feeling - MKT 450: Consumer Behavior
advertisement
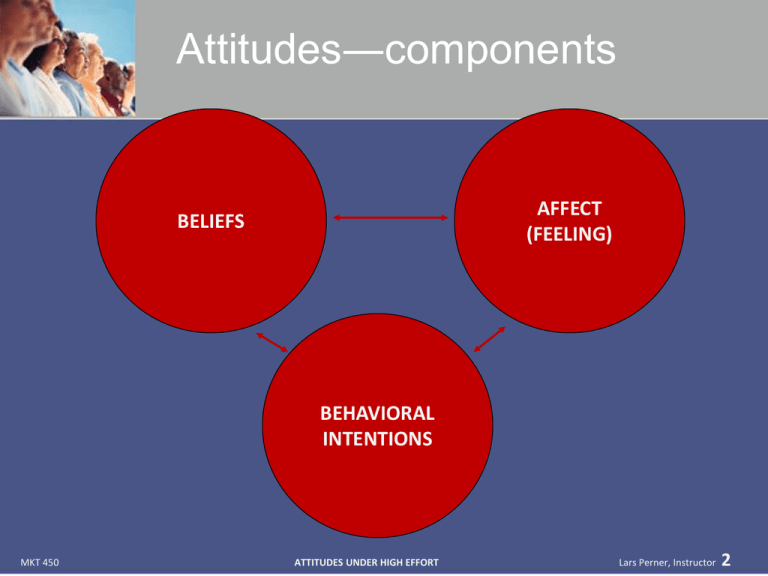
Attitudes―components AFFECT (FEELING) BELIEFS BEHAVIORAL INTENTIONS MKT 450 ATTITUDES UNDER HIGH EFFORT Lars Perner, Instructor 2 Significance of Attitudes • Cognitive: Guide thinking • Affective: Influence feelings • Connative: Impact behavior MKT 450 ATTITUDES UNDER HIGH EFFORT Lars Perner, Instructor 3 Characteristics/Dimensions of Attitudes • Favorability—Positive or negative • Accessibility—How easily the attitude is retrieved – May require thinking or evaluation – Ultimate result may be either highly positive or highly negative or in between • Confidence—Certainty with which the attitude is held MKT 450 • Persistence—Extent to which the attitude will remain accessible and relevant over time • Resistance to change— Extent to which new information is likely to change the attitude • Ambivalence—Difficulty in balancing competing positive or negative aspects ATTITUDES UNDER HIGH EFFORT Lars Perner, Instructor 4 MKT 450 ATTITUDES UNDER HIGH EFFORT Lars Perner, Instructor 5 Foundations of Attitudes • Based on cognition (thoughts at various levels of consciousness) or affect (emotion) or some combination MKT 450 ATTITUDES UNDER HIGH EFFORT Lars Perner, Instructor 6 Cognitive Foundations of Attitudes • Direct or imagined experience • Reasoning by analogy or category • Values driven attitudes • Social identity generated attitudes • Analytical processes MKT 450 • Responses – Counter arguments – Support arguments – Source derogation • Belief discrepancy: More counterarguments are likely to be generated to a message with which one disagrees ATTITUDES UNDER HIGH EFFORT Lars Perner, Instructor 7 Expectancy Value Models • Theory of Reasoned Action (TORA) MKT 450 ATTITUDES UNDER HIGH EFFORT Lars Perner, Instructor 8 Some Attitude Change Strategies • Change beliefs—usually very difficult – Strengthen positive beliefs – Weaken negative beliefs • Target normative beliefs (need to consider reactance) • Change evaluations of consequences • Add new belief • Encourage attitude formation based on imagined experience MKT 450 ATTITUDES UNDER HIGH EFFORT Lars Perner, Instructor 9 Generating Beliefs Through Advertising • Statements must be – Perceived – Comprehended – Remembered – Believed (at least in part) MKT 450 ATTITUDES UNDER HIGH EFFORT Lars Perner, Instructor 10 Adding Beliefs (True or Not): Examples • Brushing and flossing do not reach all areas of the mouth • People under stress need more vitamins • Baking soda will reduce odor of refrigerators • Fragmented hard drives may cause computer errors MKT 450 ATTITUDES UNDER HIGH EFFORT Lars Perner, Instructor 11 Positioning Through Creating Beliefs • “It’s not delivery; it’s De Journo!” • “Wal-Mart. Always low prices. Always.” • “I just saved a bunch of money on my auto insurance.” • “U-um Good!” (Campbell’s Soup) MKT 450 ATTITUDES UNDER HIGH EFFORT Lars Perner, Instructor 12 Multiattribute Models of Attitude • Attitude computed as a function of multiple attributes weighted for importance: Ab i 1WiXib n Ab= attitude toward brand b Wi: weight of attribute I Xib: belief about brand b’s performance on attribute I • Model assumes rationality Calculations will not be required on the exam. You should know conceptually what this involves conceptually—i.e., weighing importance and intensity of feeling. MKT 450 ATTITUDES UNDER HIGH EFFORT Lars Perner, Instructor 13 Influences on Cognitively Based Attitudes • Communications source – Source credibility • Trustworthiness • Expertise • Status – Company reputation • Message – Argument quality – One-sided vs. two-sided messages – Comparative messages MKT 450 ATTITUDES UNDER HIGH EFFORT Lars Perner, Instructor 14 Affective Foundations of Advertising • Engagement: Extent of personal connection to brand or object • Regulatory (goal) fit – Promotion focus – Prevention focus • Affective responses (generations of feelings and images) • Culture—appeal to ego vs. group oriented • Negative emotions may be more powerful MKT 450 ATTITUDES UNDER HIGH EFFORT Lars Perner, Instructor 15 Influences on Affect Based Attitudes • Source – Attractiveness – Match-up Hypothesis: Attractiveness is more effective when consistent with the product category – Disgust unintentionally induced (e.g., through humor) tends to have a negative impact – Discomfort with ambivalence • Message – Emotional appeals and contagion – Shame and guilt associations may not be effective MKT 450 ATTITUDES UNDER HIGH EFFORT Lars Perner, Instructor 16 Fear Appeal • Complicated to implement • Self-defense mechanism may kick in • Certain appeals that evoke guilt or regret may work • Optimal level of stimulus intensity • Offering a solution to overcome featured outcome MKT 450 ATTITUDES UNDER HIGH EFFORT Lars Perner, Instructor 17 Attitude Toward the Ad • Liking of ad may lead to liking of product • Generally used for low involvement product categories (e.g., batteries) • In higher involvement contexts: – Informative advertisements – Hedonic: Enjoyable advertisements MKT 450 ATTITUDES UNDER HIGH EFFORT Lars Perner, Instructor 18 Attitudes and Behavior • Greater consistency under – High level of involvement and elaboration – Attitude confidence – Specificity of attitude – Emotional attachment – Attitude accessibility MKT 450 • Some modifiers – Situational influences – Normative factors – Personality ATTITUDES UNDER HIGH EFFORT • High vs. low self-monitors Lars Perner, Instructor 19