Chemistry 1 help (part 2)
advertisement
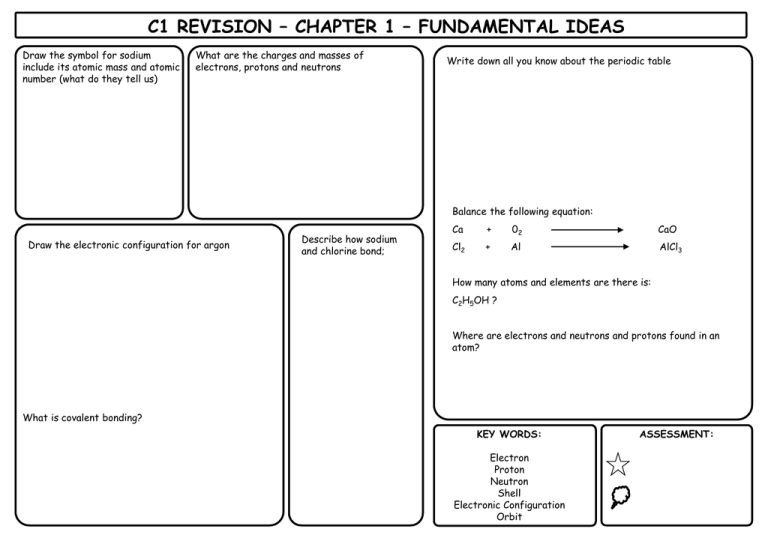
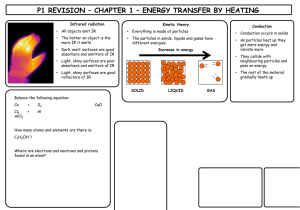
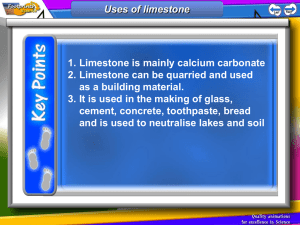
C1 REVISION – CHAPTER 1 – FUNDAMENTAL IDEAS Draw the symbol for sodium include its atomic mass and atomic number (what do they tell us) What are the charges and masses of electrons, protons and neutrons Write down all you know about the periodic table Balance the following equation: Draw the electronic configuration for argon Describe how sodium and chlorine bond; Ca + 02 CaO Cl2 + Al AlCl3 How many atoms and elements are there is: C2H5OH ? Where are electrons and neutrons and protons found in an atom? What is covalent bonding? KEY WORDS: Electron Proton Neutron Shell Electronic Configuration Orbit ASSESSMENT: C1 REVISION – CHAPTER 2 – ROCKS & BUILDING MATERIALS What is the scientific name AND chemical formula for limestone? What is produced when a carbonate reacts with an acid? What is thermal decomposition? Write the word and symbol equation for the thermal decomposition of limestone What is cement? What is concrete? What are the benefits and drawbacks to limestone quarrying? BENEFITS DRAWBACKS Complete the limestone reaction cycle: Calcium Carbonate Add CO2 Add more water & filter Heat Add water KEY WORDS: CALCIUM CARBONATE THERMAL DECOMPOSITION CONCRETE CEMENT QUARRYING LIMESTONE LIMEWATER ASSESSMENT: C1 REVISION – CHAPTER 3 – METALS & THEIR USES Put these metals in their order of reactivity Carbon, Magnesium, Copper, Iron & Potassium Explain a bit about each of the ways to extract copper: Less reactive metals are displaced by carbon. Complete the equation below and then make your own one: Copper Oxide + Carbon _______________ + _______________ Displacement: What is an ore? Smelting: Give 2 use AND properties of: i) Aluminium Bioleaching How is iron extracted? Phytomining ii) Titanium What is an alloy? KEY WORDS: Name 2 alloys: DISPLACEMENT ORE BLAST FURNACE ALLOY SMELTING BIOLEACHING PHYTOMINING ASSESSMENT: C1 REVISION – CHAPTER 4 – CRUDE OIL & FUELS Name the process by which we separate crude oil into useful components: Give a problem each pollutant causes: Carbon Dioxide BENEFITS Sulphur Dioxide What property does this process rely on? Give the benefits and drawbacks of each alternative fuel DRAWBACKS BIODIESEL (more detail required for this one!) Carbon Monoxide Nitrogen Oxide What does ‘saturated’ mean? Particulates ETHANOL Complete the table to summarise alkanes and alkenes: ALKANES Saturated or unsaturated ALKENES HYDROGEN General formula Name an example Draw an example KEY WORDS: ALKANE ALKENE SATURATED FRACTIONAL DISTILLATION ALTERNATIVE FUEL POLLUTANT COMBUSTION ASSESSMENT: C1 REVISION – CHAPTER 5 – PRODUCTS FROM OIL What does ‘cracking’ mean? What is ‘polymerisation’? What happens to the following when added to Bromine water: Draw a diagram to demonstrate it: List 3 problems with plastics: i) Alkanes ii) Alkenes How are biodegradable plastics made? Describe how 2 designer polymers work: Explain the 2 ways ethanol can be produced: What are the problems with them? KEY WORDS: CRACKING POLYMERISATION PLASTIC POLYMER MONOMER FERMENTATION BIODEGRADABLE ASSESSMENT: C1 REVISION – CHAPTER 6 – PLANT OILS What is the equation for photosynthesis? What do emulsifiers do? Name 2 products that need emulsifiers in them Describe the 2 ways to extract plant oils: Pressing Distillation Name 2 products that ARE emulsifiers Complete the diagram to demonstrate emulsification: Water What does hydrophobic mean? Use the diagram to explain how oils are hardened into spreads (hydrogenation) Oil Conditions required: What does hydrophilic mean? + Explain what is happening: KEY WORDS: PRESSING DISTILLATIOON HARDENING HYDROGENATION EMULSIFIER HYDROPHOBIC HYDROPHILIC ASSESSMENT: C1 REVISION – CHAPTER 7 – OUR CHANGING PLANET What are the layers of the Earth? How did life on Earth possibly start? Use the headings below to help you. Miller-Urey Experiment: Complete the table to show the atmosphere of Earth today Gas What is continental drift? What causes the motion of the plates? % What happens at plate boundaries Others (inc. Argon) What was Earth’s atmosphere like in the past? What is the carbon cycle? Meteorites Deep Sea Vents Explain how it changed to contain oxygen Why have carbon levels been increasing? KEY WORDS: ATMOSPHERE CARBON CYCLE MANTLE CRUST CORE MILLER-UREY ASSESSMENT: All substance are made out of ______ . Limestone is mainly composed of ________ _________ . Limestone is extracted by __________ . There are many advantages and disadvanatages to quarrying: advantages ALLOYS What is an alloy?_____________ __________________________ __________________________ What is special about smart alloys?_____________________ __________________________ __________________________ TITANIUM & COPPER These are both _________ metals found in the middle of periodic table. Titanium is good for replacement hip joints and rockets because ___________________ __________________________ _________________________ . Copper is good for pipes and wiring because____________________ __________________________ _________________________ . disadvantages Products from rocks ALUMINIUM Draw the atoms in metal and explain why they are malleable: Thermal decomposition of limestone Calcium Carbonate If a little water is added to calcium oxide you get______ ________, which can be used to raise the pH of soil. If you add more water to this you get _________ , which is used to test for carbon dioxide. Uses of limestone: _____________________ _____________________ _____________________ _____________________ Describe different methods of extracting metals What are the advantages of recycling aluminium? _________ _________________________ _________________________ NAME................................. Score /13 These are examples of unsaturated hydrocarbons (contain double bonds) Products of this reaction consist of... These are examples of saturated hydrocarbons (do not contain double bonds) The products of this process are made more useful by........(a form of thermal decomposition) F This process requires heat and a catalyst These compounds react with Bromine water in the following way..... These compounds react with Bromine water in the following way..... D Crude oil is separated by the process of... Plastic drinks bottles are made from the plastic.... Polymers Mind map Alkenes are used to make polymers by this process...... A The weak forces between molecules are called........ P These consist of many small individual..... H H C H ...which join up to make...... I F C H If we can break these easily by heating, the plastic is known as .... If the plastic also has strong chemical bonds between the polymer chains they are known as......... NAME................................. Score /13 These are examples of unsaturated hydrocarbons (contain double bonds) ALKENES Products of this reaction consist of... These are examples of saturated hydrocarbons (do not contain double bonds) ALKANES CRACKING The products of this process are made more useful by........(a form of thermal decomposition) FRACTIONAL This process requires heat and a catalyst These compounds react with Bromine water in the following way..... DECOLOURISE These compounds react with Bromine water in the following way..... NO REACTION DISTILLATION POLY(ETHENETEREPHTHALATE) OR PET Crude oil is separated by the process of... Plastic drinks bottles are made from the plastic.... Polymers Mind map Alkenes are used to make polymers by this process...... The weak forces between molecules are called........ ADDITION POLYMERISATION These consist of many small individual..... H H C MONOMERS ...which join up to make...... H THERMOSETTING PLASTICS INTERMOLECULAR FORCES C H POLYMERS If we can break these easily by heating, the plastic is known as .... If the plastic also has strong chemical bonds between the polymer chains they are known as......... THERMOSOFTENING PLASTICS