prince2 - SaLearningSchool.com
advertisement

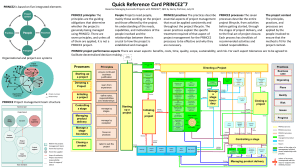
Prince 2 and Project Management By Sayed Ahmed Just E.T.C.Technologies Inc. Just E.T.C Education Inc. www.justETC.net Aspects of Prince2 Steps ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Starting up a Project Initiating a Project Directing a Project Controlling a Stage Managing Product Delivery Managing a Stage Boundary Closing a Project Related Concepts ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Business Case Analysis Organization of Teams Progress Quality Risk Change Overview of Prince2 Changes and upgrades of business processes are done by projects PRINCE2 is a scalable and flexible project management method ◦ Suitable for any type of project [ref: the book] PRINCE 2 Offers ◦ Controlled management of change ◦ Active involvement of the users in the product development PRINCE 2 Offers ◦ Efficient control of development resources PRINCE 2 distinguishes the management of the development process from the techniques for development PRINCE2’s View of Project Management Five characteristics of Project work (than regular business operations) ◦ Change: Projects are used to introduce changes to businesses ◦ Uncertainty: Projects will almost always introduce something new and unknown ◦ Temporary: Many times, a project team comes, finishes the project and goes away ◦ Unique: In some major or minor ways, projects are always unique ◦ Cross-functional: A project needs people with different skills Project Performance Variables Cost Time Quality Scope Benefits Risk Seven PRINCE2 Principles Continued business justification Learn from experience Defined roles and responsibilities Manage by stages Manage by exception Focus on products Tailor to suit the project environment Roles Project Sponsor Program Management Body (Project Board) ◦ Key decision maker ◦ May be absent in small projects An Executive ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Holds the purse string of the projects Ensures that projects meet company strategies Ensures that there is always a business case Strongly tied with the program management For small projects, sponsors become the executives A Project Manager ◦ Sets up a daily log for the projects ◦ Ensures that the project gets done within defined time limit Customer, User and Supplier Capture Previous Lessons PRINCE2 encourages to create lessons logs to ensure that the same mistakes are not done in the future projects How to capture? ◦ Use similar previous projects’ reports ◦ Corporate programmer or external lessons ◦ Previous experience of similar projects from Individuals or teams. Project Manager and Lessons Capturing Responsibilities ◦ Create a lessons log ◦ Review lessons from previous projects esp. similar projects to find out lessons that may benefit current projects ◦ Talk to people with previous project experience or people currently working with similar projects ◦ Document any useful lessons ◦ For small projects Ask people around Stages Stages in Picture (Reference: Prince2.com) Starting Up a Project A pre-project process Ensures that the pre-requisites for initiating the project are in place. Ensures that there is a project mandate describing ◦ The reasons for the project ◦ Expected Outcomes Activities ◦ Ensures that the information required by the project team is available ◦ Planning and appointing the project management team ◦ Create the initiation stage plan Initiating a Project Justify the reasons to proceed with the project Establish a stable management basis Confirm that a reasonable business case exists for the project. Document it. Agree to the commitment of resources Enable and encourage the Project Board to take ownership of the project Outline the baseline for the decision-making processes as will be required during the project’s life cycle Ensure that time and effort investment is decided wisely considering the risks to the project Managing Stage Boundaries (MSB) Provides the Project Board with key decision points on whether to continue with the project or not Objectives ◦ Assure that all deliverables from the previous stage (Current Stage) are complete ◦ Provide the information to assess the continuing viability of the project ◦ Provide the information needed to approve the current stage's completion ◦ Record any lessons that may help later Controlling a Stage (CS) Handles day-to-day management of the project ◦ Hence, this process forms the core of the Project Manager's effort on the project This process is a cycle of the following activities ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Authorize work to be done Gather progress information about that work Watch for changes Review the situation Report Take any necessary corrective action Ongoing risk management and change control Managing Product Delivery (MP) ◦ Ensure that planned products are created and delivered ◦ Ensure that the work is done ◦ Ensure that the work conforms to the requirements ◦ Ensure that the completed work meet quality requirements ◦ Obtain approval for the completed products Closing a Project Execute a controlled close to the project Wrap up the project either at its end or at premature close Check that the objectives as mentioned in the Project Initiation Document (PID) have been met Check the Customer's satisfaction with the deliverables Get formal acceptance of the deliverables Confirm that maintenance and operation arrangements are in place Prepare an End Project Report Planning Planning is an ongoing activity carried out at different stages ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Plan an initiation stage Plan a project Plan a stage Create an Exception plan Planning Framework Establish the products that are needed Determine the sequence in which the products will be produced Define the form and content for each product List activities involved for their creation and delivery Reference Prince 2: A Practical Handbook by Colin Bentley