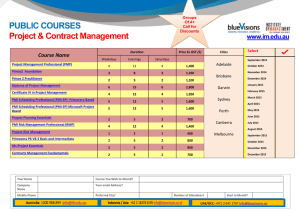
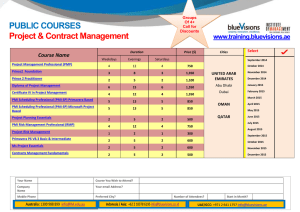
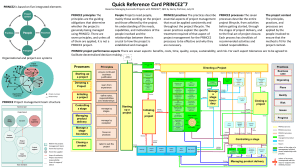
Introduction to Project Management Lecture 1 HNC/D Project Management The Module - Content Evolution of Project Management Life Cycle of Projects Project Planning Organising Project Teams Directing Project Teams Controlling Project Teams The Subject … But what is a project …? and is it different from any other management...? PMBOK Definitions PROJECT = “…a temporary endeavour or undertaking to create a unique product or service” PROJECT MANAGEMENT = “…the application of knowledge, skills, tools and techniques to project activities in order to meet stakeholder’s needs and expectations from a project.” A range of examples … Wembley Stadium (The Guardian) Pride Park Stadium (BBC Derby) Background and Definitions Organisations and Methods Project Lifecycle Terminology The Project Management Institute “Project Management Institute is the global professional association for project programme or portfolio managers and PMO officers. PMI UK is the United Kingdom branch. The core purpose of PMI is to advance the practice, science and profession of project management throughout the world. PMI's goal is that worldwide, organisations will embrace, value and utilise project www.pmi.org.uk management and attribute their success to it.” Association for Project Management (APM) “The Association for Project Management has over 35 years combining its members’ extensive experience in developing the science and art of project management. This is encapsulated in the APM Body of Knowledge, qualifications and other research activities and disseminated through its members, and more widely via print, electronic media and events.” www.apm.org.uk www.prince2.com PRINCE 2 PRINCE2 (PRojects IN Controlled Environments) is a process-based method for effective project management. “PRINCE2 is a de facto standard used extensively by the UK Government and is widely recognised and used in the private sector, both in the UK and internationally.” “The method PRINCE2 is in the public domain, offering non-proprietorial best practice guidance on project management. PRINCE2 is a registered trademark of OGC.” Key features of PRINCE2 “Its focus on business justification A defined organisation structure for the project management team Its product-based planning approach Its emphasis on dividing the project into manageable and controllable stages Its flexibility to be applied at a level appropriate to the project” www.prince2.com Background and Definitions Organisations and Methods Project Lifecycle Terminology PMBOK Definitions PROJECT = “…a temporary endeavour or undertaking to create a unique product or service” PROJECT MANAGEMENT = “…the application of knowledge, skills, tools and techniques to project activities in order to meet stakeholder’s needs and expectations from a project.” What is a Project? “ . . . an endeavour in which human (or machine) material and financial resources are organised in a novel way, to undertake a unique scope of work, of given specification, within constraints of cost and time, so as to deliver beneficial change defined by quantitative and qualitative objectives.” J R Turner (1992) What is Project Management? “ . . . a way of developing structure in a complex project, where the independent variables of time, cost, resources and human behaviour come together.” Burke (1999) Characteristics of a Project Meredith & Mantel (2003): • Purpose - clearly defined outcomes, with an element of complexity, which needs co-ordination • PLC - project, life-cycle • Interdependencies - links to other projects, and to the routine daily operations, need managing • Uniqueness - needs customising, but … • Conflict - competing for resources The 5 Phase Project Life Cycle DEFINE PLAN ORGANISE State the problem Identify activities Identify project goals Estimate time & cost Determine personnel needs List the objectives Sequence activities Determine preliminary resources Identify critical activities Identify assumptions and risks Write project proposal PLANNING Recruit Project Manager Recruit Project Team Organise team Assign work packages CONTROL Define management style Establish control tools Prepare status report Review project schedule Issue change orders IMPLEMENTATION CLOSE Obtain client acceptance Install deliverables Document the project Issue final report Conduct project audit Example of Framework Time Develop it Do it Design it Define it Level of activity The Project Life Cycle (PLC) the time distribution of project activity (Maylor 2003) Time Develop it Do it Design it Define it Cumulative Expenditure The Project Life Cycle (PLC) the time cumulative expenditure (Maylor 2003) Background and Definitions Organisations and Methods Project Lifecycle Terminology The PMI Body of Knowledge • The Project Management Framework • The Project Management Context • Project Management Processes • Project Integration Management • Project Scope Management • Project Time Management • Project Cost Management • Project Quality Management • Project Human Resource Management • Project Communications Management • Project Risk Management • Project Procurement Management Maintaining the balance … TIME COST QUALITY Tolerances PRINCE uses tolerances Is there any latitude in the quoted delivery date or budget? Define The tolerances in a project Who may use the tolerances. Activities / tasks Ideally these should : Be short Be measurable Deliver something Be able to be carried out by one type of resource Milestones Milestones are key points for the project. They have no duration – they are just target dates. e.g Obtain planning approval Roof on Wiring complete Piping complete COMPLETE 14/10/2008 Resources What is required for an activity Deliverables Outputs for activities / tasks e.g. Preliminary drawings Working drawings Bill of quantities Shell of house Gantt Charts Shows activities/ tasks and milestones Can show resources Clear indication of timescales Task Task Number Name 1 Design Prog. 2 Code Prog. 3 4 DO Res. PE AE M T W T F M T W T F SH 2 2 1 DC 4 5 Document Prog. 2 NJ 2 1 User Acc. Test. 3 ME 1 1 Planned Elapsed Actual Elapsed Issue or Risk? Issues Resolution Risks Management