Digestive Tract of the Monogastric Mammal
advertisement

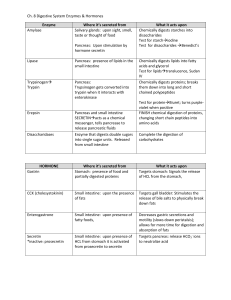
Name:_______________________ Date:________________________ Block:_______________________ HANDOUT Topic # 3045 MONOGASTRIC DIGESTION Created by: Tracey Hoffman Source: http://www.ca.uky.edu/agripedia/classes/asc106/gimono.htm Digestive Tract of the Monogastric Mammal 1. Mouth - gather and chew feed using tongue and teeth - salivary glands moisten feed to aid in swallowing - saliva begins the carbohydrate breakdown with salivary amylase 2. Esophagus - tube from mouth to stomach that is open at the mouth end - separated from stomach by the esophageal sphincter 3.Stomach - muscular gland lined sac that receives ingesta from the esophagus and conducts both physical and chemical digestion - primary secretions: pepsin - enzyme that digests protein; hydrochlorides – acids that aid in protein digestion 4. Small Intestine - enzymatic digestion and absorption - Functions of the small intestine: digestion of proteins, carbohydrates, and fats; absorption of the end products of digestion 1. duodenum - most digestion occurs here 2. jejunum - some digestion and some absorption occur 3. ileum - mostly absorption Enzymes in the Small Intestine Enzyme Trypsin Chymotrypsin Carboxypeptides Pancreatic Amylase Lipases Disaccharides Dipeptidases Function Digest proteins Source Secreted from pancreas Digests carbohydrates Digests lipids Digests carbohydrates Digests peptides Secreted from pancreas Bile made in liver stored in gall bladder active in the small intestine emulsifies fat to aid in digestion 5. Cecum - essentially non functioning in monogastrics 6. Large Intestine - bacterial activity - water absorption - waste storage Secreted from small intestine