PedsNeuro
advertisement

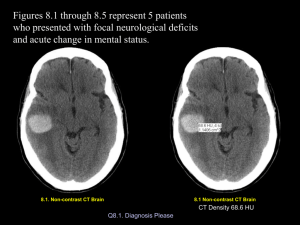
Resident on call CMH cases Collected by: Lisa H. Lowe, MD History: Not waking up for night time feeding & hypotonia a Findings: •Lens shaped hyperdense area indicates epidural hematoma •Midline shift •Some dark nonclotted blood is seen also a Dx: Epidural hematoma •Nonaccidental trauma •Surgically evacuated a Hx: 8y male s/p MVA not waking Findings: •Hyperdense perimesencephalic cisterns indicate subarachnoid blood •Narrowed midbrain worrisome for diffuse cerebral edema Dx: Subarachnoid hemorrhage •Hyperdense perimesencephalic cisterns indicate subarachnoid blood •Narrowed midbrain worrisome for diffuse cerebral edema Hx: 6y female severe headache & past hx of arachnoid cyst Findings: •Subdural fluid, hypodense bilateral (flattened gyri and no crossing vessels seen) •Not subarachnoid fluid •Arachnoid cyst seen at lower level in temporal fossa Dx: Subdural effusion due to arachnoid cyst rupture Hx: 1 yr female seizures Findings •Square shape frontal horns is seen with absent septum pellucidum •Clefts in the brain bilateral, left > right indicates schizencephaly Dx: Septooptic dysplasia Hx: 3 yr near drowning Findings •Diffuse loss of gray white differentiation •Bilateral foci of low density in the thalami Dx: Profound hypoxic ischemic injury in a child •With not so severe HIE, there is often watershed injury with preservation of thalami (due to preferential shunting of oxygenated blood to thalami) •With total anoxia or prolonged hypoxia, the shunting does not work and the thalami may take the biggest hit •This worst situation is with both involved as in this child Hx: Premature infant with drop in hematocrit Findings: •Heterogeneous lesion in the posterior fossa with high and low density indicating partially clotted blood •Linear periventricular high density and at the caudothalamic grooves indicates germinal matrix still present (arrowhead) •Cortex also high density due to extreme prematurity Dx: Posterior fossa hemorrhage Hx: Macrocephaly Findings •Prominence of the CSF spaces around the brain •There is no flattening of the gyri and there are tiny vessels in the CSF indicating it is the subarachnoid, not subdural space Dx: Benign enlarged subarachnoid spaces •Seen most 3m 3yrs •Presents with macrocephaly in an otherwise healthy child •Resolves spontaneously •Associated with slight increased risk of subdural bleed Hx: Apnea in a 2 week old Findings •Prominent venous structures, including the internal cerebral veins & straight sinus Dx: Normal prominent venous sinuses •Can mimic venous sinus thrombosus •Should do contrasted exam if unsure and if not thrombus will see enhancement Hx: Persistent vomiting in 4-yr-old male Findings: •Posterior fossa low density mass with peripheral calcification Dx: Ependymoma DDx: •Medulloblastoma •Juvenile pilocytic astrocytoma •PNET Hx: Baby fell of couch Hx: Baby fell of couch •Hyperdense subdural blood on left side indicates recent trauma •Loss of left side sulci due to subdural fluid Dx: Nonaccidental injury •Hyperdense subdural blood on left side indicates recent trauma Hx: Child stopped breathing a Findings: Mixed density left subdural blood with left to right shift a Left loss of gray white differentiation and shift left to right of midline Dx: Hyperacute subdural hematoma Mixed density indicates blood has not had time to clot yet Requires urgent surgical intervention Must distinguish from acute on chronic SDH, in which there is there is not acute mass effect a Hx: Seizure in 8 day old Findings: •Bilateral high density in the thalami •Prominent internal cerebral veins (arrowhead) •Focus of right frontal horn intraventricular blood (arrow) Dx: Venous hemorrhage due to venous sinus thrombosis •Internal cerebral vein thrombus, most common in babies, classically causes bilateral thalamic ischemia/hemorrhage Hx: Newborn with CHF and head bruit Findings: •Hydrocephalus from obstruction of 4th •Enlarged Vein of Galen and transverse sinuses Dx: Vein of Galen varix •Treated with intravenous coils Hx: Newborn with in utero hydrocephalus Findings •CSF space that connects with 4th ventricle (arrow) •Hypoplastic cerebellum and large retrocerebellar fluid collection •Hyrocephalus •Macrocephaly Dx: Dandy Walker malformation •DW cyst has NO cerebellar vermis •DW variant has some vermis •DW malformation includes DW cyst and variant •On CT hard to know if there may be a little vermis, so just say DWM and leave specifics to MRI reports Hx: Seizure and headache 15yf Findings •Hypodense area left frontal lobe •Vague •No contrast given •MRI planned Hx: Multiple sclerosis •Multiple foci in white matter on FLAIR MRI