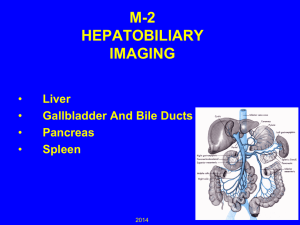
Liver
advertisement
Liver, Gallbladder, Biliary tract and portal venous system Meechai Srisai M.D. ,Ph.D. Nigun Worapunpong M.D. Department of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine Chulalongkorn University August 2010 Introduction • Digestive system consists of – GI tract – Glands and accessory organs : Salivary glands, Liver ,Gall bladder, Pancreas Liver • Largest organ in body 1200-1600 gm • Surface projection – จุดบนสุด : Rt. Midinguinal line / Rt. 5th rib – จุดลางขวา : Rt. Midaxillary line / Rt. 10th ่ costal cartilage th – จุดลางซ ่ ้าย : Lt. Midinguinal line / Lt. 5 I.C.S. Surface projection of liver Parasagittal section through liver Showing subphrenic recess and hepatorenal recess (Rutherford-Morison pouch) Liver Surfaces of Liver 1. 2. Diaphragmatic surface Visceral surface : structures lie like ‘H’ Liver Visceral surface ‘H’ 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Cross-bar of H = Porta hepatis – Hepatic artery, Portal vein, Bile ducts, Nerves and Lymphatic vss. Lt. superior of H = Ligamentum teres hepatis or round ligament of liver (Remnant of umbilical v.) Lt. inferior of H = Ligamentum venosum (Remnant of ductus venosus) Rt. superior of H = Gall bladder Rt. inferior of H = Inferior vena cava Visceral Surface ‘H’ Visceral Surface ‘H’ Liver Peritoneal relations 1. Peritoneal ligaments – – – – 2. Lesser omentum Falciform ligament Coronary ligaments Triangular ligaments Vascular ligaments – – Round ligament of the liver Ligamentum venosum Parts of stomach and lesser omentum Liver Bare areas of the liver เป็ นบริเวณที่ ไมมี ่ peritoneum คลุม 1. b/t Ant. & Post. Coronary ligaments 2. Fossa for gall bladder 3. Porta hepatis 4. Fissure for round ligament 5. Fissure for ligamentum venosum 6. Fossa for IVC Liver Lobes of liver 1. Anatomical lobation • • • • 2. Right lobe Left lobe Caudate lobe Quadrate lobe Functional lobation • • • Right lobe Left lobe By a line passing the gallbladder and IVC Anatomical lobes Anatomical lobes Functional lobes Functional lobes Liver Blood supply of liver 1. 2. 3. Rt. & Lt. hepatic arteries carry oxygenated blood (25%) Portal vein carries venous blood (75%) rich in nutrients Hepatic veins drain venous blood to IVC Liver Anterior vagal trunk Autonomic nerves • Symp : Celiac plexus • Parasymp : Ant. and Post. Vagal trunks Celiac plexus Liver Lymphatic drainage of liver Liver is a major lymph-producing organ (1/4 -1/2 of lymph → Thoracic duct) • Diaphragmatic surface of liver drains to Phrenic nodes • Visceral surface and deep lymphatics along portal triads drains to Porta Hepatis → Hepatic nodes → Coeliac nodes → Cisterna chyli → Thoracic duct Lymphatic drainage of liver Lymphatic drainage of GI tract Topographic anatomy of abdomen Topographic anatomy CT scan Gallbladder & Biliary tracts Gallbladder & Biliary tracts Biliary system consists of 1. Gall bladder 2. Biliary tracts Cystic duct, hepatic ducts, common hepatic duct and common bile duct Gallbladder • Length 6-10 mm. • Capacity ~ 45 cm3 • b/t Rt. lobe & Quadrate lobe of liver • Surface projection Fundus of gallbladder = Murphy’s point Gallbladder Spiral valve Neck Body Gallbladder has 4 portions 1. 2. 3. Fundus Body Neck Infundibulum : Hartmann’s pouch Hartmann’s pouch Internal surface : folds, spiral folds and crypts of Luschka Fundus Crypts of Luschka Gallbladder Gallbladder Blood supply of gallbladder 1. Cystic artery from Right Hepatic artery (in Calot’s triangle → Cholecystectomy) 2. Cystic vein : tributary of Portal vein Calot’s triangle Cystic artery Biliary tract 1. 2. 3. Cystic duct : ~ 3 cm : spiral valve of Heisteri Common hepatic duct : ~ 3-5 cm : from Rt. & Lt. hepatic ducts Common bile duct : ~ 7.5 cm 1+2 → 3 Biliary tract Common bile duct has 4 parts – – – – Supraduodenal Retroduodenal Infraduodenal Intraduodenal Common bile duct + Major pancreatic duct ▼ Hepatopancreatic ampulla (Ampulla of Vater) Opening is Greater duodenal papilla in 2nd part of duodenum (surrounded by Sphincter of Oddi) Icteric sclera Compression of common bile duct resulted in obstructive jaundice Biliary tract Anterior vagal trunk Nerves of Gallbladder • Symp : Celiac plexus • Parasymp : Ant. and Post. vagal trunks Celiac plexus Biliary tract Lymphatic drainage of Gallbladder • Drain to Hepatic nodes of cystic nodes ↓ Celiac nodes Radiograph of gallbladder & biliary tracts Radiograph of gallbladder & biliary tracts Portal venous system • A system of venous blood vessels from GI tract to the liver • Formation : – Superior mesenteric vein + Splenic vein (behind neck of pancreas) Portal venous system Tributaries 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Cystic vein Paraumbilical vein Right gastric vein Left gastric vein Splenic vein Superior mesenteric vein Portal venous system Portal hypertension • • • The portal vein provides about 75% of the liver's blood flow and about 60% of its O2 supply Normal portal pressure is 5-10 mmHg (7-14 cm H2O), which exceeds inferior vena caval pressure by 4-5 mm Hg (the portal venous gradient) Higher values are defined as portal hypertension Portal venous system Portal-Caval Anastomosis Anastomosis among portal vein and systemic vein (Inferior vena cava) 1. Left gastric v.→ Esophageal v.→ Azygos v. → SVC : ‘Esophageal varices’ 2. Splenic v. → Sup. rectal v. → Rectal venous plexuses → middle & Inf. Rectal v. → → → IVC : Dilated rectal venous plexuses = Internal hemorrhoids Portal-systemic anastomosis Esophageal varices Internal hemorrhoids Internal hemorrhoid External hemorrhoid Portal venous system 3. 4. Paraumbilical v. → Superficial epigastric v. → External iliac v.→ IVC : ‘Caput Medusae’ Colic v. anastomosis to Retroperitoneal v. → IVC Dilated Superficial Epigastric veins Caput medusae Portal hypertension • Signs & symptoms – Esophageal varices : Hematemesis – Internal hemorrhoids – Caput Medusae – Splenomegaly – Ascites – etc.