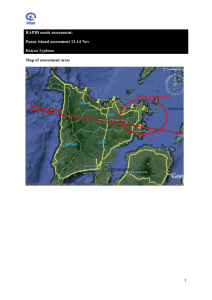
about iloilo-batiano river system
advertisement

ABOUT ILOILO RIVER BEFORE THE SPANISH REGIME Channel of Trade - a busy artery of commerce & instrumental in the economic development of several important districts of Iloilo City Fishing Ground – source of fish for the early inhabitants of the city Early Settlements - thriving settlement in Jaro District and considerable number of Chinese residents in Molo District Anchorage - provided safe harbour to coastwise shipping 1700s: Spanish Regime Seat of Spanish Government With the establishment of Fort San Pedro at the mouth of Iloilo River, Iloilo became the seat of the Spanish Government in the region. Early Development of Human Settlements Communities sprouted along the river banks after the establishment of the Fort. There were 835 residents in Iloilo in 1760 1855: Opening of the Port of Iloilo to World Trade Center of Commerce and Trade • Iloilo’s fine harbour provided the impetus for growth that led to the opening of the port of Iloilo to world trade. • Iloilo soon emerged as one of the biggest centers of trade in the country, 2nd to Manila 1855: Opening of the Port of Iloilo to World Trade Early Development of the Downtown Central Business District • British and Spanish firms began to crowd the marshy areas along Iloilo River • Warehouses, permanent offices and shops in the streets were built parallel to the river in the 1850’s and 1860’s • Soon after, Iloilo earned the title “Queen’s City of the South” Post-War Period After the war, uncontrolled human activities greatly affected the ecology and the economic viability of the Iloilo river, Among others, it was negatively impacted by the following: - Increasing number of population occupying the river banks ; - Mushrooming of fish pens and illegal structures; - Cases of encroachments: - Conversion of the river banks into fishponds or subdivisions along its course; -Unrestricted disposal of wastes and pollutant chemicals; and - Indiscriminate cutting of mature mangroves. ABOUT ILOILO-BATIANO RIVER SYSTEM ILOILO RIVER BATIANO RIVER ABOUT ILOILO-BATIANO RIVER SYSTEM San Miguel Sta. Barbara MAMBOG CREEKJIBAO-AN RIVER CABULUAN RIVER The Iloilo-Batiano River Basin Pavia Oton DUNGON CREEK CALAJUNAN CREEK Iloilo City ILOILO RIVER BATIANO RIVER Source : WQMA ABOUT ILOILO-BATIANO RIVER SYSTEM • Land Use Land Use Residential Area Covered (km2) Percentage 37.27 36.9 Commercial 4.87 4.8 Industrial 4.04 4.0 Institutional 1.81 1.8 Agricultural 45.00 44.6 Fishponds 2.01 2.0 PUD 3.07 3.0 Transport/Utilities 0.64 0.6 Open/Parks 1.05 1.0 Other Uses 1.23 1.2 101.00 100.0 Total ABOUT ILOILO-BATIANO RIVER SYSTEM A natural harbour Classified as Class “C” body of water (DENR DAO 90-34) A rich breeding ground to important fish species, crustaceans, shellfish that provide sustenance and livelihood to some residents Home to 22 mangrove species esp. Sonneratia Ovata (rare in the region) ABOUT ILOILO-BATIANO RIVER SYSTEM Economic Profile Population along the river: - Iloilo City 49,392 - Oton 23,022 Barangays - 35 out of 180 barangays of Iloilo City - 8 out of 37 barangays of the Municipality of Oton Business Establishments – 2,995 Source: LGU, Iloilo City ABOUT ILOILO-BATIANO RIVER SYSTEM Economic Activities at Iloilo Port A. Shipping a. No. of Domestic Ship calls – 22,576 b. Domestic Gross Registered Tonnage – 14,835,346 c. No. of Domestic Ship calls – 182 d. Foreign Gross Registered Tonnage – 2,822,860 B. Domestic Cargo Throughput a. Inbound – 2,651,557 MT b. Outbound – 664,937 MT C. Total Domestic Passenger Traffic a. Disembarked – 1,088,248 b. Embarked – 1,131,800 Source: PPA CY 2012 ABOUT ILOILO-BATIANO RIVER SYSTEM Economic Activities (Fisheries) ILOILO RIVER BATIANO RIVER • Fishery Catch : Milkfish, Tilapia, Seabass, Spade Fish, Ten Pounder, Tarpon, Rabbit Fish, Mullets, Mangrove Snapper, Shrimp, Prawns, Crabs • Fishery Catch : Shrimp, Crabs, Prawns, Fish • Types of Fishing Gear: Gill Net, Fish Coral, Motorized Push Net, Crab Lift nets • Income Range : P3,780 -6,160/mo. • Types of Fishing Gear: Punot, Tangab, Pasisihan, Talabahan, Panggal, Tarpon • Income Range : P125 – 800/day • Fish Catch : ranges from ½ kg to 10 kg/ day • Fish Catch : ranges from 1.5 kg to 4 kg/ day Source: Iloilo City Agriculture & Mun. Agriculture of Oton RESOURCE UTILIZATION • Fishing • Aquaculture (Fish Ponds) • Salt Production • Spawning Area for Fisheries • Transportation • Port Facilities • Research & Education • Recreation /Tourism CHALLENGES • • • • • • • • • Lack Database Inventory of All Public Land Property Lines Encroachment / Obstructions along water lines Public Awareness and Advocacy Water Pollution Presence/Relocation of Informal Settlers Siltation & Sedimentation Waste Disposal and Septage Management Indiscriminate Land Use/Noncompliance of Legal Easement • Lack of Public Access and Open Spaces • • • • • • • Disaster Risks and Flooding Climate Change Mitigation & Adaptation Alternative Livelihood Attracting Investment Plan Loss of Biodiversity Preservation of mangroves/greenbelt Institutionalization of management structure and other mechanisms for protection and conservation of the river