Break-Even Analysis: Concepts and Calculations
advertisement

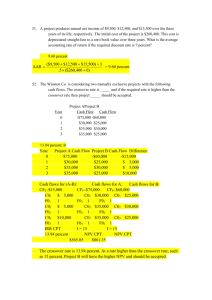
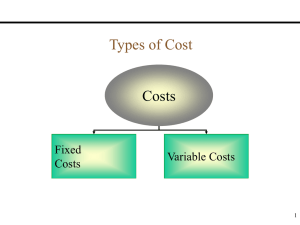
Module 5 BREAK-EVEN ANALYSIS Engr. Gerard Ang School of EECE Definition of Terms Break-Even Analysis – it involves estimating the level of sales necessary to operate a business on a break-even basis. Break-Even Point (BEP) – is defined as the point where sales or revenues equal total expenses. Break-Even Margin – is a ratio that shows the gross-margin factor for a break-even condition. The formula is total expenses divided by net revenues multiplied by 100 to get a percentage. Break-Even Graph Break-Even Chart – shows the graph of fixed cost, variable cost and expected income from sales for different production levels. Ways to Lower the Break-Even Point Lower direct costs, which will raise the gross margin. Exercise cost controls on your fixed expenses, and lower the necessary total expenses. Raise prices. Key Break-Even Factors Fixed Costs – these costs remain constant (or nearly so) within the projected range of sales levels. These can include facilities costs, certain general and administrative costs, and interest and depreciation expenses. Variable Costs – these costs vary in proportion to sales levels. They can include direct material and labor costs, the variable part of manufacturing overhead, and transportation and sales commission expenses. Contribution Margin – this is equal to sales revenues less variable costs. This amount is available to offset fixed expenses and (hopefully) produce an operating profit for the business. Appraisal of Break-Even Analysis Advantages of Break-Even Analysis It points out the relationship between cost, production volume and returns. Limitations of Break-Even Analysis It is best suited to the analysis of one product at a time. It may be difficult to classify a cost as all variable or all fixed. There may be a tendency to continue to use a break-even analysis after the cost and income functions have changed. Sample Problems on Break Even Analysis 1. An entrepreneur at the location in the United States is planning to enter the gourmet soy-based burger market. The forecast expected unit sales of 200,000 burgers in 18 months. The variable cost for making one burger is $0.85 and the fixed cost of making burgers for 18 months will be a total of $165,000 which covers for the rent, phone bill, and insurance coverage – these items tend not to vary in amount per month over the term of one year. The best estimate of what the average consumer will pay for the soy burger is $1.95. How many burgers will he have to sell to break even? Sample Problems on Break Even Analysis 2. Toyota Motor Phils. Corporation Sta. Rosa Plant has a production capacity of 700 cars per month and its fixed cost is Php100,000,000 monthly. The variable cost per car is Php300,000 and each car can be sold for Php650,000. Due to cost reduction program, fixed cost will be reduced to 10% and variable cost by 20%. Determine the new and old break break-even point. Sample Problems on Break Even Analysis 3. A farmer wants to buy a new combine rather than hire a custom harvester. The total fixed costs for the desired combine are $21,270 per year. The variable cost (not counting the operator’s labor) are $8.75 per hour. The farmer can harvest 5 acres per hour. The custom harvester charges $16.00 per acre. How many acres must be harvested per year to break-even?