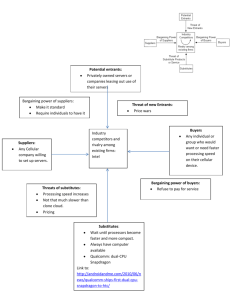
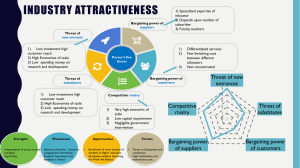
Porters 5 forces "Porter's Five Forces" is a framework developed by Michael E. Porter, a renowned economist and professor at Harvard Business School. It is a strategic analysis tool used to understand the competitive forces at work in an industry or market. The framework helps businesses assess their competitive position and formulate strategies to gain a sustainable advantage. Porter identified five key forces that shape an industry's competitive environment: 1. **Threat of New Entrants:** This force considers how easy or difficult it is for new companies to enter the industry. Barriers to entry, such as high capital requirements or strong brand loyalty, can limit the threat of new entrants. 2. **Bargaining Power of Suppliers:** Suppliers' power refers to their ability to influence prices, quality, or availability of inputs (e.g., raw materials) to the industry. When there are few suppliers and no suitable substitutes, they have higher bargaining power. 3. **Bargaining Power of Buyers:** Buyers' power relates to their ability to influence prices and demand better quality or service from companies in the industry. If buyers have many choices and are price-sensitive, they have higher bargaining power. 4. **Threat of Substitute Products or Services:** This force assesses the extent to which alternative products or services outside the industry can satisfy the same customer needs. A high threat of substitutes can limit pricing power. 5. **Intensity of Competitive Rivalry:** This force examines the level of competition among existing firms in the industry. High rivalry often results in price wars, reduced profit margins, and aggressive marketing tactics. Porter's Five Forces framework helps organizations analyze these forces and develop strategies to mitigate threats and capitalize on opportunities. By understanding the dynamics of their industry, companies can make informed decisions about how to position themselves for success. This analysis can be used as a starting point for crafting a broader business strategy.