P1_Revision_Sheets 404KB
advertisement

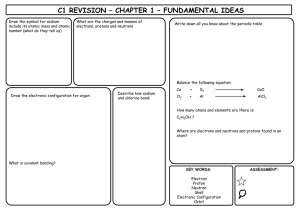
P1 REVISION – CHAPTER 1 – ENERGY TRANSFER BY HEATING Infrared radiation Kinetic theory All objects emit IR • Everything is made of particles • The hotter an object is the more IR it emits • The particles in solids, liquids and gases have different energies • Dark, matt surfaces are good absorbers and emitters of IR • Light, shiny surfaces are poor absorbers and emitters of IR • Light, shiny surfaces are good reflectors of IR Balance the following equation: + 02 Cl2 AlCl3 + Al CaO How many atoms and elements are there is: C2H5OH ? Where are electrons and neutrons and protons found in an atom? • Conduction occurs in solids • As particles heat up they get more energy and vibrate more • They collide with neighbouring particles and pass on energy • The rest of the material gradually heats up Increase in energy SOLID Ca Conduction • LIQUID GAS C1 REVISION – CHAPTER 2 – ROCKS & BUILDING MATERIALS What is the scientific name AND chemical formula for limestone? What is produced when a carbonate reacts with an acid? What is thermal decomposition? Write the word and symbol equation for the thermal decomposition of limestone What is cement? What is concrete? What are the benefits and drawbacks to limestone quarrying? BENEFITS DRAWBACKS Complete the limestone reaction cycle: Calcium Carbonate Add CO2 Add more water & filter Heat Add water KEY WORDS: CALCIUM CARBONATE THERMAL DECOMPOSITION CONCRETE CEMENT QUARRYING LIMESTONE LIMEWATER ASSESSMENT: C1 REVISION – CHAPTER 3 – METALS & THEIR USES Put these metals in their order of reactivity Carbon, Magnesium, Copper, Iron & Potassium Explain a bit about each of the ways to extract copper: Less reactive metals are displaced by carbon. Complete the equation below and then make your own one: Copper Oxide + Carbon _______________ + _______________ Displacement: What is an ore? Smelting: Give 2 use AND properties of: i) Aluminium Bioleaching How is iron extracted? Phytomining ii) Titanium What is an alloy? KEY WORDS: Name 2 alloys: DISPLACEMENT ORE BLAST FURNACE ALLOY SMELTING BIOLEACHING PHYTOMINING ASSESSMENT: C1 REVISION – CHAPTER 4 – CRUDE OIL & FUELS Name the process by which we separate crude oil into useful components: Give a problem each pollutant causes: Carbon Dioxide BENEFITS Sulphur Dioxide What property does this process rely on? Give the benefits and drawbacks of each alternative fuel DRAWBACKS BIODIESEL (more detail required for this one!) Carbon Monoxide Nitrogen Oxide What does ‘saturated’ mean? Particulates ETHANOL Complete the table to summarise alkanes and alkenes: ALKANES Saturated or unsaturated ALKENES HYDROGEN General formula Name an example Draw an example KEY WORDS: ALKANE ALKENE SATURATED FRACTIONAL DISTILLATION ALTERNATIVE FUEL POLLUTANT COMBUSTION ASSESSMENT: C1 REVISION – CHAPTER 5 – PRODUCTS FROM OIL What does ‘cracking’ mean? What is ‘polymerisation’? What happens to the following when added to Bromine water: Draw a diagram to demonstrate it: List 3 problems with plastics: i) Alkanes ii) Alkenes How are biodegradable plastics made? Describe how 2 designer polymers work: Explain the 2 ways ethanol can be produced: What are the problems with them? KEY WORDS: CRACKING POLYMERISATION PLASTIC POLYMER MONOMER FERMENTATION BIODEGRADABLE ASSESSMENT: C1 REVISION – CHAPTER 6 – PLANT OILS What is the equation for photosynthesis? What do emulsifiers do? Name 2 products that need emulsifiers in them Describe the 2 ways to extract plant oils: Pressing Distillation Name 2 products that ARE emulsifiers Complete the diagram to demonstrate emulsification: Water What does hydrophobic mean? Use the diagram to explain how oils are hardened into spreads (hydrogenation) Oil Conditions required: What does hydrophilic mean? + Explain what is happening: KEY WORDS: PRESSING DISTILLATIOON HARDENING HYDROGENATION EMULSIFIER HYDROPHOBIC HYDROPHILIC ASSESSMENT: C1 REVISION – CHAPTER 7 – OUR CHANGING PLANET What are the layers of the Earth? How did life on Earth possibly start? Use the headings below to help you. Miller-Urey Experiment: Complete the table to show the atmosphere of Earth today Gas What is continental drift? What causes the motion of the plates? % What happens at plate boundaries Others (inc. Argon) What was Earth’s atmosphere like in the past? What is the carbon cycle? Meteorites Deep Sea Vents Explain how it changed to contain oxygen Why have carbon levels been increasing? KEY WORDS: ATMOSPHERE CARBON CYCLE MANTLE CRUST CORE MILLER-UREY ASSESSMENT: