China Power Point - Scholarsglobe.org
advertisement
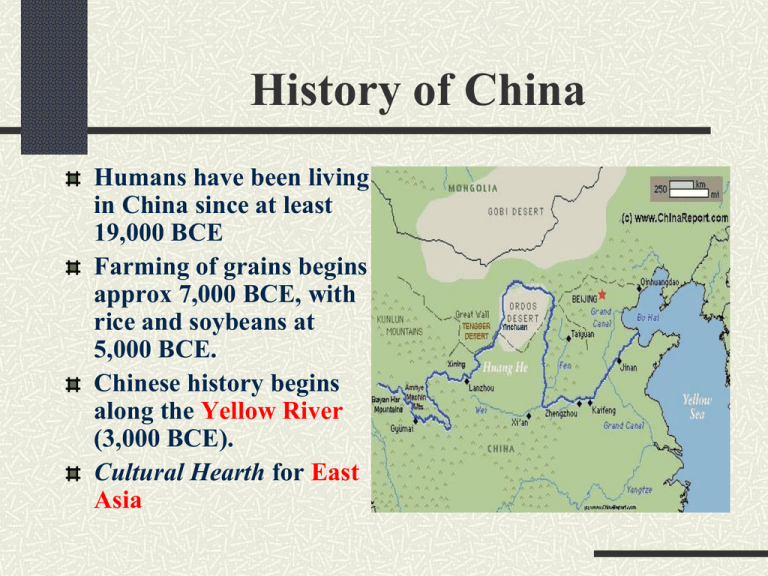
History of China Humans have been living in China since at least 19,000 BCE Farming of grains begins approx 7,000 BCE, with rice and soybeans at 5,000 BCE. Chinese history begins along the Yellow River (3,000 BCE). Cultural Hearth for East Asia Early civilization Earliest form of writing dates back to 5,500 BCE. Pictographic Later used in Chinese character symbols Early States of China Most early Chinese governments were Dynasties (ruled by a select few or royal family). Xia- (2100-1600BCE) Probably oldest, but poorly recorded or understood. Shang Dynasty- (1600-1046BCE) Known for keeping records on Oracle Bones Development of Chinese Pictograms Shang Dynasty Fought constant wars with nomads of the steppes Developed bronze as a metal Shang Zhou is the last Emperorfaces rebellion, commits suicide. Lost the “Mandate of Heaven”fell out of favor with the Gods and could be replaced by the Gods. Zhou Dynasty- (1027-221BCE) Longest of the Chinese Dynasties Tended to weaken over time; rival warlords and governors created chaos and disorder Kung-fu Tzu (551-479BCE) Philosophy based on Relationships (Filial Piety) Proper rituals time the day Known as Confucianism Rise of Daoism Sometimes spelled Taoism Developed by Lao Tzu (600sBCE) Means “the Path” or “Way” Focus on nature, and living in harmony with nature Man is unhappy because he is unbalanced Live in moderation, simplicity, compassion Belief in spirits and many gods. Qin Dynasty (221-206BCE) Brutal warlords that unite much of northern China Legalism- EVERYTHING must be put into law, under the power of the Emperor. Qin: Ying Zheng became Shi Huangdi after uniting China- possibly crazy, built both the Great Wall of China and a Terra Cotta Army. Wanted to be immortal, and burned books and banned any ideas other than Legalism. Qin Accomplishments Han Dynasty (202BCE-220CE) Continue to unify China Open the Silk Route to the West. Confucianism becomes the dominant Chinese philosophy. The Silk Road Buddhism arrives in 1st Century Heated debates as to whether Buddhists should be allowed into China Granted in the 400’sCE. Becomes the dominant religion during the 600’CEs. Rise and fall of Chinese Dynasties Various families take control of China from 220-1211. Mongols invade in 1211-1376 Ming Dynasty (1300’s-1644)are vast buildersCanals connecting the Rivers Completed the Great Wall Built a huge military Navy and Army. “Forbidden City” Ming Dynasty Construction Forbidden City The Ming NavySet out under Admiral He to explore the Indian and Pacific Oceans in 1403 Visited and traded with Africa, India…and North America! So..why didn’t China colonize America? Think about and this and share with the class. So, why don’t we speak Chinese? After the death of Admiral He, money is diverted to other projects Conquest of Vietnam draws off troops and funds Court distrust of men like He (he’s Muslim) Mongol invasions in the North Results: Chinese ships pulled out of water; allowed to rot. Court records about He’s expeditions are burned. All trade with the outside world was cut. Canals were allowed to be filled. Other Ming innovations ended. End of the Ming Dynasty Europeans arrive in 1513 Reign of Wan Li (1572-1620) Emperor withdraws into studying Confucianism Earthquakes, plagues, crop failure and economic collapse Manchu soldiers revolt; overthrow the Emperor Manchu Qing Dynasty (1644-1912) Will rule China until overthrown in the 20th Century “Queue Order”- get a haircut- on pain of death! Writing heavily censored Reigns are marked with serious rebellions Growing outside control of China Europeans gain control of China 1793- China refuses to buy European goods; only wants silver, gold 1838- Opium War 1842- China surrenders; Treaty of Nanking open ports to Europeans Europeans divide China into Mandate areas “Boxer Rebellion” (1898-1901) Monarchy Overthrown (1911) Revolution is led by Dr. Sun YatSen Republic of China declared Republic begins to dissolve into warlordoms Power passes to Nationalist and Communist Rivals Chinese Civil War Fought between 1927-1950 Stopped during WWII (1937-45) Fought between General Chang Kai-Shek (Nationalists) Mao Tze Dung (Mao Zedong)- leading the Communists China & WWII (1937-45) Invaded by Japan in 1937 Major war crimes committed by Japanese Liberated by Russian forces, 1945 Allied nation during the War Member of the United Nations Security Council End of the Chinese Civil War Chang Kai-Shek’s Nationalists are defeated after WWII Flee to Formosa (Taiwan) China becomes a Communist People’s Republic of China Fights in the Korean War against the United Nations/United States China in Korean War Images of the Civil War Modern China China remains divided between Taiwan and Mainland China Chinese Communist Party remains in control of China Communism abandoned in the 1990’s- moving toward market economy Major industrial and financial leader today Own’s over half of the United States Debt. Modern China The world’s most populous country. In the 1870’s there was a terrible drought. Crops failed and people began to starve. 10 million die of starvation. Modern China In the 1980’s, China became the first country to reach 1 billion people. Feeding a huge population is challenging. China is working to achieve a zero population growth. This happens when a the number of births match the number of deaths each year. Modern China China is working to achieve a zero population growth. This happens when a country’s population stops growing. One-Child Policy implemented by Mao Zedong. Families receive benefits, including cash, for having just one child.











