Study Guide 2
advertisement

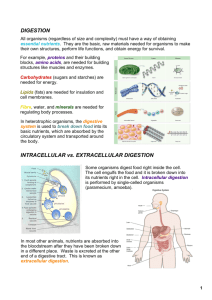
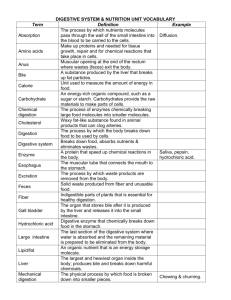
Study Guide 2 (Chapter 3) Digestion and Absorption Nutr 12 Digestion and Absorption Overview Define “digestion”, and list the products of digestion that are eventually absorbed into the intestinal cells and blood. Define “enzymes” and list the major categories of digestive enzymes. Can digestive enzymes be digested? Explain why consumption of food enzymes and enzyme supplements is not necessary or beneficial for digesting food. What is the approximate transit time of dietary substances? Define ”absorption.” Approximately what percent of the macronutrient intake is eventually absorbed? Why is the GI tract itself not digested by the digestive secretions? How is backflow (of food material) prevented during the journey through the GI tract? Define: peristalsis; sphincters. Identify sphincter locations in the GI tract. Define these terms: mucosa, lumen, bolus, chyme. Process of Digestion List the organs of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract and the accessory organs that help in digestion. Where are the larynx and epiglottis located; what are their functions? For each organ or tissue involved in digestion, describe: Organ functions Mechanical processes Digestive secretions and their specific roles in digestion Common Digestive Disorders What is GERD; which sphincter is malfunctioning in GERD? What suggestions would you have for a person with GERD? What are the main causes of peptic ulcer formation? What role does “stress” possibly play? Test yourself on some basic concepts: Where does digestion of carbs begin? Where does digestion of proteins begin? Why does stomach acid need to be neutralized in the small intestine? Which organ secretes the base that neutralizes this acid? Is anything absorbed in the stomach? Compare the rates of stomach emptying for carbohydrates and fats. Explain why the stomach emptying rate affects blood glucose levels after a meal. Explain why emulsification is necessary for fat digestion. What does it mean to “emulsify” fat? Compare the digestibility of meat vs. plant products. What dietary substances do not require digestion? Absorption Where are most nutrients absorbed? Describe the 3 general mechanisms by which nutrients are absorbed into cells. What 3 main features of the small intestine allow it to have such a huge surface area? Contrast both the pathways and destinations of the fat-soluble and water-soluble nutrients after digestion. Describe how the liver processes the nutrients that arrive after digestion. Describe the general role(s) of the lymphatic system. Large Intestine Identify the contents of the colon after digestion, and describe how the colon processes the remaining chyme. Do the bacteria in the colon have any useful roles? Explain why gas may accumulate in the digestive tract. What are possible causes of constipation and diarrhea? Describe possible ways to prevent or treat these conditions, when necessary. Explain the folklore related to “colon cleanses”. Read an opinion about this “therapy” here: http://quackwatch.com/01QuackeryRelatedTopics/gastro.html Regulation of Digestive/Absorptive Function How are the processes of digestion and absorption regulated by the body? Identify the hormones that regulate the secretion of specific digestive substances in the GI tract.