients ( %)
no. of patients ( %)
no. of patients ( %)
TAVR
AVR
p-value
TAVR
AVR
p-value
TAVR
AVR
p-value
ITT
17 (5.1)
8 (2.4)
0.07
9 (3.8)
4(1.7)
0.15
8 (8.3)
4 (4.3)
0.26
AT
17 (5.2)
8 (2.7)
0.11
8 (3.5)
3(1.4)
0.15
9 (9.4)
5(5.9)
0.37
TAVR Neuro Events in PARTNER B
10 10
8 strokes occurred when patients were in AF
9
Number of Events
88
6
6
4
4
2
2
0
0
5
4
5strokes
0-3 day
3
0-5 Days
6-30 Days
31Days - 1 Year
>1Year
Paravalvular Aortic Regurgitation
P< 0.001
P< 0.001
30 Days
6 Months
1 Year
Patients, %
P< 0.001
None
Trace
Mild
Moderate
Severe
Implications
•TAVR is an acceptable alternative to AVR in
selected high-risk operable patients.
• A multidisciplinary valve team benefits patients
and recommended for all valve centers.
• Future RCT should focus on lower risk patients
who are candidates for operation.