Types of Joints & Ligaments and Tendons
advertisement

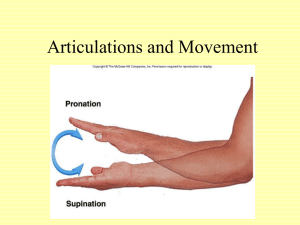
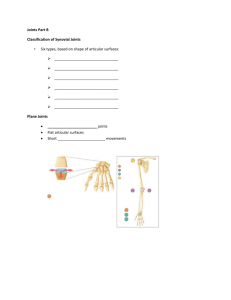
Types of Joints & Ligaments and Tendons l l Types of Joints Joint: where two or more bones meet Joints and Movement: Different joints have varying degrees of movement Three types of joints -fibrous joints -cartilaginous joints -synovial joints Fibrous Joints Fibrous joints: Bones that are connected together without gaps. Fibrous joints, movement: Not mobile Cartilaginous Joint Cartilaginous joints: Bones connected by a small cushion of cartilage. This cartilage acts as a shock absorber, protecting the joint from impact. Cartilaginous joints and Movement: Restricted movement Synovial Joints Synovial joints: Joints where the surface of the bone is covered with a layer of slippery cartilage. Found in the arms and legs Synovial joints and movement: Joints that move freely Synovial Membrane: Found in the joining surface. Secretes a slippery fluids onto the surface of the joint Types of Movement Hinge A hinge joint allows extension and retraction of an appendage. Found in: Elbow and knees Types of Movement Ball and Socket: A ball and socket joint allows for radial movement in almost any direction. found in: hips and shoulders. Types of Movement Gliding In a gliding or plane joint bones slide past each other. Found in: Midcarpal and midtarsal Types of Movement Saddle: A saddle joint allows movement back and forth and up and down (not rotation). Found in: Where fingers connect to hand Types of joints Pivot: Pivot joints allow rotation around an axis. Found in: neck and forearms Ligaments and Tendons Ligaments: Connective tissue that joins bones to other bones. Found in: Ankles, wrists, knees, and hands Ligaments and Tendons Ligaments: Connective tissue that joins bones to other bones. Found in: Ankles, wrists, knees, and hands Tendons: Connective tissue that joins bone to muscle. Found in: Where ever muscle and bone connect. Tendons Brusae: Fluid filled sacs between bone and tendon. Function of the brusae: Reduce the rubbing of the tendon on bone