Presented By: Sam Lund, Donovan Parker,
Tom Srebernak
1. Extract nutrients from food
2. Transform nutrients into useful forms
Ex. Oreo= Glucose (sugar)
3. Absorb nutrients and distribute them where
they are needed
Ingestion: Intake of nutrients
Digestion: Breakdown of large particles into
smaller ones
Absorption: Uptake of nutrient molecules
Defecation: Elimination of undigested
residues
1. Intake
-
Breaks up food
Moves food through the GI tract (Peristalsis)
Mixes with digestive enzymes
2. Secretion
-
Release of enzymes and hormones for chemical
digestion and regulation
3. Membrane Transport
-
Absorption of nutrients from the tissues by the
blood and lymph for transport
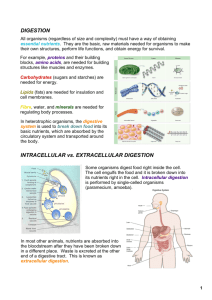
Mechanical: Physical breakdown of food
Chemical: Digestive enzymes hydrolyze food
particles to break larger molecules into smaller
ones
Some nutrients are absorbed without digestion
Vitamins, minerals, cholesterol, water
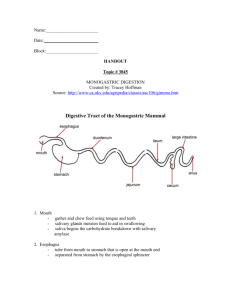
Oral Cavity
Pharynx
Esophagus
Stomach
Small Intestine
Large Intestine
6 meters in length
Functions:
Chemical Digestion
Nutrient Absorption
Nutrient Transportation
Digestion and
absorption of food
Digestive enzymes
secreted by the
pancreas
Enter the small
intestine via the
pancreatic duct.
Duodenum (25 cm)
Food mixes with bile
from the gallbladder.
Jejunum (2.5m)
Absorbs nutrients into
the bloodstream.
Ileum (3.6 m)
Reabsorbs bile acids.
1.5 meters long
Responsible for absorption of water from the
indigestible residue of food
Ascending Colon:
Up the right side
Descending Colon:
Down the left side
Cecum: Sac on
lower right side
Sigmoid Colon:
S-shaped
Ascending Colon-Removes water and
other nutrients
Transverse Colon-Expulsion of waste
materials, continues leaching out
Descending Colon-Absorbs water from
fecal matter. Stores food particles that
are to be emptied into the rectum.
Sigmoid Colon- Make and eliminate
feces. Contains 60 varieties of bacteria
Rectum- Temporary storage for fecal
matter before it’s eliminated from the
body through the anal canal.
Functions:
A. Ingestion: Cheeks
lips and tongue mobilize
food
B. Digestion:
Mechanical
Mastication
Chemical
3 salivary glands
Digests some
starches and fat
Purpose: Pharyngeal
constrictors force food
down during
swallowing
Divided into 3 parts:
Epipharynx
Mesopharynx
Hypopharynx
Straight Muscular
tube about 1 foot long
Purpose: Muscular
contraction moves
food towards stomach
Muscular sac on the left
side of the peritoneal
cavity
Functions:
Food storage
Mechanical
digestion
Chemical digestion
Saliva:
Amylase: Breaks down starch
Lipase: Breaks down fats when it enters the stomach
Stomach:
HCL: Activates enzymes, breaks up foods
Pepsin: Digests proteins
Renin: Digests milk
Starches bloodstream
Fats lymph vessels (lacteals)
Proteins bloodstream