Human Body Systems
advertisement
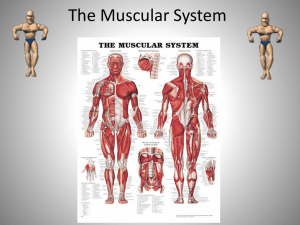
Human Body Systems Can you…. • name all of the body systems? • tell what each system does? Body System Rap I can … • identify the subsystems that make up the human body. • identify the parts and label the functions of the human body’s 8 systems. • explain how systems of the human body are interrelated and regulate the body’s internal environment. How is the body organized? Lesson 1 Cells Working Together • Body is made up of cells – 75 trillion cells – Different body parts are made up of different cells • Cells depend on each other to keep the body running smoothly – Body processes can only happen within a particular temperature range (98.6) so the cells work together to make sure the body stays in that range. Levels of Organization • Each type of cell performs certain activities or functions • Cells are organized by the activities they do – Cells that contract = muscle tissue – Cells that carry messages = nerve tissue • Two or more tissues working together = organ • Each organ in the body is part of an organ system Wrapping it up Create a flow chart that shows how the body is organized. • Include cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems. • Explain / define each component. What systems help move body parts? Lesson 2 I can … • identify the subsystems that make up the human body. • identify the parts and label the functions of the human body’s 8 systems. • explain how systems of the human body are interrelated and regulate the body’s internal environment. Skeletal System Skeletal System • Bones are made of living tissue and nonliving minerals • Bones have several functions: – Support body – Give you height – Protect organs – Form new blood cells – Store minerals Skeletal System • Adult body has 206 bones – 22 in skull – 33 in spine – 27 in hand – 26 in foot • Babies bones are made of cartilage which are then replaced by hard bone Wrapping it up Why do bones have several parts that vary in density? Muscular System Muscular System • More than 600 muscles in your body • Make up 40-50% of your body weight • Muscles and the tissues that attach them to bones = muscular system Muscular System • Three types: – Cardiac muscle (heart) – able to contract repeatedly without getting tired – Smooth muscle (digestive system and blood vessels) – involuntary; control movements inside your body – Skeletal muscle (biceps, quads) – voluntary muscles that move your limbs Keeping Muscles and Bones Healthy • Muscles can get injured • Ways to stay healthy: – Eat healthy foods – Plenty of sleep – Exercise (warm up first and stretch after) Wrapping it up Why is it important to have voluntary and involuntary muscles? How do systems control the body? Lesson 3 I can … • identify the subsystems that make up the human body. • identify the parts and label the functions of the human body’s 8 systems. • explain how systems of the human body are interrelated and regulate the body’s internal environment. Nervous System Nervous System • Parts: – – – – Brain Spinal cord Nerves Sense organs • Continually collects information from inside and outside your body • Functions: – Helps you speak, think, taste, hear, see Nervous System • How it works: – Nerve cells (neurons) pass messages throughout the body along the spinal cord – Dendrites get messages from other neurons and give them to the cell body – Axon moves messages away from that neuron to other nerve cells – Brain gets message and tells body how to react Nervous System • Motor nerves: carry signals from the brain to the body • Sensory nerves: carry information from the body to the brain Reflexes • A response that happens automatically without the brain “thinking” about it • Protect the body from dangerous situations Reflexes • Ways to protect your nervous system: – Avoid alcohol – Avoid drugs – Wear protective gear when playing sports – Wear seat belts in the car – Never dive into a shallow pool Wrapping it up Tell how a reflex action differs from other actions directed by the brain. Explain why this process is important in protecting the body. Endocrine System Endocrine System • Helps balance what goes on in the body • Controls body growth and blood sugar levels • Made up of glands: – Gland – organ that makes chemicals • Glands release chemicals (hormones) into the blood to help control the body’s functions Wrapping it up One of the endocrine glands often is called the “master gland.” Which gland do you think that is”? Why? How do systems transport materials? Lesson 4 I can … • identify the subsystems that make up the human body. • identify the parts and label the functions of the human body’s 8 systems. • explain how systems of the human body are interrelated and regulate the body’s internal environment. Digestive System Digestive System • Takes the food that you eat and changes it into a form cells can use • Parts: – – – – – Mouth Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine • Helper Parts: - Liver - Gallbladder - Pancreas • Types: – Mechanical digestion – tearing, crushing, and mashing food (ex. Biting and chewing food) – Chemical digestion – chemicals (enzymes) break food down into nutrients to give us energy Circulatory System Circulatory System • Parts: – Heart – Blood – blood vessels • Main job: move nutrients and other materials throughout your body through blood vessels to your cells Circulatory System • Heart is the size of your fist • Beats 70 times every minute Circulatory System • How it works: – Blood moves away from the heart through arteries (thick muscular tubes) and back to the heart through veins (large blood vessels) – Capillaries are the smallest blood vessel in your body – allow material to pass through their walls to other cells Circulatory System • Plasma – part of blood that is liquid – Mostly made of water, but has nutrients and waste products – Contains red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets • Red blood cells – carry oxygen • White blood cells- attack germs • Platelets – pieces of cells formed in bone marrow that help blood clot to stop bleeding Wrapping it up Why does blood leave the heart in arteries and return in veins? Why not in the same structure? Respiratory System Respiratory System • Parts: – Lungs – Nose – Trachea – Bronchial tubes • Job: take oxygen from the air and get rid of CO2 from your body Respiratory System • How it works: – Cells use oxygen to release energy from nutrients = produces carbon dioxide – CO2 is a waste that must be removed from your cells – Blood carries oxygen to your cells and takes away the CO2 Wrapping it up Why is it harder to breathe when you have a cold? Explain. How do systems keep the body healthy? Lesson 5 I can … • identify the subsystems that make up the human body. • identify the parts and label the functions of the human body’s 8 systems. • explain how systems of the human body are interrelated and regulate the body’s internal environment. Immune System • Pathogens – organisms that make you sick – Found everywhere Immune System • How to fight pathogens: – Prevent them from coming into the body • Skin • Tears • Mucus in nose, mouth, and throat – Kill them once in your body • Saliva and stomach juices • Extra blood flows to the pathogen so white blood cells can fight it • Antibodies – chemicals that kill certain pathogens if they come into your body again – Body reflexes • Sneezing • Coughing Wrapping it up How would life be different if we didn’t have an immune system? Explain. Systems Working Together • Body systems are involved in everything we do and ALWAYS work together • Important to take care of your body – Start at young age – Most adult health problems start when younger Mr. Immunity Wrapping it up Why is it important to develop a healthy lifestyle at a young age? Body System Rap