Chinese Dynasty Overview - Mr. G's AP World History
advertisement

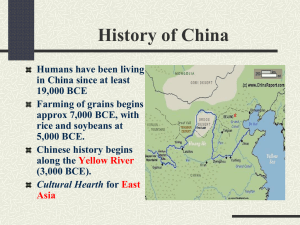
Chinese Dynasty Overview Shang to Qing AP World History Shang (1700 - 1027 BCE) • First recorded Dynasty (Xia no written records) • Ruled by aristocracy • First Chinese cities, center of court life • Developed writing, worked with bronze, created silk • Honored ancestors, used oracle bones • Shang tyrant emperor overthrown Zhou (1027 - 250 BCE) • Longest lasting Chinese Dynasty • Beginning of Mandate of Heaven • Early: Feudal system, lords had total authority • Later: City-states • Built roads, expanded trade, made agricultural advancements Zhou (1027 - 250 BCE) • Taoism and Confucianism introduced • Decline: Inefficient rulers can’t control fighting between city-states • Period of Warring States Qin (221 - 207 BCE) • Qin She Huanshi - only emperor • Adopted Legalism • Developed highly centralized gov’t with bureaucratic administration • Standardized currency, language, measurements, laws • Built first Great Wall Qin (221 - 207 BCE) • Brutal ruler executed dissenters, burned books • Many enemies, dynasty falls after his death Han (202 BCE - 221 CE) • Legalism replaced by Confucianism • Introduced civil service examination (scholar gentry) • Silk Roads developed, opens trade Han (202 BCE - 221 CE) • Buddhism introduced, paper invented • Great increase in population, land holdings Decline • Nomadic raiders • Corruption, weak leaders • Collapse of bureaucracy 221 - 581 (CE) • Warlords control china - no centralized gov’t • Non-Chinese nomads control much of China • Buddhism becomes popular Confucianism failed Sui (581 - 618 CE) • Completed Grand Canal • High taxes, forced labor • Military failures (couldn’t conquer Korea) • Assassination ends dynasty Tang (618 - 907 CE) • High point of Chinese culture • Rebuilt bureaucracy – Examination system – Confucian education – Limited social mobility • Buddhism supported, then oppressed • Invention of movable print, porcelain, gun powder Tang (618 - 907 CE) • Wu Zetian - Only Empress in Chinese history Decline • Weak emperors, nomadic incursions, economic difficulties • Warlords take control Song (969 - 1279 CE) • Large centralized bureaucracy (NeoConfucian) • Mercantile class grows, increased trade • Magnetic compass, growing sea power • Weak military Yuan (1279 - 1368 CE) • Mongol Khubilai Khan conquers China • Economic stability and prosperity • China more open to trade and travel (Marco Polo) • Ignored Chinese traditions, replaced bureaucrats with non-Chinese • Unsuccessful attacks on Japan, corruption weakens dynasty • Peasant rebellion ends Yuan Ming (1368 - 1644 CE) • Tried to erase all signs of Mongols • Reinstated civil service, Confucian scholars • Eunuchs play growing role (Zheng He) resented by scholar gentry • Rebuilt and extended Great Wall • Collapsed after famines and riots Qing (1644 - 1911 CE) • Manchus (from Manchuria) move south • Take Korea, Japan, then China • Manchus hold top posts, but relied upon scholar gentry • “Son of Heaven” concept emphasized • Would be final Chinese Dynasty • Eventually would be weakened by European / American interventions Chinese Dynasty Song Shang, Zhou, Qin, Han Shang, Zhou, Qin, Han shang, joe, chin, hahn Sui, Tang, Song Sui, Tang, Song sway, tang, soong Yuan, Ming, Qing, Republic Yuan, Ming, Qing, Republic yooan, ming, ching, Republic Mao Zedong Mao Zedong mou dzu dong