Materials covered in lecture
advertisement
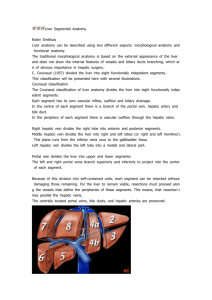
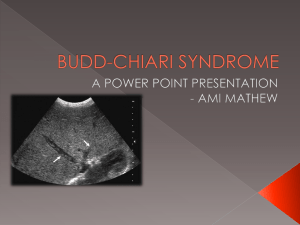
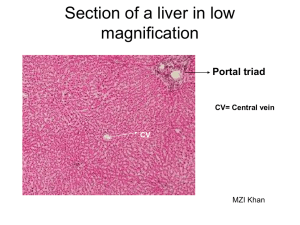
M-2 HEPATOBILIARY IMAGING • • • • Liver Gallbladder And Bile Ducts Pancreas Spleen 2014 HEPATIC ANATOMY Catalano, O. A. et al. Radiographics 2008;28:359-378 GOALS Review anatomy of hepatobiliary system. Correlate imaging with pathology. Discuss radiologic imaging options. Choose treatment ANATOMY / PHYSIOLOGY Portal vein flow Hepatic arterial flow Hepatic vein flow Biliary drainage PORTAL BLOOD FLOW The Portal vein is formed by the juncture of the Splenic vein and the Superior Mesenteric vein. The Inferior Mesenteric vein usually joins the Splenic vein. PORTAL VEIN CT Coronal and Axial images US HEPATIC ARTERIAL FLOW LATERAL AORTOGRAM SHOWS ORIGIN OF CELIAC ARTERY AND THE SUPERIOR MESENTERIC ARTERY CELIAC SMA The Celiac Artery splits into 3 branches: Supplies Diaphragmatic organs 1- Common Hepatic Artery. 2- Splenic Artery. 3- Lt. Gastric Artery. THE COMMON HEPATIC ARTERY BECOMES THE PROPER HEPATIC ARTERY AFTER THE GASTRODUODENAL BRANCH DESCENDS. Proper hepatic * Celiac Gastroduodenal SMA The Lt. gastric is small and out of the section on this image HEPATIC VEINS Coronal scan HEPATIC VEINS ENTERING IVC What is the presentation of hepatic vein thrombosis? WHAT IS THE PRESENTATION OF HEPATIC VEIN THROMBOSIS? (Budd Chiari syndrome) • • • • • • • Enlarged edematous liver Painful-capsular pressure Ascites-pressure effects Hypercoagulable states- etiology Elevated liver enzymes- infarction Diagnosed with Hepatic Venography Or CT NORMAL BILIARY ANATOMY ULTRASOUND GALLBLADDER COMMON BILE DUCT Silva, A. C. et al. Radiographics 2004;24:677-687 NORMAL BILIARY ANATOMY MR CHOLANGIOGRAM (MRCP) Silva, A. C. et al. Radiographics 2004;24:677-687 ENDOSCOPIC RETROGRADE Cholangio - Pancreatography ERCP MR cholangiogram shows signal from the bile and other fluids. ERCP has iodinated contrast injected with an endoscope with the canula in the distal common bile duct. OPERATIVE CHOLANGIOGRAM HEPATO-BILIARY SCAN - HIDA PANCREATIC ANATOMY CT SCAN Transverse CT sections and corresponding US CT US DARK GREEN EMESIS WOULD BE TYPICAL FOR GI OBSTRUCTION. • Pyloric stenosis • Duodenal atresia • Annular pancreas • Gallstone ileus ANNULAR PANCREAS PANCREATIC EMBRYOLOGY MALROTATION AND FUSION WHO PRESENTS FOR IMAGING? Right upper quadrant pain Altered laboratory data Staging of malignancy / infection Physical exam findings Abdominal trauma ACUTE RIGHT UPPER QUADRANT PAIN Differential Diagnosis: Acute Cholecystitis PUD / Gastritis / Reflux Acute Hepatitis Pancreatitis RIGHT UPPER QUADRANT PAIN Gallstone = cholelithiasis- 10% prevalence Stone impaction and obstruction cystic duct Pain with contraction after fatty meal 20-30 minutes Adult 40+- female more common DIAGNOSIS ULTRASOUND Cost / Availability Fluid background is ideal for imaging Helpful to assess for any associated biliary dilatation or inflammatory change CHOLELITHIASIS MURPHY’S SIGN A Sonographic Murphy’s sign is focal tenderness corresponding to the gallbladder. Along with other ultrasound evidence of inflammation (gallbladder wall thickening, pericholecystic fluid) it helps physicians separate Acute Cholecystitis from gallstones alone. CHOLECYSTITIS With diffuse wall thickening and edema. Ultrasound and CT demostration of edema in and around GB wall QUESTION? CHOLECYSTITIS Pain is often referred to other location with cholecystitis, Which is the correct answer? 1--Shoulder 2--Umbilicus 3--EG junction 4--Back IMAGING ALTERNATIVES Nuclear medicine - HIDA CT X-ray Cholangiography - MR or Endoscopic HEPATO - BILIARY SCINTIGRAM Gall bladder Obstructed cystic duct doesn’t allow for filling of radionuclide into the GB. Absent Gall bladder GALLSTONES 15-30% calcify COMPLICATIONS OF GALLSTONES • Cystic duct obstruction Cholecystitis A • Common bile duct obstruction Obstructive jaundice B Ascending cholangitis A • Pancreatic duct obstruction Pancreatitis C B C ALTERED LABORATORY DATA Bilirubin - jaundice Amylase / lipase - pancreatitis QUESTION? HOW CAN A HEMOLYTIC ANEMIA (SICKLE CELL ANEMIA) GIVE AN ELEVATED DIRECT BILIRUBIN? 1--Hemolytic crisis 2--Transfusion Hepatitis 3--Choledocholithiasis 4--Hepatic infarction CBD Obstructed duct due to distal calculus PV Normal bile duct size Diameter < portal diameter Note dilated CBD with impacted calculus *Note dilated bile ducts. (Low density branching structures anterior to portal veins) Normal The Portal vein is opacified (white) from IV contrast administration. The biliary tree is of lower density and shows as a branching structure anterior to the portal vein. Dilated CBD with calculi Normal size CBD ERCP Endoscopic retrograde Cholangiopancreatography PANCREATITIS elevated AMYLASE & LIPASE Biliary calculi-obstruction Alcohol- chemical toxicity ACUTE PANCREATITIS EDEMATOUS There is diffuse edema in and adjacent tissues around the pancreas. A patient with diagnosis of pancreatitis who had developed a pseudocyst over past month Comes to the hospital with worsened pain and a blood pressure of 80/60. 1-Mesenteric arterial infarction 2-Portal vein thrombosis 3-Perforated ulcer 4-Leaking pseudoaneurysm Normal vasculature Pseudo aneurysm DRAINAGE OF PANCREATIC ABSCESS COMPLICATIONS OF PANCREATITIS Pseudocyst Pain Infection Hemorrhagepseudoaneurysm Pancreatic insufficiency Large retrogastric fluid collection is a pseudocyst related to pancreatic enzyme break down of tissue. SPECIAL CASES Emphysematous cholecystitis Acalculous cholecystitis Gallstone ileus A 64-year-old man with insulin-dependent adult-onset diabetes mellitus seeks emergency medical treatment after 2 days of increasingly severe abdominal pain in the right upper quadrant that has spread over the entire abdomen and is associates with nausea, vomiting, fever and chills. On examination, he is alert and oriented but appears to be quite acutely distressed. Vital signs are temperature 39.4C (103F), pulse 140 beats per minute, and blood pressure 100/60mmHg. His sclerae are mildly icteric. His abdomen is diffusely tender with marked guarding in the right upper quadrant. EMPHYSEMATOUS CHOLECYSTITIS DIABETIC PATIENTS - AIR IN WALL QUESTION? IN GALLSTONE ILEUS OBSTUCTION OF THE GI TRACT OCCURS COMMONLY IN THE: 1--Pyloric channel 2--Duodenal C loop 3--Ileocecal valve 4--Hepatic flexure GALLSTONE ILEUS Small Bowel Obstruction at IC valve due to migration of gallstones that erode into duodenum from GB. 1999 2002 ACALCULOUS CHOLECYSTITIS BILIARY STASIS - FASTING / ICU PATIENTS SAME PATIENT ABDOMEN SCAN DONE 2/25/08 CHOLECYSTOSTOMY RUQ PAIN IMAGING EVALUATION Ultrasound – 1st CT / HIDA – 2nd JAUNDICE VIRAL HEPATITIS IMAGING- LIMITED VALUE Acute – usually normal helps to exclude obstruction Chronic – increased malignancy risk THE MOST COMMON CAUSES OF OBSTRUCTIVE JAUNDICE IN THE UNITED STATES 1--Neoplasms of the pancreas 2—Choledocholithiasis 3--Pancreatitis 4--Iatrogenic strictures of the biliary tree JAUNDICE BILIRUBIN Painless Malignancy Chronic obstruction Painful Hepatitis / liver edema Choledocholithiasis / acute obstruction PANCREATIC CANCER OBSTRUCTIVE JAUNDICE PALPABLE GALL BLADDER A palpable gall bladder in an asymtomatic patient can be seen with pancreatic carcinoma due to distal obstruction (Courvoisier sign) SCLEROSING CHOLANGITIS A 35 yo patient with history of ulcerative colitis comes to see you for pruritus. You notice yellow sclera and mucous membranes. His alkaline phosphatase is elevated and the MR cholangiogram reports abnormal appearance with multiple stenoses and focal dilated segments appearing beaded. 25 yo with 2yr dx of ulcerative colitis was managed well. Now he has increasing pain and diarrhea. • Physical examination of this thin, pale young man, who appears acutely ill, reveals these vital signs: Temperature 37.8C (100F), pulse 110 beats per minute, and blood pressure 120/70mmHg. The lower abdomen is mildly and diffusely tender, but there is no rebound tenderness and bowel sounds are active. Stool is grossly bloody. Sigmoidoscopy, shows marked mucosal erythema and friability; diffuse ulceration is present, and an exudate contains pus and blood. • Three hours after the Sigmoidoscopy the man’s abdominal pain worsened markedly. Vital signs now are temperature 39.6C (103.2F), pulse 130 beats per minute, and blood pressure 90/60 mmHg. On examination the abdomen is distended and diffusely tender with rebound. PSEUDOPOLYPS with ulcerative colitis may progress TOXIC MEGACOLON STAGING MALIGNANCY / INFECTION Mesenteric blood flow spreads disease to liver GI malignancy often spreads to liver as first site of hematogenous extention. HEPATIC ABSCESS FROM GI INFECTION Mesenteric venous blood flow can spread infection to the liver. PALPABLE PHYSICAL EXAM FINDINGS Enlarged liver Enlarged spleen Ascites - distention PALPABLE LIVER-metastatic disease A palpable enlarged liver edge is nonspecific but raises questions of mass or liver pathology. ENLARGED PALPABLE SPLEEN Enlarged spleen raises issue of lymphoproliferative diseases or infection. ENLARGED SPLEEN ON ULTRASOUND AND CT. SPLEEN *Note left kidney SPLENOMEGALY WITH CIRRHOSIS AND PORTAL HYPERTENSION * SPLENOMEGALY *Note dilated splenic vein VARICES Varices are at risk for hemorrhage. They can be treated by embolization at GI endoscopy or vascular shunt of portal blood flow by surgery or radiology to decrease portal pressure. CIRRHOSIS Portal hypertension Here long standing cirrhosis has lead to a scarred shrunken liver. Portal hypertension resulting leads to varices and redirection of blood flow into a recanalized umbilical vein. Lucent fluid at tip of liver on ultrasound Fluid on CT Ascites displacing bowel medially on Xray SAGITTAL ULTRASOUND Small nodular echogenic liver shows cirrhotic change SURGICAL PORTOCAVAL SHUNTS AS THERAPY FOR BLEEDING AND ASCITES INTERVENTIONAL RADIOLOGY SHUNT HEPATIC VEIN - PORTAL VEIN TIPS Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt TRAUMA QUESTION? IN ADDITION TO CARBON TETRACLORIDE WHAT PAIN KILLER IS ASSOCIATED WITH LIVER TOXICITY? 1--Aspirin - salicylic acid 2--Tylenol - acetaminophen 3--Advil - ibuprofen 4--Aleve - naproxen TRAUMA UNSTABLE—SURGERY X-ray-- Chest/ Abd / Pelvis if possible FAST SCAN-to look for peritoneal fluid STABLE– CT SCANNING F.A.S.T. SCAN (Focused Assessment with Sonography for Trauma) Ultrasound survey for free peritoneal fluid F.A.S.T. SCAN (Focused Assessment with Sonography for Trauma) Ultrasound survey for free peritoneal fluid Need 400-500 ccs Not good for organ injury or bowel injury HEPATIC / SPLENIC LACERATION Note rib fractures on x-ray POST TRAUMATIC PANCREATITIS SEAT- BELT INJURY There is diffuse edema and hemorrhage in adjacent tissues around the pancreas. WHAT IMAGING POSSIBILITIES? ULTRASOUND---GB / CBD / LIVER Plain x-ray---ERCP CT---PANCREAS / LIVER Nuclear Medicine---HIDA MR---MRCP These are the imaging modalities and important sites of assessment