Digestion Digesiton
advertisement

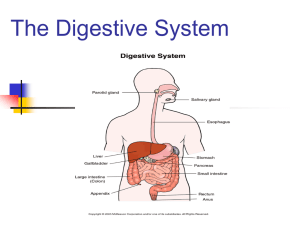
DIGESTION (and the absorption of biomolecules) What is digestion? • Define at your table-groups What is digestion? • Digestion is the breakdown of food into smaller components, so that can be more easily absorbed and assimilated by the body …Essentially the processes organisms use to obtain the essential biomolecules from the food they eat Where does digestion occur? Where are the nutrients absorbed? Biomolecule Carbohydrate Lipid Protein What it gets broken down into Where and how it gets broken down Where it gets absorbed Biomolecule What it gets broken down into Where and how it gets broken down Where it gets absorbed into the bloodstream Carbohydrate Glucose 1. Small intestine 2. Lipid Protein Mouth and stomach: enzymes in the saliva and pancreatic juices in the stomach break it down into maltose. Small intestine: enzymes break maltose into glucose Biomolecule What it gets broken down into Where and how it gets broken down Where it gets absorbed into the bloodstream Carbohydrate Glucose 1. Mouth and stomach: enzymes in the saliva and juices in the stomach break it down into maltase. 2. Small intestine: enzymes break maltase into glucose Small intestine Lipid Fatty acids and cholesterol Stomach: stomach acid “dissolves” large lipids into water, so they can be broken down by enzymes in the stomach. Lymphatic Vessels (located in stomach and small intestine) Protein Amino acids 1. Stomach: enzymes begin to break proteins down 2. Small intestine: pancreatic juices and enzymes break it down into amino acids Small intestine Do we see a theme? • Small intestine is where nutrients are absorbed into the bloodstream!