immunotherapy
advertisement

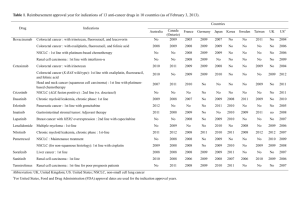
IMMUNOTHERAPY Vanesa Gregorc MD IRCCS San Raffaele, Milano LUNG CANCER AS AN IMMUNOLOGICMEDIATED DISEASE AND TARGET FOR IMMUNOTHERAPY Although many immunotherapies are being investigated in NSCLC, currently none have been FDA approved, as vaccines and other immune-modulators have yet to demonstrate considerable improvements inOS in phase III clinical trials NOVEL ASPECTS Immune-related response criteria Endpoints The immune-related toxicities All differ considerably from conventional cytotoxic agents and targeted therapies RESPONSE EVALUATION FOR IMMUNOTHERAPY •Permissive not restrictive •RECIST/mWHO modified by immunological criteria •First radiological examination the most critical (pseudoprogressions) •irResponders with new lesions also but decrease in baseline lesions •PD should be confirmed after 4 w Wolchok JD, et al Clin Cancer Res 2009; 15:7412-7420. NSCLC IMMUNOTHERAPY IMMUNOMODULATORS ANTI PD1-PDL1 ANTI CTLA4 VACCINES MAGE A3 MUC1 BELAGEN-PUMATUCEL L Tumor/T cells Mechanism of action IMMUNOMODULATORS PROGRAMMED DEATH-1 IMMUNE CHECKPONT (PD-1) PD-1 (cell receptor) is overexpressed on NSCLCinfiltrating T cells and these are functionally exhausted cells Ligands: PDL-1 and PDL-2 (tumor cell /APC) Higher tumoral PDL-1 expression correlates with decreased OS RATIONALE Blocking the PD-1 or PDL-1 pathway would restore/promote the function of chronically exhausted tumor-specific T cells and decrease tumor-induced immune suppression Zhang Y et al. Cell Mol Immunol. 2010;7:389- 395. OF T CELL OF TUMOR CELL CLINICAL DEVELOPMENT OF INHIBITORS OF PD-1 IMMUNE CHECKPOINT Inhibitors of PD-1 – Phase I trial CT-O11 CT-O11 (0.26.0mg/kg N=17 0.2-6.0 mg/kg IV 1YEAR SURVIVAL=42%, 2 YEAR SURVIVAL 24% Lambrolizumab in NSCLC Garon E. et al Abstract MO18.02 IALS 2013 INHIBITORS OF PDL1- phase I trial Inhibitors of PD-L1-Activity in NSCLC PD L1 Expression Pd-L1 Is broadly expressed in NSCLC UPDATE UPDATE EGFR STATUS AND IMMUNOTHERAPY EGFR wild type has higher PD-L1 expression vs EGFRm MO18.01 EGFR status and MPDL3280A Activity in NSCLC Horn et al. IPILIMUMAB Co-stimulation via CD28: CTLA-4 blocks co-stimulation: Ipilimumab blocks CTLA-4: T-cell activation No T-cell activation T-cell activation T cell T cell T cell CTLA4 CTLA4 TCR CD28 APC CD28 CD28 B7 MHC TCR TCR MHC APC B7 MHC ipilimumab B7 APC Adapted from Lebbé et al. ESMO 2008 APC, antigen-presenting cell; CTLA-4, cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen-4; MHC, major histocompatibility complex; TCR, T-cell receptor. Adapted from DoomC. 2012 PILC RANDOMIZED PHASE II STUDY OF IPILIMUMAB AND CT IN ADVANCED NSCLC [TITLE] Lynch TJ, et al. phase II study. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30:2046-2054. Adapted by J. Brahmer, 2013 ASCO Annual Meeting RESULTS RANDOMIZED PHASE II STUDY OF IPILIMUMAB AND CT IN ADVANCED NSCLC [TITLE] Lynch TJ, et al. phase II study. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30:2046-2054. Adapted by J. Brahmer, 2013 ASCO Annual Meeting OUTCOME BY HISTOLOGY OS IN SQUAMOUS ONGOING PHASE III OF IPILIMUMAB IN SQUAMOUS CELL LUNG CANCER Carbo – paclitaxel placebo R Carbo AUC 6 Paclitaxel 175 mg/mq Ipilimumab 10 mg/kg q3w Carbo – paclitaxel ipilimumab Double blind Primary endpoint: OS Secondary: OS in patients who receive one dose of ipi/placebo, PFS, RR Adapted by J. Brahmer, 2013 ASCO Annual Meeting LUNG CANCER VACCINATION. NSCLC ONGOING PH 3 TRIALS setting Phase III Early stage Post surgery MAGE-A3 MAGRIT Target 2270 recruited Loc.adv. Stage L-BLP25 START target 1300 Reported ASCO 2013 Post chemorad > 8000 Advanced In combo with chemo Belagenpumatucel-L STOP target 700 Reported ESMO2013 rEGF target 1000 ongoing TG4010 TIME target 1000 ongoing 1E10 Target 1082 ongoing L-BLP25 MUC1 is a mucinous glycoprotein that is overexpressed and aberrantly glycosylated in many human malignancies. BLP25 is a synthetic, liposomal cancer vaccine that targets the extracellular tandem repeat sequences of Butts ASCO2013 the MUC1 tumour-associated antigen. START TRIAL – STUDY DESIGN stage IIIA/B post CT/RT (DC) [TITLE] START TRIAL – PRIMARY ENDPOINT OS START TRIAL – SECONDARY ENDPOUINT TIME TO PROGRESSION START TRIAL – OS SUBGROUP ANALYSES BY RANDOMIZATION DATA STOP TRIAL stage III/IV in DC after 1° line belagenpumatucel-L Primary endpoint: OS Other endpoints: PFS, RR, QoL, CNS metastases, safety Belagenpumatucel-L(Lucanix®) uses genetically modified whole tumour cells to stimulate the patient's own immune system to attack the tumour. It is comprised of 4 transforming growth factor (TGF)-ß2 antisense gene-modified, Giaccone et al.ESMO 2013 irradiated, allogeneic NSCLC cell lines. STOP TRIAL did not meet predefined end point-OS BUT: Significantly prolonged overall survival in patients who began belagenpumatucel-L within 12 weeks of the completion of front-line chemotherapy or RT in Sq and Non-Sq conclusions Immunotherapy has promising anti-tumor activity in NSCLC and an unique set of side effects consistent with the immune mechanism of action Patient selection (biomarker) might be the key to further development as a single agent and in combination with other therapies Phase III trials are ongoing in order to make immunotherapy a reality for the treatment of NSCLC