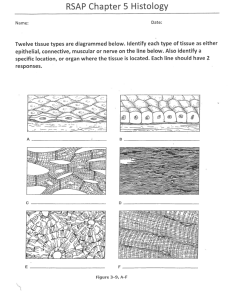
Connective, Muscular, and Nervous Tissue
advertisement

CONNECTIVE, NERVOUS, AND MUSCULAR TISSUE Connective Tissue • Basic elements – Cells – matrix CONNECTIVE TISSUE • Consists of living cells surrounded by a matrix • Type of fiber and the amount of fibers in the matrix determines the different types Connective tissue cells • • • • Fibroblasts Macrophages Mast cells Adipocytes MATRIX • Noncellular • Varies from a solid to semi fluid to fluid • Contains collagen – strong flexible proteins • Elastin – proteins that stretch • Reticular fibers – very thin collagen that are branched to form a supporting network CONNECTIVE TISSUE • • • • • • Binds organs together Provides support and protection Fills spaces Produces blood cells Stores fat TYPES OF CONNECTIVE TISSUE • • • • • Bone cartilage Dense connective Loose connective blood BONE • • • • • • • Rigid Protection Support Osseous Lacunae matrix 2 types : compact spongy CARTLIAGE • 3 types – Hyaline cartilage – Elastic cartilage – fibrocartilage • More flexible • Location of each type Matrix Connective tissue • Dense • Collagen fibers main element in matrix • Fibroblasts • Forms strong rope like structures • Found in tendons, and ligaments • Makes up dermis • Loose • Has more cells and less fibers • Supports epithelial tissue, organs, blood vessels TYPES OF LOOSE CONNECTIVE TISSUE • • • • AREOLAR TISSUE ADIPOSE TISSUE RETICULAR CONNECTIVE TISSUE BLOOD ADIPOSE TISSUE • • • • Stores body fat Insulation Organ protection Found beneath the skin – subcutaneous Reticular tissue • Delicate network of interwoven reticular fibers • stroma • Also called lymphoid tissue • Found in lymph nodes, spleen, and bone marrow • Produce all blood cells AREOLAR TISSUE • Most widely distributed connective tissue • mostly water • universal packing material between other tissues • wraps small blood vessels and nerves • edema AREOLAR TISSUE • • • • Soft pliable tissue Underlies all mucous membranes Loose and fluid in mature Reservoir of water and salts for surrounding tissues and cells BLOOD • • • • Atypical connective tissue transportation system Plasma is the matrix Fibers are soluble proteins MUSCLE TISSUE • Contracts to produce movement • 3 types skeletal (involuntary) smooth (visceral) cardiac SKELETAL MUSCLE STRIATED VOLULNTARY ATTACHED TO BONES MULTIPLE NUCLEI CARDIAC MUSCLE • Makes up the walls of the heart • Contracts to make the pumping of the blood possible • Striated • Involuntary • Uninucleated • Intercalated discs SMOOTH MUSCLE • Nonstriated • Involuntary • Slower contractions than other types of muscles • Found in the walls of hollow organs and blood vessels • Peristalsis - wavelike motion due to contractions NERVOUS TISSUE • Neuron – nerve cell • Receives and conducts electrochemical impulses • Cytoplasm can get up to 3 feet (leg area) • • • • Selectively permeable polar phospholipids - liquid at normal BT fluid - mosaic Marfan syndrome