consumer diversity - MKT 450: Consumer Behavior
advertisement
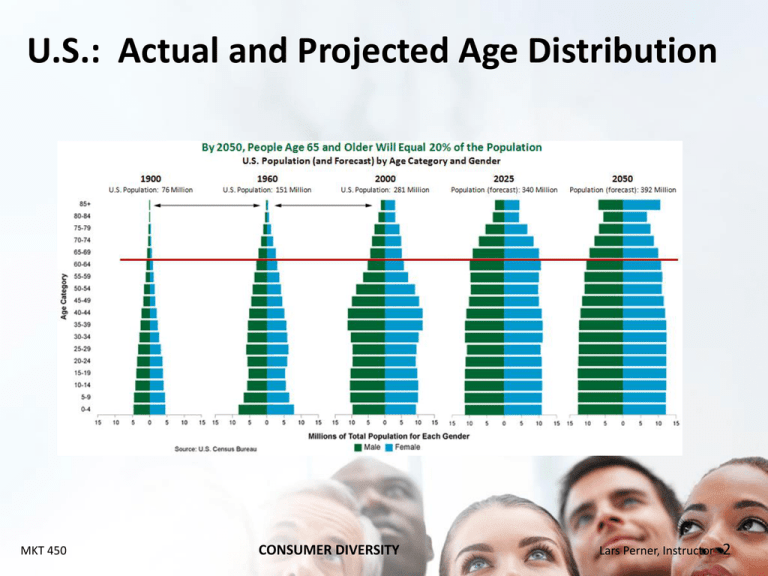
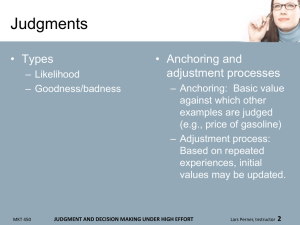
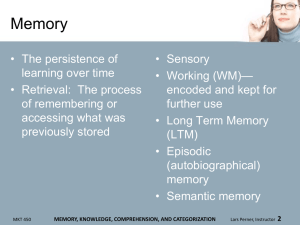
U.S.: Actual and Projected Age Distribution MKT 450 CONSUMER DIVERSITY Lars Perner, Instructor 2 Japan: Actual and Projected Population Figures MKT 450 CONSUMER DIVERSITY Lars Perner, Instructor 3 China: Actual and Projected Population Figures MKT 450 CONSUMER DIVERSITY Lars Perner, Instructor 4 Age Distribution Across the U.S. MKT 450 CONSUMER DIVERSITY Lars Perner, Instructor 5 U.S. Teen Market • More skeptical about traditional branding, but brand preferences may nevertheless set in early • Emphasis on non-traditional media MKT 450 CONSUMER DIVERSITY Lars Perner, Instructor 6 Generation X (Born 1965-1979) • Considerable diversity in accomplishment • Less likely than previous generations to surpass parents in terms of living standards MKT 450 CONSUMER DIVERSITY Lars Perner, Instructor 7 Baby Boomers (Born 1946-1964) • Tend to have high levels of buying power • Have grown up with television and tend to watch more than other groups • Many are now retired • Sandwich generation: May be caring both for older children and their own parents MKT 450 CONSUMER DIVERSITY Lars Perner, Instructor 8 Seniors (65+): Gray Market • Many are still active and relatively healthy • Some are not into advanced information search (yet others have a great deal of time for online search) MKT 450 CONSUMER DIVERSITY Lars Perner, Instructor 9 Gender Issues • Current and traditional gender roles – U.S. – International variations • Consumption practices • Consumer behavior MKT 450 CONSUMER DIVERSITY Lars Perner, Instructor 10 Gay and Lesbian Consumers • Increasing numbers of firms reaching out despite threats of boycotts – Targeted advertising • Discrimination from other consumers MKT 450 CONSUMER DIVERSITY Lars Perner, Instructor 11 MKT 450 CONSUMER DIVERSITY Lars Perner, Instructor 12 Geographical Diversity • Regional Differences – Traditional differences – Effects of mobility – Political • “Red” vs. “Blue” states (diversity within each state) • “God, Guns, and Guts” bumper stickers • Community clustering – PRIZM system: Community characteristics by zip code • 66 “segments” • Based on Census data • Used by firms and U.S. military (“Guns & Pickup Communities”) MKT 450 CONSUMER DIVERSITY Lars Perner, Instructor 13 Ethnicity and Acculturation • Ethnic groups – Diversity within groups • Group differences (e.g., U.S. Mexican, Cuban, and Guatemala origin Latinos) • Individual variations – Large impact of overall national identity – Considerable impact of ethnic identity (e.g., culture, religious beliefs as well) • Acculturation: Process by which cultural characteristics are internalized over time – Reinforcement: Rewards and punishments for behavior (may be subtle) MKT 450 CONSUMER DIVERSITY Lars Perner, Instructor 14 Hispanic American Consumers • Considerable diversity – Wide variation in English language usage—some may speak little English; some may speak little Spanish – Extent of identification – Subgroups based on national origin • Overall label may not be meaningful – Variations within Spanish spoken • Specific traditions—e.g., quinceañera MKT 450 CONSUMER DIVERSITY Lars Perner, Instructor 15 African American Consumers • Large variations (e.g., degree of interest in assimilation with the majority culture) • Media (e.g., BET) • Historical experience of discrimination – Discrimination was legal in the U.S. up until the 1960s – High rates of store mistreatment and suspicion of shoplifting although rates of shoplifting among African American consumers are actually lower than for other groups – Subtle and less subtle stereotypes • Spending on housing is often disproportionately lower than income with spending diverted elsewhere MKT 450 CONSUMER DIVERSITY Lars Perner, Instructor 16 Asian American Consumers • Higher than average U.S. income (but large variations) • Large variations – Between specific groups (e.g., Chinese, Vietnamese, Korean) – Among individuals MKT 450 CONSUMER DIVERSITY Lars Perner, Instructor 17