f - Weebly
advertisement

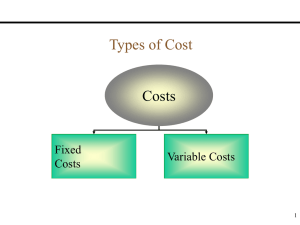
Optimization Methods Profit Equation Profit = Revenue – (Fixed cost + Variable cost) Profit = (Selling price per unit)(number of units sold) – [Fixed cost + (Variable costs per unit)(Number of units sold)] sX – [f + vX] sX – f – vX Profit = Profit = where s = selling price per unit f = fixed cost v = variable cost per unit X = number of units sold break-even point equation 0 = sX – f – vX, or 0 = (s – v)X – f Solving for X, we have f = (s – v)X f X= ____________ s-v BEP = Fixed cost (Selling price per unit) – (Variable cost per unit) Example 1 • • • • If the fixed cost = 350 selling price per unit 15 variable cost per unit 8 Unit of the sell 20 How much the value Profit? What is the value of break even point? Problem 1 The Barclay Brothers company is a large manufacturer of adult parlor games. Its marketing vice president, Rudy Barclay, must make the decision whether to introduce a new game called Strategy into the competitive market. Naturally, the company is concerned with costs, potential demand, and profit it can expect to make if it markets Strategy. Rudy identifies the following relevant costs: fixed cost (f ) = $36,000 (costs that do not vary with volume produced, such as new equipment, insurance, rent, and so on) variable cost (v) per (costs that are proportional to the number of games game produced = $4 produced, such as materials and labor) The selling price(s) per unit is set at $10. What is the value of break-even point? Problem 2 • Ray Bond sells handcrafted yard decorations at county fairs. The variable cost to make these is 20 $ each, and he sells them for 50 $. The cost to rent a booth at the fair is 150 $ per unit. How many of these must Ray sell to break even?