Unit 5 and 6 revsion
advertisement

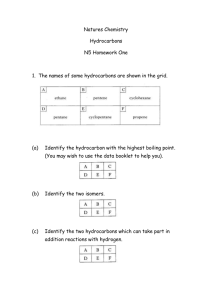
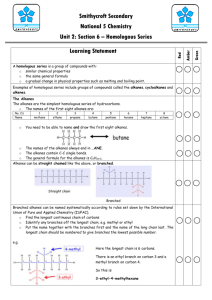
Standard Grade Revision Units 5 and 6 Q1. Crude oil is an example of a fossil fuel. (a) What is meant by the term ‘fuel’? (b) Name two other fossil fuels. (c) Describe how crude oil is formed. (a) A chemical which burns giving out energy. (b) Coal and natural gas. (c) Formed from dead sea animals. Remains buried under layers of rock for millions of years. Heat and pressure changed remains into oil. Q2. What are the tests for Standard Grade Chemistry (a) Oxygen (a) Relights a glowing splint. (b) Carbon dioxide. (b) Turns lime water chalky (milky). (c) Hydrogen. (c) Burns with a ‘pop’ Units 5 and 6 Revision Q3. Which gas makes up (a) about 80% of the air? (a) Nitrogen. (b) about 20% of the air? (b) Oxygen. Q4. The fossil fuels are a finite resource. What is meant by the term ‘finite resource’? A finite resource is a substance whose supply will run out in the future. Q5. The word box gives the formulae of some oxides. H2O NO2 K2 O CaO CO SO2 (a) Identify the oxide produced by the sparking of air in car engines. (b) Identify the two oxides produced by burning hydrocarbons. (c) Identify the two oxides which are mainly responsible for acid rain. (a) NO2. (b) H2O Standard Grade Chemistry and (c) NO2 and SO2. CO. Units 5 and 6 Revision Q6. The word box shows the formulae of some hydrocarbon compounds. CH4 C2H4 C6H14 C5H12 C3H8 C4H8 (a) Identify the molecular formula for pentane. (b) Identify the two molecular formulae which represent alkenes (c) Identify the hydrocarbon which has a boiling point of 69oC. (You may want to use page 6 of the data booklet to help you). (d) Identify the two hydrocarbons formed when propane is cracked. (a) C5H12 C2H4. (b) C2H4 and C4H8 (c) C6H14 (d) CH4 and Q7. The word box shows the names of some hydrocarbons. cyclobutane propane Standard Grade Chemistry cyclopentane ethane butane butene (a) Identify the hydrocarbon which is a liquid at 25oC. (b) Identify the two isomers. (c) Identify the hydrocarbon that reacts quickly with bromine solution. (a) Cyclopentane (b) Cyclobutane and butene (c) butene. Units 5 and 6 Revision. Q8. Hexane can be cracked using aluminium oxide as the catalyst Mineral wool soaked in hexane One of the reactions taking place is C6H14 C2H4 + X (a) Draw the structural formula for hexane. (a) (b) Write the molecular formula for X. (b) C4H10 (c) Name the product C2H4. (c) Ethene (d) Aluminium oxide is a white solid but at the end of the experiment it is covered with a black substance. Suggest what the black substance could be. Standard Grade Chemistry (d) Carbon (soot) Standard Grade Chemistry Units 5 and 6 Revision. Q9. Dienes are a homologous series of hydrocarbons which contain two double bonds per molecule. (a) What is meant by the term “homologous series”? (a) (b) Suggest a general formula for the dienes. (c) Write the molecular formula for the product of the complete (b) (c) reaction of penta-1,3-diene with bromine. (d) Draw the full structural formula for an isomer of buta-1,3-diene which contains only one double bond per molecule. (d) Family of compounds with same general formula. CnH2n-2. C5H8Br4. Q10. The diagram shows the names and boiling ranges of some of the fractions which are obtained from crude oil. (a) Name the process which is used to separate the crude (a) Fractional distillation. oil into fractions. (b) As shown in the diagram is (i) flammability increasing or decreasing? (b) (i) Increasing (ii) Decreasing. (ii) viscosity increasing or decreasing? (c) Gases. (c) ) In which fraction is propane found? (Use your data booklet) (d) Decane is a compound found in the kerosene fraction. Standard Grade Chemistry To which family of hydrocarbons does decane belong? (d) Alkanes. Units 5 and 6 Revision. Q11. The alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons. The alkenes are unsaturated hydrocarbons. (a) What is meant by the term ‘saturated’? (b) What is meant by the term ‘unsaturated’? (c) What is the general formula of the (i) alkanes? (ii) alkenes? (d) Describe a chemical test that can be used to distinguish between alkanes and alkenes. (a) Saturated means the compound contains only single C-C bonds. (b) Unsaturated means the compound contains a C=C double bond. (c) (i) Alkane general formula is CnH2n+2. (ii) Alkenes general formula is CnH2n. (d) Alkanes do not immediately decolourise bromine solution. Alkenes immediately decolourise bromine solution. Standard Grade Chemistry Units 5 and 6 Revision. Q12. Hydrocarbons are compounds which contain hydrogen and carbon only. (a) Which box (A to E) shows the hydrocarbon which reacts with hydrogen to form butane. (b) Which two boxes show hydrocarbons which are isomers. (c) Which two boxes show hydrocarbons which are the first members of a homologous series (a) Box F Standard Grade Chemistry (b) Boxes C and D (c) Boxes A and C Units 5 and 6 Revision. Q13. Propene has the structural formula shown below. Propene quickly decolourises bromine water, Br2(aq). (a) Name the type of chemical reaction which takes place when propene reacts with bromine water. (b) Draw the full structural formula for the product of the reaction. (c) Write a balanced equation for the complete combustion of propene. (a) Addition. (b) Br Br H H – C – C – C –H H H H Standard Grade Chemistry (c) 2C3H6 + 9O2 6CO2 + 6H2O Units 5 and 6 Revision. Q14. The burning of fossil fuels is a major source of air pollution. (a) Name the acidic gas formed when air in a car engine is sparked. (b) Name the acidic gas formed when coal with a high sulphur content is burned. (c) Name the toxic gas formed when methane is burned in a limited supply of air. (d) A catalytic converter fitted to a car exhaust reduces the amount of dangerous gases emitted into the atmosphere. Name the catalyst used in a catalytic converter. (a) Oxides of nitrogen such as nitrogen dioxide. (b) Sulphur dioxide. (c) Carbon monoxide. (d) Platinum. Standard Grade Chemistry