Exposure, Attention, and Comprehension in Marketing
advertisement
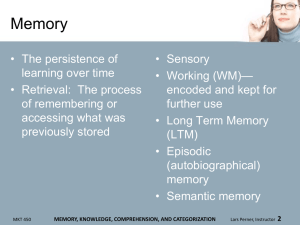
Exposure • Coming into contact with a stimulus • Some factors influencing exposure – Ad placement – Shelf placement of items MKT 450 • Selective exposure— limiting exposure— e.g., – “Do not call” lists – Ad blocking software – Skipping through ads • Zipping: Fast forward through pre-recorded ads • Zapping: Channel surfing during ads EXPOSURE, ATTENTION, AND COMPREHENSION Lars Perner, Instructor 2 Responding to Consumer Ad Avoidance • Control measures – On-line ad clickthroughs—must find “X” to close the ad – Disabled fast forwarding feature – Short ad must be watched to see content • Alternatives – Op-in – Advertising at places of boredom (e.g., on public transportation and airline baggage claim areas) • Variation: “Can skip ad in __ seconds.” MKT 450 EXPOSURE, ATTENTION, AND COMPREHENSION Lars Perner, Instructor 3 Characteristics of Attention • Limited—cannot give priority to all that is ongoing – Information overload • Selective – Some stimuli are given priority based on • Can be divided – Some potential for multi-tasking – Excessive distractions can cause problems (e.g., cell phones and driving) • Interest/relevance • Situation MKT 450 EXPOSURE, ATTENTION, AND COMPREHENSION Lars Perner, Instructor 4 Focal vs. non-focal • Focal • Non-focal – Stimuli chosen for attention MKT 450 – May involve unconscious (preattentive) processing – May have impact on brand choice and affect EXPOSURE, ATTENTION, AND COMPREHENSION Lars Perner, Instructor 5 Enhancing Attention • Personal relevance • Pleasantness of stimuli – Attractive models – Music – Humor (subject to certain caveats) • May get the consumer to focus on the advertisement but not the product MKT 450 • Novelty • Unexpectedness/ surprise • Puzzles • Prominent stimuli (contrast) • Concrete stimuli • Minimum competing stimuli EXPOSURE, ATTENTION, AND COMPREHENSION Lars Perner, Instructor 6 Habituation • Details may be ignored as their presence is experienced more routinely • May need to vary and/or change – Packaging – Advertising MKT 450 EXPOSURE, ATTENTION, AND COMPREHENSION Lars Perner, Instructor 7 Perception • Process of determining qualities of a stimulus based on five senses: – – – – – MKT 450 Vision Hearing Taste Smell Touch EXPOSURE, ATTENTION, AND COMPREHENSION Lars Perner, Instructor 8 Perceiving Through Vision • Size and shape • Lettering • Image location on page • Color – Judgment of stimulus – Mood – Liking MKT 450 EXPOSURE, ATTENTION, AND COMPREHENSION Lars Perner, Instructor 9 Perceiving Through Hearing and Taste • Hearing • Taste – Sounds associated with brands – Difficult to tune out MKT 450 – Evolutionary preferences – Individual variations EXPOSURE, ATTENTION, AND COMPREHENSION Lars Perner, Instructor 10 Perceiving Through Smell • Strong emotional link • High sensory priority • Impact on people – – – – MKT 450 Aroma therapy Liking Trial Purchasing EXPOSURE, ATTENTION, AND COMPREHENSION Lars Perner, Instructor 11 Sensory Thresholds • Absolute thresholds • Differential thresholds – “Just noticeable difference” (JND) • “Down-sizing” of products MKT 450 • Subliminal messages – Generally cannot pick up on more than one or two syllables – Logos may influence affect EXPOSURE, ATTENTION, AND COMPREHENSION Lars Perner, Instructor 12 Perception of Stimuli • Perceptual organization (making sense of disparate stimuli as a whole) • Figure and ground • Grouping MKT 450 EXPOSURE, ATTENTION, AND COMPREHENSION Lars Perner, Instructor 13 Comprehension • Source identification – Determining what is perceived – May involve categorization • Objective comprehension: Is meaning taken away consistent with actual statement? MKT 450 • Subjective comprehension: Additional meaning and inferences • Miscomprehension • Cultural impact: High vs. low context cultures EXPOSURE, ATTENTION, AND COMPREHENSION Lars Perner, Instructor 14 Consumer Inferences • From brand names and symbols – Numbers in brand names • From product features and packaging • From price • From retail setting MKT 450 EXPOSURE, ATTENTION, AND COMPREHENSION Lars Perner, Instructor 15