File - Biology with Radjewski
advertisement

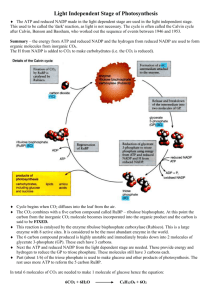
AP Biology 2013 Also called phosphorylation ATP hydrolysis is when an inorganic phosphate breaks off ATP Forms ADP Requires water Does take a small amount of energy to take the P off, but more energy is transferred as hydrogen and oxygen atoms from water bind to ADP and P releasing free energy! Oxidation because AH lost a hydrogen Reduction because NAD+ gained a hydrogen Oxidation because NADH lost a hydrogen Reduction because B gained a hydrogen Most reduced is Propane Lowest free energy is Propanoic acid Most oxidized state is propanoic acid Highest free energy is propane Facilitates movement of protons across cell membrane Creates concentration gradient along inner membrane due to high concentration of protons outside matrix Does not create energy, it sets up a bank of stored potential energy Couples movement of protons back down the conc. Gradient and binding ADP and PO4 forming ATP Occurs in the inner mitochondrial membrane 6 molecules of ATP must be hydrolyzed to start the process 30 molecules of NADH are produced 6 molecules of FADH2 are produced 18 molecules of ATP are produced via substrate phosphorylation (12 in glycolysis and 6 in Krebs) 18 molecules of water are produced in ETS 18 molecules of CO2 are released from the process Alcoholic fermentation produced smaller carbon compounds compared to lactic acid fermentation Pyruvate converts to acetaldehyde and then is reduced to ethanol. It uses enzymes at both steps Two molecules of CO2 and 2 ATP are produced in this anaerobic pathway Lipids Broken down into glycerol and fatty acids Glycerol is then converted to an intermediate in glycolysis; Fatty Acids are converted to acetyl CoA which then enters the Kreb’s cycle Proteins Broken down into amino acids Amino group is removed and then fed into glycolysis/Kreb’s cycle at different points. (depends on the amino acid) EX. Glutamate is converted to alphaketo glutarate Absorbs light at 680 nm Passes electrons to the ETS Produces ATP Oxidizes water into oxygen, hydrogen and electrons Absorbs light at 700 nm Passes electrons to NADP+ make NADPH Carbon Fixation Adds the 1 carbon CO2 to RuBP Produces a 6C molecule that immediately splits into 2 PGA Slow rubisco is needed Reduction and Sugar Production Phosphorylation occurs ATP and NADPH are needed Product is G3P Regeneration of RuBP Most of G3P ends up as RuMP, so ATP is used to convert this to RuBP 50% of protein in leaves of plants is composed of Rubisco Enzyme responsible for the 1st major step in carbon fixation in the Calvin Cycle Without rubisco, CO2 cannot be converted to glucose It catalyzes the reaction of CO2 and RuBP to form 3PG, which is necessary for next step Nathan is correct. Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration rely upon one another, with the molecules necessary for one reaction coming from the end products of the opposite reaction. Plant life could not exist without both photosynthesis and cellular respiration