Chapter 4: The Human Body: From Food to Fuel
advertisement

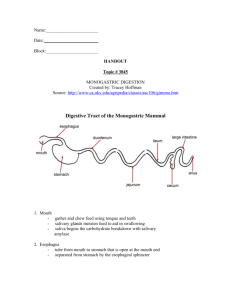
The Human Body: From Food to Fuel Chapter 4 The Gastrointestinal Tract • Organization – Mouth anus – Accessory organs • Salivary glands, liver, pancreas, gallbladder Organization of the Gastrointestinal Tract • Functions – Ingestion – Transport – Secretion – Absorption – Movement – Elimination Organization of the Gastrointestinal Tract • Layers – Mucosa – Circular muscle – Longitudinal muscle – Spincter Overview of Digestion • Physical movement – Peristalsis – Segmentation • Chemical breakdown – Enzymes – Other secretions • Acid • Base • Bile • Mucus Overview of Absorption • The road to nutrition absorption – Passive diffusion – Facilitated diffusion – Active transport Assisting Organs • Salivary glands – Moisten food – Supply enzymes • Liver – Produces bile – “Chemical factory” • Gallbladder – Stores and secretes bile • Pancreas – Secretes bicarbonate – Secretes enzymes Putting It All Together: Digestion and Absorption • Mouth – Enzymes • Salivary amylase acts on starch • Lingual lipase acts on fat – Saliva • Moistens food for swallowing • Esophagus – Transports food to stomach – Esophageal sphincter Putting It All Together: Digestion and Absorption • Stomach – Hydrochloric acid prepares protein for digestion and activates enzymes – Pepsin begins protein digestion – Gastric lipase has some fat digestion – Gastrin (hormone) stimulates gastric secretion and movement – Intrinsic factor is needed for absorption of vitamin B12 Putting It All Together: Digestion and Absorption • Small intestine – Sections of small intestine • Duodenum, jejunum, ileum – Digestion • Bicarbonate neutralizes stomach acid • Pancreatic and intestinal enzymes – Carbohydrates – Fat – Protein Putting It All Together: Digestion and Absorption • Small intestine – Absorption • Folds, villi, and microvilli expand absorptive surface • Most nutrients absorbed here • Fat-soluble nutrients go into lymph • Other nutrients go into blood Putting It All Together: Digestion and Absorption • Large intestine – Digestion • Nutrient digestion already complete • Some digestion of fiber by bacteria – Absorption • Water • Sodium, potassium, chloride • Vitamin K (produced by bacteria) – Elimination Circulation of Nutrients • Vascular system – Veins and arteries – Carries oxygen and nutrients to tissues – Removes wastes • Lymphatic system – Vessels that drain lymph Circulation of Nutrients • Excretion and elimination – Lungs • Excrete water and carbon dioxide – Kidneys filter blood • Excrete waste; maintain water and ion balance Signaling Systems: Command, Control, Defense • Nervous system – Regulates GI activity • Enteric nervous system • Autonomic nervous system • Hormonal system – Increases or decreases GI activity Signaling Systems: Command, Control, Defense • Immune system – Protects us from foreign invaders – Role of GI tract • Barrier • Immune response – Natural killer cells – Macrophages • Location of lymphoid tissues –Lymphocytes • Antibodies Influences on Digestion and Absorption • Psychological influences – Taste, smell, and presentation of food • Chemical influences – Type of protein you eat and the way it is prepared • Bacterial influences – Hydrochloric acid Nutrition and GI Disorders • Constipation – Hard, dry, infrequent stools – Reduced by high fiber, fluid intake, exercise • Diarrhea – Loose, watery, frequent stools – Symptom of diseases/infections – Can cause dehydration – Broth, tea, toast, and other low-fiber foods can help reduce Nutrition and GI Disorders • Diverticulosis – Pouches along colon – High-fiber diet reduces formation • Heartburn and GERD – Reduced by smaller meals, less fat Nutrition and GI Disorders • Irritable bowel syndrome – Stress and certain foods aggravate the symptoms – Controlled by diet and lifestyle modifications • Reduce stress Nutrition and GI Disorders • Colorectal cancer – Fiber-rich diet may reduce risk • Gas – Most foods that contain carbohydrates can cause • Ulcers – Bacterial cause (H. Pylori) Nutrition and GI Disorders • Functional dyspepsia – Chronic pain in the upper abdomen – Treat with medicine and stress-reduction