Prince 2
advertisement

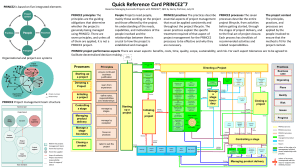
Prince 2: PRojects IN Controlled Environments 2 (PRINCE2) is a structured project management method endorsed by the UK government as the project management standard for public projects. The methodology encompasses the management, control and organisation of a project. PRINCE2 is also used to refer to the training and accreditation of authorised practitioners of the methodology who must undertake accredited qualifications to obtain certification. PRINCE2 describes eight components which need to be present for a successful project: • • • • • • • • Business Case – The reason for the project Organisation – defining the roles and responsibilities of the people involved Plans – defining the project’s products, how the work should be carried out, when and by whom Controls – how the project manager and project board distribiute control over the project Management of Risk – how the project should approach and manage risk Quality in a Project Environment – how the project should ensure that quality products are delivered Configuration Management – how the project’s products are identified and tracked Change Control – how to manage changes to specification or scope of the products Techniques; Processes of PRINE2 include: • Product Based Planning – defining the project in terms of its outputs rather than its activities • Change Control – how to log, assess impact and escalate issues and changes • Quality Reviews – A structured technique for assessing a product’s ‘fitness for purpose’ Advantages and disadvantages: PRINCE2 is a structured approach to project management. It provides a method for managing projects within a clearly defined framework. PRINCE2 describes procedures to coordinate people and activities in a project, how to design and supervise the project, and what to do if the project has to be adjusted if it doesn’t develop as planned. In the method each process is specified with its key inputs and outputs and with specific goals and activities to be carried out, which gives an automatic control of any deviations from the plan. Divided into manageable stages, the method enables an efficient control of resources. On the basis of close monitoring the project can be carried out in a controlled and organized way. Being a structured method widely recognized and understood, PRINCE2 provides a common language for all participants in the project. The various management roles and responsibilities involved in a project are fully described and are adaptable to suit the complexity of the project and skills of the organization. PRINCE2 is sometimes considered inappropriate for small projects or where requirements are expected to change, due to the work required in creating and maintaining documents, logs and lists. However the OGC claim that the methodology is scalable and can be tailored to suit the specific requirements and constraints of the project and the environment. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Rz4o-kR87ls PMbok (Project management Body of Knolwedge) PMBOK recognises 5 basic process groups and 9 knowledge areas typical of almost all projects. The basic concepts are applicable to projects, programs and operations. The five basic process groups are: 1. Initiating 2. Planning 3. Executing 4. Monitoring and Controlling 5. Closing Processes overlap and interact throughout a project or phase. Processes are described in terms of: Inputs (documents, plans, designs, etc.) Tools and Techniques (mechanisms applied to inputs) Outputs (documents, products, etc.) The nine knowledge areas are: 1. Project Integration Management 2. Project Scope Management 3. Project Time Management 4. Project Cost Management 5. Project Quality Management 6. Project Human Resource Management 7. Project Communications Management 8. Project Risk Management 9. Project Procurement Management Each knowledge area contains some or all of the project management processes. CMMI CMMI (Capability Maturity Model Integration) is a process improvement approach that provides organizations with the essential elements of effective processes, which will improve their performance. CMMI-based process improvement includes identifying your organization’s process strengths and weaknesses and making process changes to turn weaknesses into strengths.