Chapter 3 The Enduring Vision
advertisement
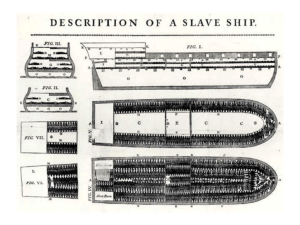
The Colonial Regions • Pilgrims • King Charles I (1625) • The Anglican Church • Governor John Winthrop • “A city upon a hill” • Enforced Conformity • “State” Church • Reading the Bible • Harvard College • Dissenters • Roger Williams • Anne Hutchinson • Restrictions on Women • Thomas Hooker • Male Dominance • Voting Rights • Puritan Villages • Watchful Women • A proper Puritan family • Divorce • Women’s rights • Large families • Rocky soil/short growing seasons • Subsistence farming • Lumber/shipbuilding • Fishing/whaling • Rum distilling • Port cities/shallow rivers • Salem (1691) • Accusations • Escalations • Executions • Challenges to the Puritan way of life • Chesapeake Society • Church and state in Virginia • Bicameral Legislature • The Anglican Church • Little emphasis on religion • Cecilius Calvert (Lord Baltimore) • Catholics • Puritans vs. Catholics • The Act of Religious Toleration • Growing tobacco • Population • Deep Rivers • Lack of towns • First slaves (1619) • Slave laws • Slave population • Reasons for the increase in slavery • Heading for the Caribbean • Sugar • Caribbean slave population • King Charles II • Tobacco • Use of slaves • Rice • Split in the Carolinas • New Netherland • New Sweden • English Conquests • New York • New Jersey • Charles II • William Penn • Religious Tolerance • Growing Grains • Immigration • Delaware • Louis XIV • Fur Traders • Ohio Valley • Mississippi Basin • Treatment of Natives