Osteo-genesis
advertisement

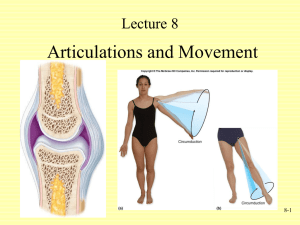
Osteo-genesis • Bones develop through a process called Osteogenesis or Ossification. In embryo, primitive Skeleton is composed of either fibrous membranes or hyaline cartilage. • Bones can form either by intra-membranous method or by intracartilaginous/endo-chondral method. Intra-membranous Ossification • In Intra-membranous bone formation, primitive mesenchyme can give rise directly to bone. Mesenchyme is embryonic connective tissue that is derived from the mesoderm and that differentiates into hematopoietic and connective tissue. The mesoderm is one of the three primary germ layers in the embryo. The other two layers are the ectoderm (outside layer) and endoderm (inside layer), with the mesoderm as the middle layer between them. MesodermMesenchymeOsteoblastBone What is Cartilage? • Strong but slightly flexible connective tissue. It is found around and in between some bones. It is made up of cells(chondrocytes) suspended in an Extra-cellular matrix. Cartilage is of three types • Hyaline(glass-like on appearance) • Fibrous • Elastic Location • Hyaline Cartilage is the most common type. It is present in • Skeleton of Embryo • Articular(articular=related to Joints) Cartilage • Larynx, Trachea, Bronchi • Costal Cartilages (connecting Ribs to Sternum) • Inferior Part of Nose • Fibro-cartilage is found in • Intervertebral Discs • Pubic Symphysis • Menisci of Knee Joint Elastic Cartilage is found in Pinna of ear Auditory Tube Epiglottis of Larynx Endochondral Classification Classification of Joints • 1. Synarthroses or Solid Joints • 2. Diarthroses or Cavitated Joints • Solid joints are further divided into Fibrous Joints and Cartilaginous Joints. • Fibrous Joints are mainly immovable. They include Sutures, Syndesmoses(Interosseous membranes) and Gomphoses(teeth) • Cartilaginous Joints are classified as Primary and Secondary Cartilaginous Joints. Primary are also called Synchondroses, while secondary are called Symphyses(singular is Symphysis). Primary Cartilaginous joints are temporary, and play a role in growth of bones by endochondral method. They consist of Hyaline Cartilage between two growing bones. Secondary Joints are permanent and consist of fibrocartilage between bones. Synovial Joints? (Cavitated Joints) • Articular Cartilage, Fibrous Capsule, Ligaments, Synovial Membrane, Synovial Fluid. • Menisci: Crescent-shaped wedge of fibro-cartilage. Nervous System • Central Nervous System: Brain and Spinal Cord • Peripheral Nervous System: Nerves and Ganglia(group/collection/bundle of neurons) • Peripheral Nervous System or PNS(12 pairs of Cranial Nerves, 31 pairs of spinal nerves) • PNS is further divided into Somatic and Visceral Nervous System. Somatic means related to body, Visceral means related to Organs/Viscera. • Somatic Nervous System has a sensory and a motor part. Sensory part receives input from skin, skeletal muscles, tendons, joints, tongue, eyes and ears. Motor Part brings information or output from Central Nervous System to skin, skeletal muscles, tendons, joints, tongue, eyes and ears. • Visceral system also has sensory and motor part. The input is from organs of digestive, respiratory, cardiovascular, urinary and reproductive system. • Afferent/sensory, Efferent/Motor. Typical Spinal Nerve Typical Neuron Autonomic Nervous System • It is part of motor section of Visceral PNS. It is exclusively the motor system controlling the activity of cardiac muscle, smooth muscles and glands. • It has two components. Sympathetic System and Para-Sympathetic System. Sympathetic system is activated during fight, flight or fright. Parasympathetic system is like the default/background setting. • Both systems have two sets of neurons in their pathway. The first neuron, that is usually located in CNS is called pre-ganglionic neuron. It synapses at a ganglion. Then there is the second neuron, the cellbody of which is located in ganglion. It is called post-ganglionic neuron. Line of Pull? • A description of the direction of force exerted by a muscle, depending on the orientation of its fibers, its skeletal attachments, the disposition of its tendons, and the axis of movement of any joints affected. Skin • Skin is the largest organ in the body. It covers all external free surfaces. • Skin has two main layers, the Epidermis is outer layer consisting of Stratified Squamous epithelium. Dermis is a thicker layer of connective tissue. • Layers of Epidermis(From Below upwards) Stratum Basale, Stratum Spinosum, Stratum Granulosum, Stratum Lucidum, Stratum Corneum.