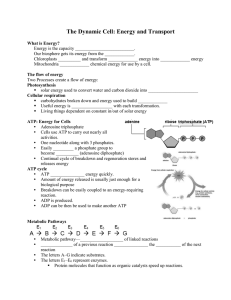
Photosynthesis
advertisement

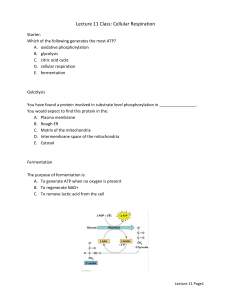
Fungi : - heterotrophic, without chlorophyll - nourishment are organic substances obtained in symbiotic or saprophytic relationships Animals - as a source of energy serving organic substancies; heterotrophic - source of building material for body The energy is gained from organic substances by gradual oxidation or by controlled combustion. Cell respiration is biochemical process, when chemical energy is released from bonds of organic substances (typically sacharides) • formation of energy source for cell – ATP • sugar oxidation of is very similar for animals and plants • outlet products are CO2 and water • animal, plant (at night) and bacterial cells • dissimilation ΔH = 1961 kJ/mol Glycolysis Anaerobic conditions - glucose converts into 2 molecules of pyruvate, the end product of anaerobic glycolysis is lactate. Profit is 2 molecules of ATP. Enough energy for low-evolutional level organisms and probably for progenitor organisms. Aerobic conditions - pyruvate converts into molecules of water and carbon dioxid, the profit is of 36 molecules ATP. Glucose is decomposed, molecules are oxidized and carbon dioxide is released as an outlet product. Ions and electrons of hydrogen released during oxidation are transferred by coenzymes NAD+ and FADH, which are temporarily reduced onto NADH + H+ and FADH2. Hydrogen atoms are used as a source of energy for synthesis of ATP from ADP and consequently react with oxygen to product water. Energy for animal cells Krebs cycle. Pyruvate is transferred to mitochondria and then is oxidized, converts to acetyl-CoA. Acetyl-CoA enters Krebs cycle. During Krebs cycle are released 2 molecules of ATP, mainly coenzymes are reduced. They transfer hydrogen protons and electrons onto inner mitochondria membrane. A outlet product is released carbon dioxide. - decarboxylation, dehydrogenation Electron transport chain Hydrogen atoms from reduced coenzymes are transferred by electron transport chain enzymes, (flavoproteins, coenzyme Q, cytochromes located in inner mitochondria membrane. Cytochromes hand on electrons and energy, which are released during red-ox processes. There is used the place between outer and inner mitochondria membrane for overdrawal of protons. Et the end of electron transport chain is overdrawn proton oxidized by oxygen into water. Oxidative phosphorylation Inner mitochondria membrane is impermeable for hydrogen ions. Due to proton‘s pumps of electron chain reactions is created electrochemical gradient. Ions are tasked to balance concentration at both sides of membrane. Only way for hydrogen ions to get through the membrane is ATP-synthase enzyme, which shape intake for protons. Their energy is used for formation of ATP. Fermentation Dissimilation in anaerobic conditions is called fermentation. Lactic acid fermentation It occurs in the muscles of animals it is this type of bacteria that converts lactose into lactic acid in yogurt and others glucosis 2 ADP + 2P 2 ATP ethanol CH3-CH2-OH acid pyruvic CH3-CO-COOH acid lactic CH3-CH-COOH OH Ethanol fermentation a form of anaerobic respiration used primarily by yeasts. Sugars such as glucose, fructose, sucrose are converted into cellular energy and thereby produce ethanol and carbon dioxide as metabolic waste products. Animalia subkingdom Metazoa Unit B Triblastica line ß Deuterostomia phylum Chordata subphylum Vertebrates class Mammalia order Primates suborder Anthropoidea family Hominidae kind Homo sapiens sapiens kingdom Vertebrates • Sensory organs • Cuticle [skin] of more levels and with derivatives • Special blood cells carry oxygen, closed circulatory system • Pairing kidneys of mesoderm origin • Nervous system and system of glands of internal secretions operate all life functions • Ability to deposite of molecules of high energy - Land vertebrate have egg with amniotic sac and allantois, Agnatha and Gnathostomata from pharyngeal slits • Mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, classes of fishes Mammalia Perfect thermoregulation - adaptation to fluctuating tamperatures Cornification of skin, hair Epidermic glands, lactic, milk glands Two-generation set of teeth Two atrias, two ventriculi, left alveolar arch Non-nucleated erythrocytes Diaphragma Placenta / placental mammals and marsupials