Energy
advertisement

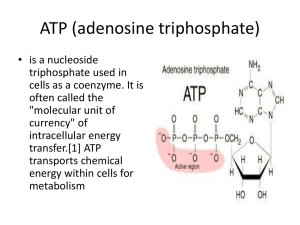
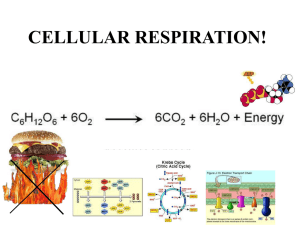
Chapter 4 Kinetic = Energy of Moving Objects Potential = Stored Energy Energy can not be created or destroyed Energy can change forms – heat, light, chemical, matter A) a ball rolling down a hill B) flowing water turning a turbine C) a chameleon tongue catching a bug D) a covalent bond linking phosphate molecules E) a pitcher throwing a baseball A) be transferred and transformed; created or destroyed B) be produced and generated; moved or relocated C) hustle; flow D) be increased and decreased; eliminated E) cycle; flow Uses about 1% or less of energy from sun ◦ 30% is reflected back into space or ◦ 70% absorbed by Earth and converted to heat energy A) water. B) sunlight. C) sugar molecules. D) oxygen. E) carbohydrate molecules. Plants have pigments that can absorb light of certain wavelengths Light is a form of kinetic energy that is packets of energy called photons moving in a wave Different sizes of wave produce the different parts of electromagnetic spectrum Our eyes can see 740 (red) - 400 (blue) nm Plant pigments absorb light in different wavelengths like our eyes ◦ Chlorophyll a and b = absorb red/orange and blue/violet ◦ Thus they reflect green light, which is why plants are green There are other plant pigments in smaller amounts. In the fall, the chlorophylls break down first, leaving other pigments that reflect more orange and red light. A) the violet-blue portion. B) the yellow-green portion. C) the red-orange portion. D) Both a) and b) are correct. E) Both a) and c) are correct. Built up potential energy When released = kinetic energy which can be used to form ATP A) in the stroma of the chloroplast B) in the thylakoid membrane C) in the Hobbesian membrane D) in the cellular cytoplasm E) around the chlorophyll molecule A) glucose B) Oxygen C) Sugars D) carbon dioxide E) None of the above; all are products of photosynthesis. A) Pigments absorb light energy, which excites electrons. B) The energy of the sun is captured as potential energy. C) Water molecules split, providing a source of electrons. D) Only a) and c) are correct. E) a), b), and c) are all correct. A) oxygen and carbon dioxide diffuse out of vacuoles when vacuole pressure is reduced. B) thylakoids become depressurized and release nitrogen gas. C) oxygen is a by-product of photosynthesis. D) the cell wall is permeable to the gases released by the stomata. E) due to anaerobic conditions underwater, the plant must resort to fermentation, causing the production of excess carbon dioxide. A) to replace electrons that are excited by light energy and passed from molecule to molecule down an electron transport chain. B) to serve as a high-energy electron carrier. C) to concentrate the beams of light hitting a leaf, focusing them on the reaction center. D) to provide the protons necessary to produce chlorophyll. E) to replenish oxygen molecules that are lost during photosynthesis. A) rubisco. B) ribulose biphosphate. C) ATP-synthase. D) glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate. E) crassulacean acid. Pleural form = stomata A) stroma. B) stomata. C) grana. D) thylakoid. E) roots. Leaves have evolved to maximize photosynthesis while minimizing water loss ◦ Broad surface oriented toward sunlight ◦ Small stomata regulating air intake and transpiration Which is why plants from different ecosystem communities can have very different leaves ◦ Plants compete for sunlight, so some leaf modifications help a plant climb to sunlight Large leaves of tropical forest floor plants ◦ Collect as much light as possible Pine trees can photosynthesize in winter due to compounds in sap that act as antifreeze. Pine trees can lose up to 26 gallons of water on a sunny, hot day. Under dry conditions, they lose less water than other types of trees 1) pine needle has small surface area, 2) leaves (needles) have a waxy cuticle layer and 3) stomata are recessed into the needle surface, so somewhat protected from the wind so less evaporation. Examine the structure of a typical leaf and briefly describe how each of the following features contributes to the leaf’s function. 1. Interior air spaces 2. Various shapes and sizes, but always relatively thin 3. Stomata 4. Veins All organisms need a form of energy ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Cell metabolism Muscle action Eliminating waste Reproduction Growth of tissues, development Behavior Not all use oxygen, but eukaryotes do Overview of Process A) oxygen is produced during metabolic activity. B) light energy is converted into kinetic energy. C) oxygen is used to transport chemical energy throughout the body. D) energy from the chemical bonds of food molecules is captured by an organism. E) ATP molecules are converted into water and sugar. Glyco = sugar Lysis = splitting Aerobic Respiration 1. Krebs Cycle 2. Electron transport phosphorylation or chain 32 ATP from 1 sugar molecule! Total: 2 from glycolysis, 2 from Krebs Cycle + 32 from ETC = 36 ATP net gain Oxygen + glucose = Carbon dioxide + water + 36 ATP Why we breathe ◦ Oxygen is carried to blood the transported to all cells ◦ Waste product, carbon dioxide, diffuses to blood and transported to lungs for release Interesting note: Water produced = metabolic water. Some grain beetles live in dry grain & can exist without ever drinking – live on metabolic water only. A) is not performed in plants, which get their energy solely through photosynthesis. B) occurs in all cells. C) is performed solely on the glucose ingested by the organism. D) is also referred to as the Krebs cycle. E) completely oxidizes glucose to carbon dioxide. A) lactic acid; O2; acetaldehyde B) pyruvate; ATP; NADH C) acetyl-CoA; ADP; Pi D) galactose; H2O; ATP E) sucrose; lactic acid; FADH A) the products of glycolysis are further broken down, generating additional ATP and the high-energy electron carrier NADH. B) cellular respiration can continue even in the absence of oxygen. C) the products of glycolysis are completely converted into ATP. D) high-energy electron carriers pass their energy to molecules of sugar which store them as potential energy. E) the products of glycolysis are further broken down, generating additional ATP and the high-energy electron carrier NADPH. A) extreme sensitivity to UV light, resulting in skin cancer at a very young age B) fragile bones and arthritis C) extreme muscle weakness D) color blindness E) inability to absorb iron, resulting in extreme anemia Hydrothermal vents •First discovered by explorers of the ocean floor in the 1970’s •Surprise discovery: vents support large community of animals •Too deep for photosynthesis •What food supports animals there? •Turns out- bacteria capable of digesting and getting energy from the sulfides released by the vents A) Fermentation is a less efficient energy producer than aerobic respiration. B) Fermentation utilizes the electrons generated in the glycolytic breakdown of glucose. C) Fermentation is an anaerobic process. D) In fermentation, the molecules that are used as final electron acceptors differ from those used when glycolysis occurs in the presence of oxygen. E) All of the above are correct. Why is energy stored in sugar molecules rather than in ATP? Why is long term storage in the form of lipids and not sugars?