memory, knowledge, comprehension, and categorization
advertisement
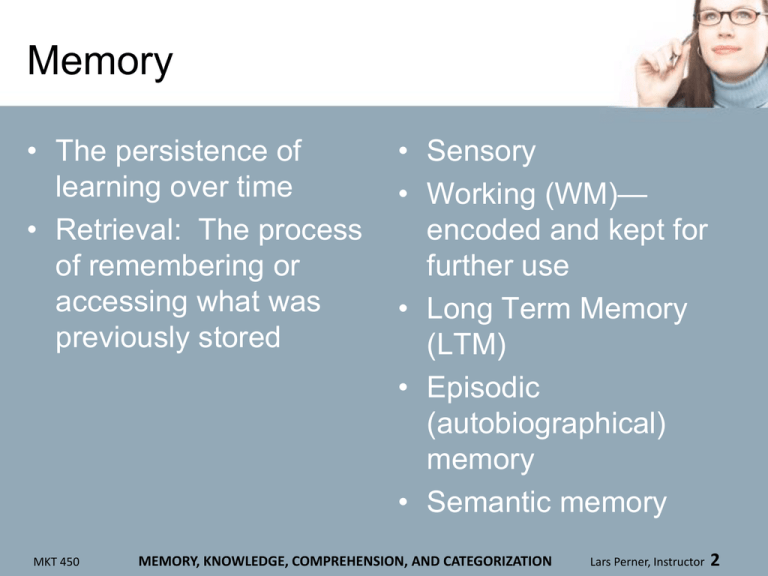
Memory • The persistence of learning over time • Retrieval: The process of remembering or accessing what was previously stored MKT 450 • Sensory • Working (WM)— encoded and kept for further use • Long Term Memory (LTM) • Episodic (autobiographical) memory • Semantic memory MEMORY, KNOWLEDGE, COMPREHENSION, AND CATEGORIZATION Lars Perner, Instructor 2 More Memory Issues • Implicit vs. explicit • Memory enhancement – Recognition – Recall – Elaboration MKT 450 • Some communication strategies to enhance memory – – – – Chunking Rehearsal Recirculation Elaboration MEMORY, KNOWLEDGE, COMPREHENSION, AND CATEGORIZATION Lars Perner, Instructor 3 Knowledge • Information already learned and stored • Knowledge structure: How knowledge is stored and organized • Schema: Associations between entities (e.g., brands, product categories, experiences) MKT 450 • Associative Network of Knowledge— knowledge elements— when accessed--trigger other elements • Priming: Increased sensitivity to associations due to prior implicit memory MEMORY, KNOWLEDGE, COMPREHENSION, AND CATEGORIZATION Lars Perner, Instructor 4 Specific Schemas • Brand image: associations with the brand • “Brand Personality:” The way the brand would have been described if it were a person (anthropomorphism)— e.g., – Sincerity – Competence – Ruggedness MKT 450 MEMORY, KNOWLEDGE, COMPREHENSION, AND CATEGORIZATION Lars Perner, Instructor 5 Associate Network of Knowledge SANDWICH PEANUT BUTTER MITT ROMNEY FAT PEANUTS REPUBICAN PARTY ELEPHANT 7 BLIND MEN TRUNK ZOO GIRAFFE MEDICINE TIGER MKT 450 MEMORY, KNOWLEDGE, COMPREHENSION, AND CATEGORIZATION Lars Perner, Instructor 6 Scripts • Knowledge of steps needed to carry out an activity – Make it easier to carry out routine activities with limited conscious involvement – For novel or infrequent experiences, lack of a script can make these difficult MKT 450 • Practical implications – Inclusion of specific brand names as defaults (e.g., for oil change, drive to Jiffy Lube which will use Pennzoil when changing your oil and filter) – Advertisements to make an activity easier MEMORY, KNOWLEDGE, COMPREHENSION, AND CATEGORIZATION Lars Perner, Instructor 7 Categorization • Taxanomical structure where exemplars are organized into categories • Levels – – – – MKT 450 • In general, the basic category level is recognized faster than superordinate and subordinate Superordinate Basic Subordinate Category members (exemplars) MEMORY, KNOWLEDGE, COMPREHENSION, AND CATEGORIZATION Lars Perner, Instructor 8 Graded Structure • Some exemplars are “better” examples of category than others – E.g., for the category of dog, a Germen Shepherd is a better example than a Yorkshire Terrier – Better examples are retrieved more easily MKT 450 MEMORY, KNOWLEDGE, COMPREHENSION, AND CATEGORIZATION Lars Perner, Instructor 9 Prototypicality • The “perfect” example • May not correspond with reality • Often more abstracted (simplified) MKT 450 MEMORY, KNOWLEDGE, COMPREHENSION, AND CATEGORIZATION Lars Perner, Instructor 10 Blurring of product category and brand name distinctions • Some commonly used category descriptors and verbs not intended to refer to the specific brand – Xerox (photo copy) – Kleenex (facial tissue) – To “FedEx” a package (possibly with another carrier) MKT 450 • Implications of brand name misuse – Possible loss of trademark protection in extreme cases (“genericide”) – Default choice in the product category – Positioning against the prototype MEMORY, KNOWLEDGE, COMPREHENSION, AND CATEGORIZATION Lars Perner, Instructor 11 Knowledge flexibility • Goal derived categories--e.g., – Things to eat and do while on a diet – Baby care items • Influences on categorization – Culture (“Women, fire, and dangerous things”) – Expertise • Construal level: The generality or specificity with which a goal is described MKT 450 MEMORY, KNOWLEDGE, COMPREHENSION, AND CATEGORIZATION Lars Perner, Instructor 12 Memory and retrieval • Sources of failure – Decay (knowledge has been left unaccessed for a long period of time) • • • • Geographical directions Lock combinations Foreign languages Activities and associated needs (including brand information) – Interference • Proactive: Existing knowledge interferes with learning new info • Retroactive: New knowledge dominates over earlier knowledge • Timing – Primacy – Recency • Retrieval errors MKT 450 MEMORY, KNOWLEDGE, COMPREHENSION, AND CATEGORIZATION Lars Perner, Instructor 13 Stimuli Characteristics and Memory • Some stimuli are better remembered – – – – MKT 450 Salience Prototypicallity Redundancy Medium of processing (combination of sensory input) • Retrieval cues – Stimuli that facilitate activation of memory • Situations (goals) • Colors and shapes • Fit with product function (e.g., Mr. Clean) MEMORY, KNOWLEDGE, COMPREHENSION, AND CATEGORIZATION Lars Perner, Instructor 14 Consumer characteristics and memory • Mood (congruence) • Expertise MKT 450 MEMORY, KNOWLEDGE, COMPREHENSION, AND CATEGORIZATION Lars Perner, Instructor 15