Porter`s 5 Forces - Guide to Business Planning
advertisement
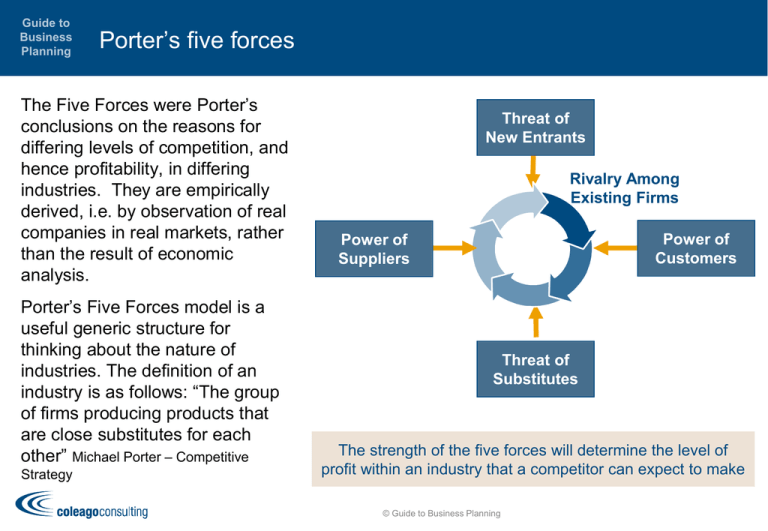
Guide to Business Planning Porter’s five forces The Five Forces were Porter’s conclusions on the reasons for differing levels of competition, and hence profitability, in differing industries. They are empirically derived, i.e. by observation of real companies in real markets, rather than the result of economic analysis. Porter’s Five Forces model is a useful generic structure for thinking about the nature of industries. The definition of an industry is as follows: “The group of firms producing products that are close substitutes for each other” Michael Porter – Competitive Strategy Threat of New Entrants Rivalry Among Existing Firms Power of Customers Power of Suppliers Threat of Substitutes The strength of the five forces will determine the level of profit within an industry that a competitor can expect to make © Guide to Business Planning






![[5] James William Porter The third member of the Kentucky trio was](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/007720435_2-b7ae8b469a9e5e8e28988eb9f13b60e3-300x300.png)